|
||||||||||||||||||||||
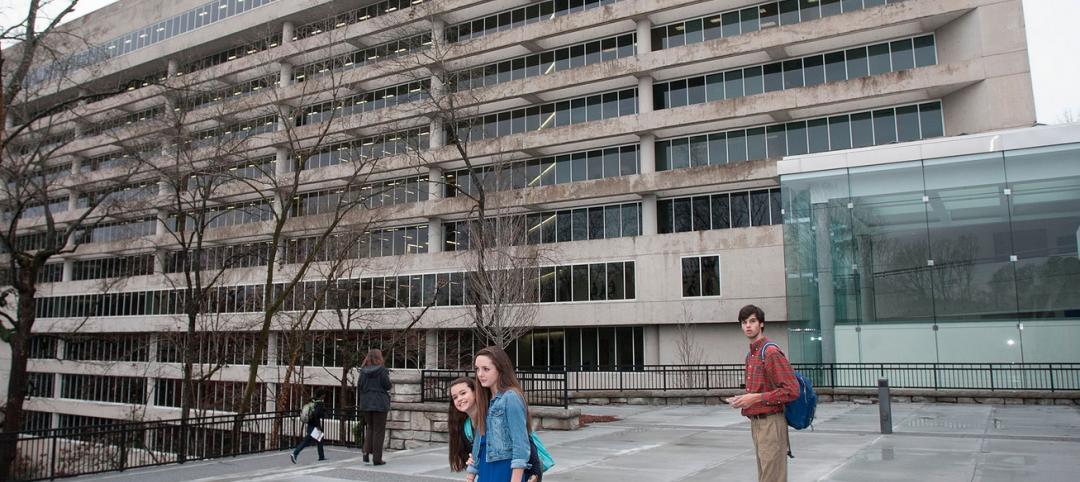
| Lincoln High School in Tacoma, Wash., was built in 1913 and spent nearly a century morphing into a patchwork of outdated and confusing additions. A few years ago, the Tacoma School District picked Lincoln High School to be the first high school in the district to be part of its newly launched Small Learning Communities program, thus beginning a $74.2 million renovation of the 222,000-sf high school. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lincoln High School in Tacoma, Wash., was built in 1913 and spent nearly a century morphing into a patchwork of outdated and confusing additions. A few years ago, the Tacoma School District picked Lincoln High School, dubbed “Old Main,” to be the first high school in the district to be part of its newly launched Small Learning Communities program. The Building Team was given only 13 months to get the school ready to participate in the project. Community members, administrators, students, teachers, and parents worked with architects from the Seattle office of DLR Group to reconfigure the high school for new academy-based educational delivery methods. The architects led them through extensive scenario planning, overlaying each educational program component over the building plans.
The DLR plan divided the school into six zones (two zones in each wing, one on each floor) that would house six academies, each of which would function independently within the larger school building. Shared spaces were to include an auditorium, a cafeteria, a gymnasium, a library, and science labs. Funding for the $74.2 million renovation came from a bond issue and a grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. As work got under way in fall 2006, the existing 222,000-sf, L-shaped school received a number of structural upgrades and nips and tucks. To address seismic concerns, 13 shear walls (using double-sided plywood) were installed, running from grade all the way up to the attic floors. An existing 1980s addition was demolished; in its place arose a two-story structure that expands the school to 264,000 sf and houses the new library and science labs. The addition also acts as a buttress to the existing school structure, providing added seismic support. The school received all new plumbing and electrical systems, as well as new HVAC equipment that was installed in the attic. The Building Team specified aluminum equipment to diminish the weight load on the existing wood-frame structure. Insulation was beefed up to dampen equipment noise. Despite all that’s new with the school, much of its historic character remains intact. The Collegiate Gothic-style school’s original details were restored or replicated; some were relocated and reused in the addition to connect old and new. Also left intact were the school’s 75- to 80-year-old, three-by-seven-foot operable windows, some with original stained glass windows of Tacoma milk glass, so called because of its milky white color. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Project Summary Lincoln High School Tacoma, Wash. Building Team Submitting firm: DLR Group (architect, structural engineer) Owner: Tacoma School District Architectural consultant: TCF Architecture General contractor: Lease Crutcher Lewis Electrical engineer: Coffman Engineers Mechanical engineer: Hargis Engineers General Information Area: 264,000 sf Construction cost: $74.2 million Construction time: August 2006 to September 2007 |
Related Stories
| Mar 12, 2014
14 new ideas for doors and door hardware
From a high-tech classroom lockdown system to an impact-resistant wide-stile door line, BD+C editors present a collection of door and door hardware innovations.
| Mar 4, 2014
If there’s no ‘STEM crisis,’ why build more STEM schools?
Before you get your shorts in a knot, I have nothing against science, technology, engineering, or even mathematics; to the contrary, I love all four “STEM” disciplines (I’m lying about the math). But I question whether we need to be building K-12 schools that overly emphasize or are totally devoted to STEM.
| Feb 26, 2014
Adaptive reuse project brings school into historic paper mill
The project features nontraditional classrooms for collaborative learning, an arts and music wing, and a technologically sophisticated global resource center.
| Feb 14, 2014
Crowdsourced Placemaking: How people will help shape architecture
The rise of mobile devices and social media, coupled with the use of advanced survey tools and interactive mapping apps, has created a powerful conduit through which Building Teams can capture real-time data on the public. For the first time, the masses can have a real say in how the built environment around them is formed—that is, if Building Teams are willing to listen.
| Feb 5, 2014
'School Security' PDF available to BD+C readers - CORRECTED
I've received several requests from BD+C readers who design and build K-12 schools about the 3-part series we ran in our January issue ("Can Design Prevent Another Sandy Hook?"). They wanted to send the issue to their school boards and other public officials with responsibility for school safety. In light of the importance of this topic, as a special service to our readers we're making the series available in PDF form.
| Feb 5, 2014
Extreme conversion: Atlanta turns high-rise office building into high school
Formerly occupied by IBM, the 11-story Lakeside building is the new home for North Atlanta High School.
| Jan 30, 2014
What to expect in the metal building industry in 2014
Every year brings changes. This one won’t be any different. We’ll see growth in some areas, declines in others. Here’s a little preview of what we’ll be writing about 2014 when 2015 comes rolling in.
| Jan 28, 2014
White Paper: How metal buildings deliver long-term value to schools
A new white paper from Star Building Systems outlines the benefits of metal buildings for public and private school building projects.
| Jan 28, 2014
16 awe-inspiring interior designs from around the world [slideshow]
The International Interior Design Association released the winners of its 4th Annual Global Excellence Awards. Here's a recap of the winning projects.
| Jan 15, 2014
Report: 32 U.S. buildings have been verified as net-zero energy performers
The New Buildings Institute's 2014 Getting to Zero Status report includes an interactive map detailing the net-zero energy buildings that have been verified by NBI.