The buckling restrained braced frame system was introduced to the U.S. construction market in 1999 as a solution for meeting hardened building codes following the 1994 Northridge earthquake. Since then, BRBF has been used to stabilize hundreds of buildings along the West Coast, especially in earthquake-prone California.
As seismic codes play a larger role in building projects east of the Sierras, Building Teams across the country are turning to seismic design solutions like BRBF that were perfected in the West to meet increasingly stringent code requirements.
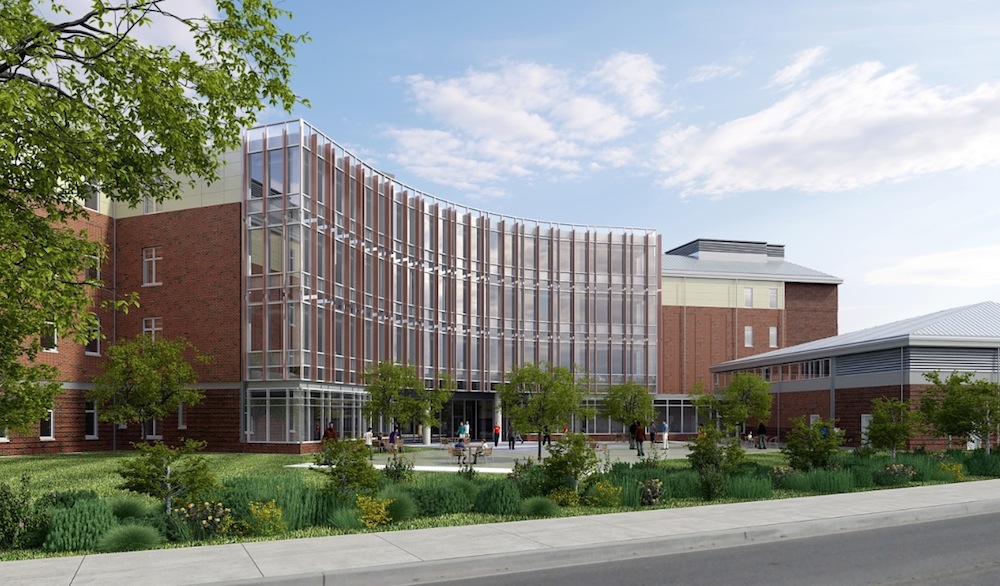
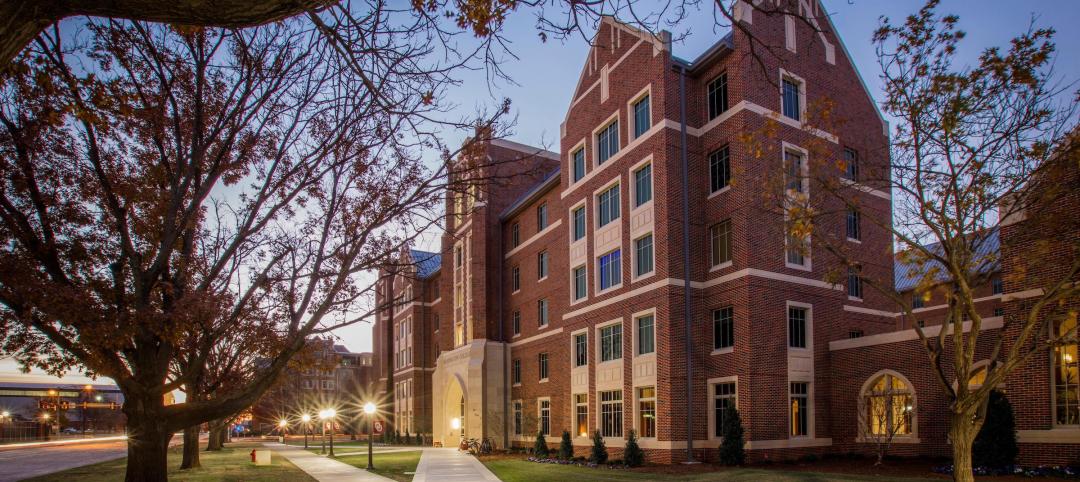
The latest example is the five-story, 179,000-sf Adult Behavioral Health Center, recently completed as part of the Dormitory Authority of the State of New York’s rebuilding of the Bronx Psychiatric Center campus, on behalf of the New York State Office of Mental Health.
