The buckling restrained braced frame system was introduced to the U.S. construction market in 1999 as a solution for meeting hardened building codes following the 1994 Northridge earthquake. Since then, BRBF has been used to stabilize hundreds of buildings along the West Coast, especially in earthquake-prone California.
As seismic codes play a larger role in building projects east of the Sierras, Building Teams across the country are turning to seismic design solutions like BRBF that were perfected in the West to meet increasingly stringent code requirements.
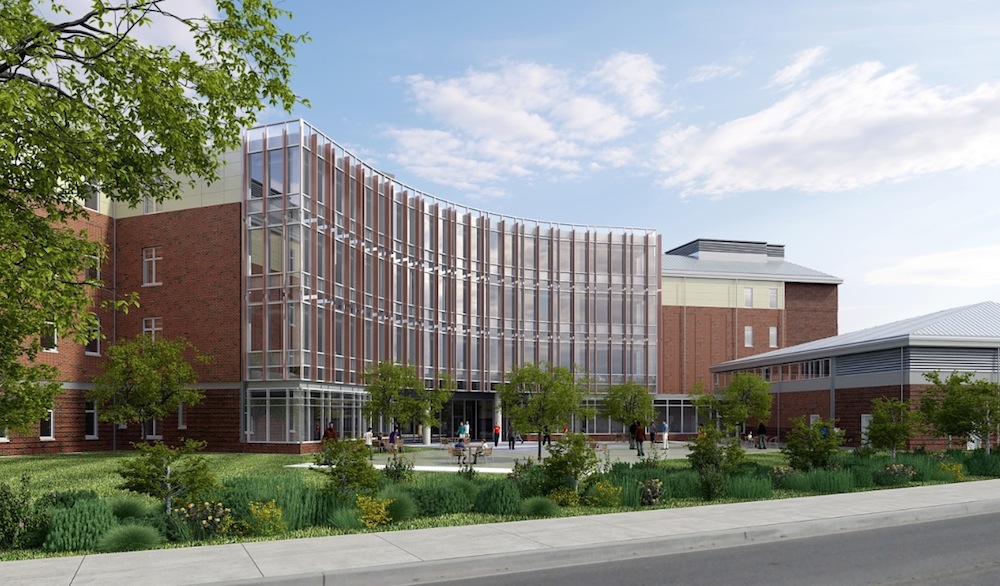
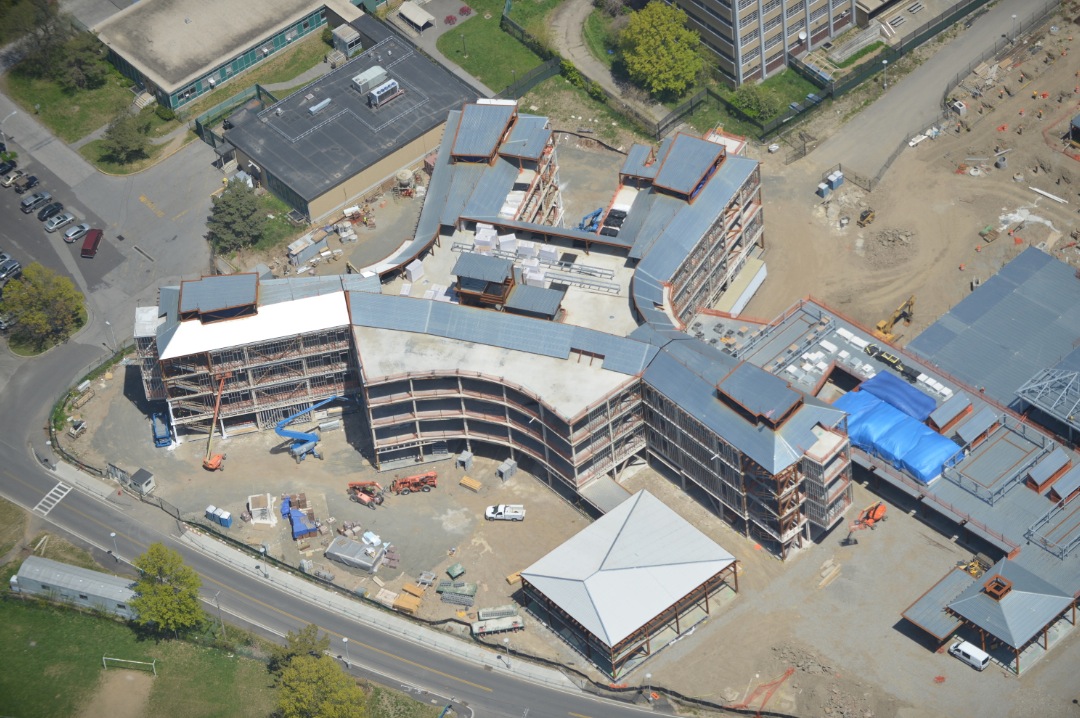
The latest example is the five-story, 179,000-sf Adult Behavioral Health Center, recently completed as part of the Dormitory Authority of the State of New York’s rebuilding of the Bronx Psychiatric Center campus, on behalf of the New York State Office of Mental Health.
Unlike many large-scale New York City structures built on solid rock foundations, the 156-bed Bronx healthcare facility is situated on wetlands that had been filled in with four million cubic yards of material generated from the construction of the Cross Bronx Expressway from 1948 to 1972. The poor soil conditions resulted in a Site Class F categorization and a Seismic Design Category D for the site. It called for an expanded geotechnical investigation and assessment, as well as seismic mitigation measures that were recently implemented under the New York State Building Code.
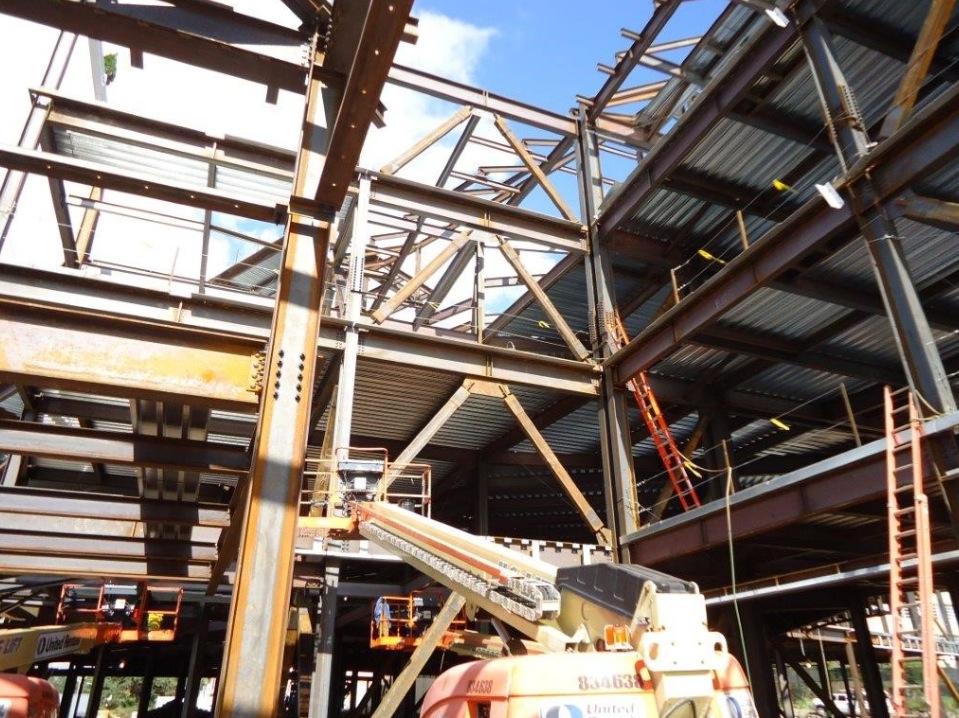 Situated on wetlands, the five-story, 179,000-sf Adult Behavioral Health Center in the Bronx, N.Y., required special seismic mitigation measures. Buckling restrained braces were the most economical, efficient solution.