Unlike many large-scale New York City structures built on solid rock foundations, the 156-bed Bronx healthcare facility is situated on wetlands that had been filled in with four million cubic yards of material generated from the construction of the Cross Bronx Expressway from 1948 to 1972. The poor soil conditions resulted in a Site Class F categorization and a Seismic Design Category D for the site. It called for an expanded geotechnical investigation and assessment, as well as seismic mitigation measures that were recently implemented under the New York State Building Code.
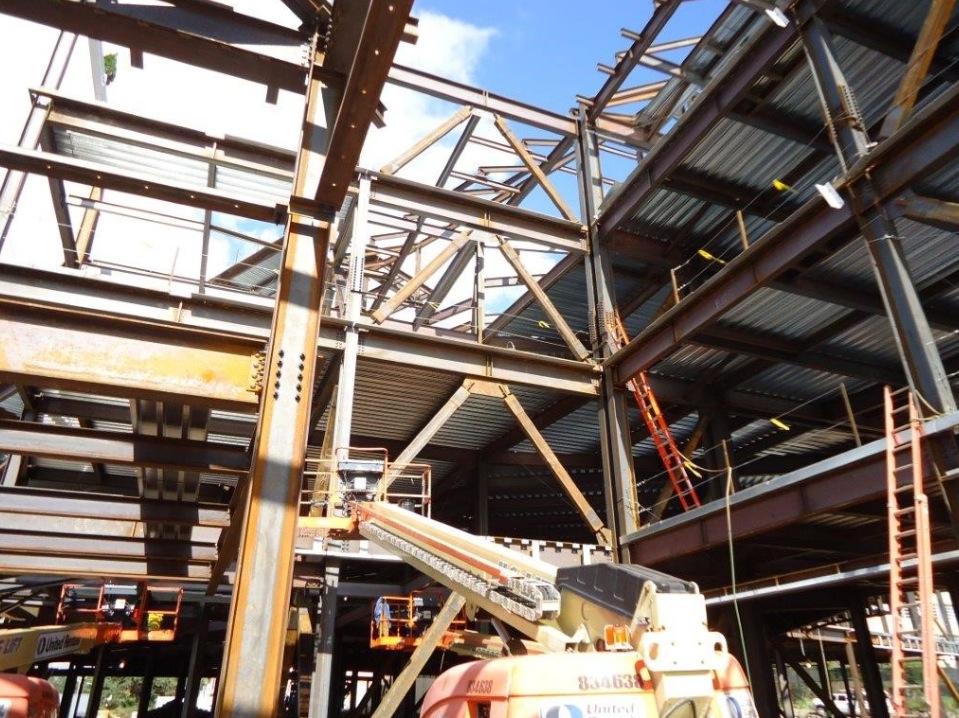 Situated on wetlands, the five-story, 179,000-sf Adult Behavioral Health Center in the Bronx, N.Y., required special seismic mitigation measures. Buckling restrained braces were the most economical, efficient solution.
Situated on wetlands, the five-story, 179,000-sf Adult Behavioral Health Center in the Bronx, N.Y., required special seismic mitigation measures. Buckling restrained braces were the most economical, efficient solution.
The structural design team, led by STV, first considered a traditional concentric braced frame lateral system. The solution met seismic requirements, but posed space-planning concerns for the client. Its relatively sizable structural elements and supporting walls would have bumped up against the health center’s programmatic requirements for rooms and circulation and would have jeopardized the architect’s open, airy indoor design scheme.
The final design approach, developed in conjunction with engineers in STV’s Los Angeles office, called for a BRBF system—a first for the Northeast—to enhance the structural performance of the building and greatly reduce steel frame member sizes. It also minimized the number of supporting walls needed for the project, and saved approximately $500,000 in material costs, according to Chris Cerino, PE, SECB, VP and Director of Structural Engineering, Building & Facilities Division, with STV. The firm also served as the design architect and electrical, civil, geotechnical, and telecom engineer on the project.
With the BRBF approach, certain braced frame steel columns could be downsized from W14x426 to W14x342, and select braced frame steel beams were reduced from W36x150 to W24x68.
“Smaller frame members gave STV designers flexibility in considering the movement of staff, residents, and food and building services,” says Cerino. “It also improved sightlines in all staff and resident areas to reduce the dependency on electronic monitoring.”