Situated on wetlands, the five-story, 179,000-sf Adult Behavioral Health Center in the Bronx, N.Y., required special seismic mitigation measures. Buckling restrained braces were the most economical, efficient solution.
The structural design team, led by STV, first considered a traditional concentric braced frame lateral system. The solution met seismic requirements, but posed space-planning concerns for the client. Its relatively sizable structural elements and supporting walls would have bumped up against the health center’s programmatic requirements for rooms and circulation and would have jeopardized the architect’s open, airy indoor design scheme.
The final design approach, developed in conjunction with engineers in STV’s Los Angeles office, called for a BRBF system—a first for the Northeast—to enhance the structural performance of the building and greatly reduce steel frame member sizes. It also minimized the number of supporting walls needed for the project, and saved approximately $500,000 in material costs, according to Chris Cerino, PE, SECB, VP and Director of Structural Engineering, Building & Facilities Division, with STV. The firm also served as the design architect and electrical, civil, geotechnical, and telecom engineer on the project.
With the BRBF approach, certain braced frame steel columns could be downsized from W14x426 to W14x342, and select braced frame steel beams were reduced from W36x150 to W24x68.
“Smaller frame members gave STV designers flexibility in considering the movement of staff, residents, and food and building services,” says Cerino. “It also improved sightlines in all staff and resident areas to reduce the dependency on electronic monitoring.”

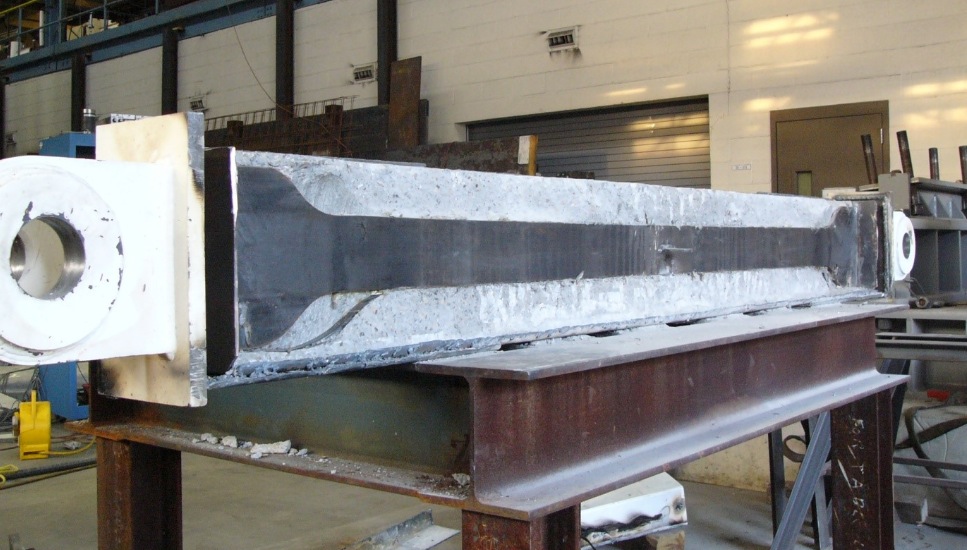
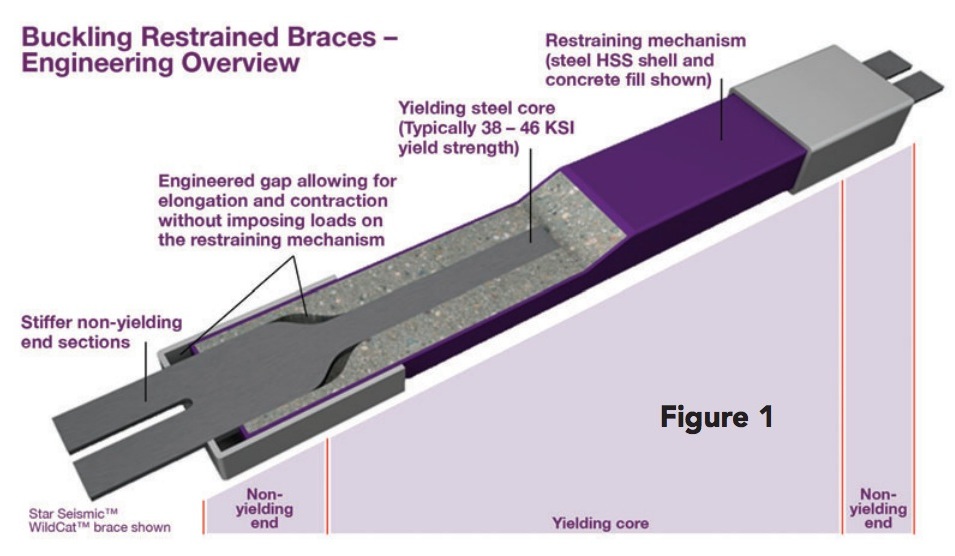
Buckling restrained braces (BRBs) vary slightly based on the manufacturer, but all BRBs include five basic components: a steel-plate core shaped like a kayak paddle (1) is placed within a hollow steel tube (2) that is coated with a low-friction material (3), which is then grouted in place (4) and capped (5). The grouted steel tube design prevents the steel core from buckling when in compression, while the coating prevents axial load from being transferred to the encasement.
The result is a “full, balanced response in relation to the forces being applied,” says Cerino. “Because the steel core is restrained, it develops nearly uniform axial strains across the section, resulting in efficient energy dissipation.”
This balanced energy dissipation, in turn, permits design teams to use much smaller beam sizes than with a standard braced frame.
On the Adult Behavioral Health Center project, Cerino’s team specified a proprietary system manufactured by Star Seismic. According to Cerino, Star’s Wildcat BRB system, which features single-pin connections, reduced erection time because it eliminated the need for stiffener plates. “Its patented collar reduces welding, since simple fillets can be used,” says Cerino. “That factored into the overall monetary savings.”
Cerino offers a few tips for Building Teams evaluating BRBFs:
- Watch out for the added special seismic requirements and details that become triggered when using a high-performance seismic system. “Not that a BRBF has different triggers than a special concentrically braced frame system, but since much of the design is deferred to the specialty brace contractor, some of the details can become out of sight, out of mind,” he says.
- Decide on the system early so you can address any client/procurement obstacles. “If it becomes too late, it can simply be easier to do nothing,” says Cerino. “That doesn’t help the project.”
 Buckling restrained braces include several basic components: a steel-plate core is placed within a hollow steel tube that is coated with a low-friction material and then grouted in place and capped. The grouted steel tube design prevents the steel core from buckling when in compression, while the coating prevents axial load from being transferred to the encasement.
Buckling restrained braces include several basic components: a steel-plate core is placed within a hollow steel tube that is coated with a low-friction material and then grouted in place and capped. The grouted steel tube design prevents the steel core from buckling when in compression, while the coating prevents axial load from being transferred to the encasement.
Related Stories
Building Owners | Aug 23, 2023
Charles Pankow Foundation releases free project delivery selection tool for building owners, developers, and project teams
Building owners and project teams can use the new Building Owner Assessment Tool (BOAT) to better understand how an owner's decision-making profile impacts outcomes for different project delivery methods.
Fire-Rated Products | Aug 14, 2023
Free download: Fire-rated glazing 101 technical guide from the National Glass Association
The National Glass Association (NGA) is pleased to announce the publication of a new technical resource, Fire-Rated Glazing 101. This five-page document addresses how to incorporate fire-rated glazing systems in a manner that not only provides protection to building occupants from fire, but also considers other design goals, such as daylight, privacy and security.