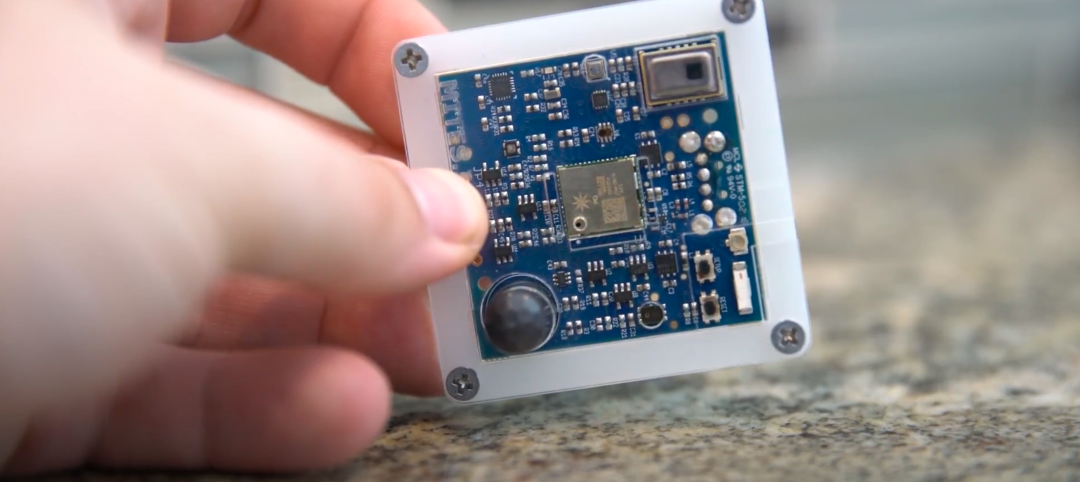
Buckling restrained braces (BRBs) vary slightly based on the manufacturer, but all BRBs include five basic components: a steel-plate core shaped like a kayak paddle (1) is placed within a hollow steel tube (2) that is coated with a low-friction material (3), which is then grouted in place (4) and capped (5). The grouted steel tube design prevents the steel core from buckling when in compression, while the coating prevents axial load from being transferred to the encasement.
The result is a “full, balanced response in relation to the forces being applied,” says Cerino. “Because the steel core is restrained, it develops nearly uniform axial strains across the section, resulting in efficient energy dissipation.”
This balanced energy dissipation, in turn, permits design teams to use much smaller beam sizes than with a standard braced frame.
On the Adult Behavioral Health Center project, Cerino’s team specified a proprietary system manufactured by Star Seismic. According to Cerino, Star’s Wildcat BRB system, which features single-pin connections, reduced erection time because it eliminated the need for stiffener plates. “Its patented collar reduces welding, since simple fillets can be used,” says Cerino. “That factored into the overall monetary savings.”
Cerino offers a few tips for Building Teams evaluating BRBFs:
- Watch out for the added special seismic requirements and details that become triggered when using a high-performance seismic system. “Not that a BRBF has different triggers than a special concentrically braced frame system, but since much of the design is deferred to the specialty brace contractor, some of the details can become out of sight, out of mind,” he says.
- Decide on the system early so you can address any client/procurement obstacles. “If it becomes too late, it can simply be easier to do nothing,” says Cerino. “That doesn’t help the project.”
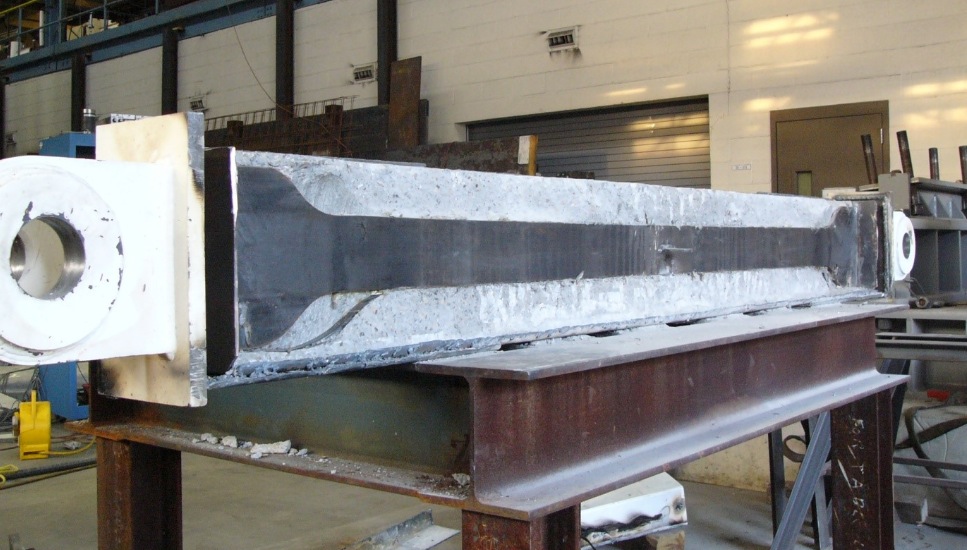 Buckling restrained braces include several basic components: a steel-plate core is placed within a hollow steel tube that is coated with a low-friction material and then grouted in place and capped. The grouted steel tube design prevents the steel core from buckling when in compression, while the coating prevents axial load from being transferred to the encasement.
Buckling restrained braces include several basic components: a steel-plate core is placed within a hollow steel tube that is coated with a low-friction material and then grouted in place and capped. The grouted steel tube design prevents the steel core from buckling when in compression, while the coating prevents axial load from being transferred to the encasement.
Related Stories
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Apr 5, 2023
Façade innovation: University of Stuttgart tests a ‘saturated building skin’ for lessening heat islands
HydroSKIN is a façade made with textiles that stores rainwater and uses it later to cool hot building exteriors. The façade innovation consists of an external, multilayered 3D textile that acts as a water collector and evaporator.
Project + Process Innovation | Mar 22, 2023
Onsite prefabrication for healthcare construction: It's more than a process, it's a partnership
Prefabrication can help project teams navigate an uncertain market. GBBN's Mickey LeRoy, AIA, ACHA, LEED AP, explains the difference between onsite and offsite prefabrication methods for healthcare construction projects.
Building Tech | Mar 14, 2023
Reaping the benefits of offsite construction, with ICC's Ryan Colker
Ryan Colker, VP of Innovation at the International Code Council, discusses how municipal regulations and inspections are keeping up with the expansion of off-site manufacturing for commercial construction. Colker speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield.
Student Housing | Mar 13, 2023
University of Oklahoma, Missouri S&T add storm-safe spaces in student housing buildings for tornado protection
More universities are incorporating reinforced rooms in student housing designs to provide an extra layer of protection for students. Storm shelters have been included in recent KWK Architects-designed university projects in the Great Plains where there is a high incidence of tornadoes. Projects include Headington and Dunham Residential Colleges at the University of Oklahoma and the University Commons residential complex at Missouri S&T.
AEC Innovators | Mar 3, 2023
Meet BD+C's 2023 AEC Innovators
More than ever, AEC firms and their suppliers are wedding innovation with corporate responsibility. How they are addressing climate change usually gets the headlines. But as the following articles in our AEC Innovators package chronicle, companies are attempting to make an impact as well on the integrity of their supply chains, the reduction of construction waste, and answering calls for more affordable housing and homeless shelters. As often as not, these companies are partnering with municipalities and nonprofit interest groups to help guide their production.
Modular Building | Mar 3, 2023
Pallet Shelter is fighting homelessness, one person and modular pod at a time
Everett, Wash.-based Pallet Inc. helped the City of Burlington, Vt., turn a municipal parking lot into an emergency shelter community, complete with 30 modular “sleeping cabins” for the homeless.
Multifamily Housing | Mar 1, 2023
Multifamily construction startup Cassette takes a different approach to modular building
Prefabricated modular design and construction have made notable inroads into such sectors as industrial, residential, hospitality and, more recently, office and healthcare. But Dafna Kaplan thinks that what’s held back the modular building industry from even greater market penetration has been suppliers’ insistence that they do everything: design, manufacture, logistics, land prep, assembly, even onsite construction. Kaplan is CEO and Founder of Cassette, a Los Angeles-based modular building startup.
Sustainability | Feb 8, 2023
A wind energy system—without the blades—can be placed on commercial building rooftops
Aeromine Technologies’ bladeless system captures and amplifies a building’s airflow like airfoils on a race car.