Digital Twin | Jul 31, 2023
Creating the foundation for a Digital Twin
Aligning the BIM model with the owner’s asset management system is the crucial first step in creating a Digital Twin. By following these guidelines, organizations can harness the power of Digital Twins to optimize facility management, maintenance planning, and decision-making throughout the building’s lifecycle.
Sustainability | Jul 26, 2023
Carbon Neutrality at HKS, with Rand Ekman, Chief Sustainability Officer
Rand Ekman, Chief Sustainability Officer at HKS Inc., discusses the firm's decarbonization strategy and carbon footprint assessment.
Sponsored | Fire and Life Safety | Jul 12, 2023
Fire safety considerations for cantilevered buildings [AIA course]
Bold cantilevered designs are prevalent today, as developers and architects strive to maximize space, views, and natural light in buildings. Cantilevered structures, however, present a host of challenges for building teams, according to José R. Rivera, PE, Associate Principal and Director of Plumbing and Fire Protection with Lilker.
Mass Timber | Jul 11, 2023
5 solutions to acoustic issues in mass timber buildings
For all its advantages, mass timber also has a less-heralded quality: its acoustic challenges. Exposed wood ceilings and floors have led to issues with excessive noise. Mass timber experts offer practical solutions to the top five acoustic issues in mass timber buildings.
Green | Jun 26, 2023
Federal government will spend $30 million on novel green building technologies
The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies. The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance.
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
AEC Innovators | Jun 15, 2023
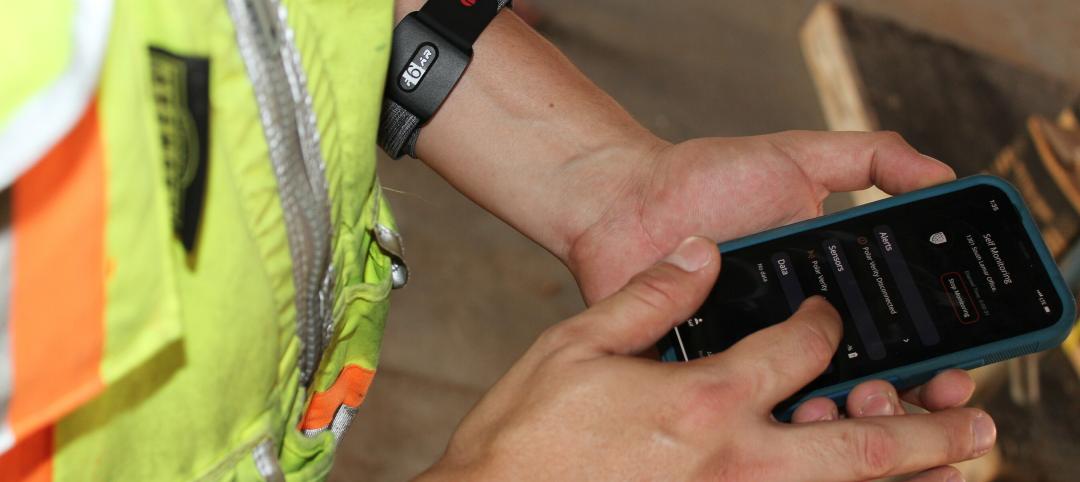
Rogers-O'Brien Construction pilots wearables to reduce heat-related injuries on jobsites
Rogers-O'Brien Construction (RO) has launched a pilot program utilizing SafeGuard, a safety-as-a-service platform for real-time health and safety risk assessment. Non-invasive wearables connected to SafeGuard continuously monitor personnel to prevent heat exhaustion on jobsites, reducing the risk of related injuries. RO is the first general contractor to pilot this program.
Mass Timber | Jun 13, 2023
Mass timber construction featured in two-story mixed-use art gallery and wine bar in Silicon Valley
The Edes Building, a two-story art gallery and wine bar in the Silicon Valley community of Morgan Hill, will prominently feature mass timber. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glulam posts and beams were specified for aesthetics, biophilic properties, and a reduced carbon footprint compared to concrete and steel alternatives.