All key construction measures for multifamily housing rose by double-digit percentages in 2015, and demand for rentals (which continue to account for the lion’s share of that construction) is expected to remain robust over the next decade, according to “The State of the Nation’s Housing Market 2016,” which the Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard University released today.
That’s good news and bad news for renters, as vacancy rates continue to fall and rents continue to rise.
Growth in multifamily starts topped 10% for the fifth consecutive year in 2015, reaching a 27-year high of 397,300 units. Multifamily accounted for more than 30% of all housing starts last year, and permits—the barometer of future construction—rose 18.2% to 486,600 units.
More than 36% of all U.S. households opted to rent last year, the largest share since the late 1960s. Over the past decade, in fact, the number of renters increased by over nine million, the largest 10-year gain on record, with palpable demand across all age groups, income levels, and household types.
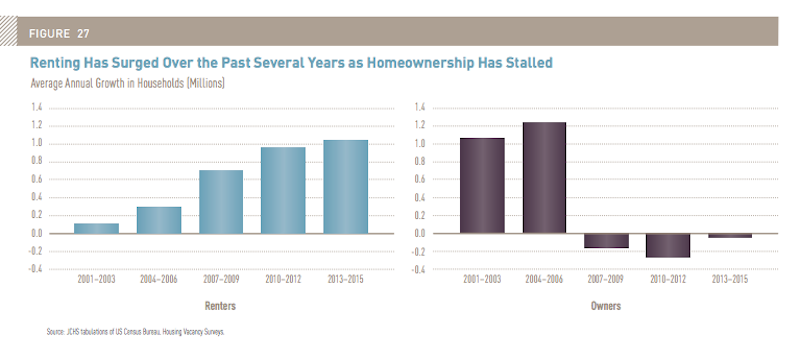
The number of renters increased by 9 million in the past decade, the largest 10-year gain on record. Image: Joint Center for Housing Studies' “The State of the Nation's Housing Market”
Somewhat counter-intuitively, given all the press about Millennials not being able to afford to buy a house, Current Population Survey data indicate that much of the jump in rental demand is coming from middle-aged households. Renters in their 50s and 60s rose by 4.3 million between 2005 and 2015. Renters aged 70 or older increased by more than 600,000 during that decade. And even though their cohort’s population actually dipped a bit, households in their 30s and 40s accounted for three million net new renters.
Households under age 30, by comparison, made up only one million net new renters. “reflecting the steep falloff in headship rates among the Millennial generation following the Great Recession,” according to the Harvard report.
The micro-apartment trend for urban markets seems to be having a greater impact on what’s being built overall. The median size of multifamily units fell from nearly 1,200 sf at the 2007 peak to 1,074 sf in 2015, reflecting the shift in the focus of development from the owner to the rental market.
Many new multifamily units are in large structures, with nearly half of the units completed in 2014 in buildings with 50 or more apartments. And about 36 percent of all new multifamily units added between 2000 and 2014 were in high-density neighborhoods, and another 30 percent each in medium- and low-density sections of metro areas. Even so, growth in the multifamily housing stock during this period was even more rapid in rural areas (up 24 percent) than in urban areas (up 19 percent).
The Joint Center has long decried the scarcity of affordable housing in the U.S. A sizable percentage of the multifamily buildings under construction targets higher-end and luxury renters. In addition, the rental vacancy rate last year fell to a 30-year low of 7.1%, a telling indication that supply isn’t keeping up with demand, and that rent appreciation is likely to present challenges for renters at all income levels.
Still, the report postulates that expanding construction of market-rate multifamily product “should provide some slack to tight markets, as older units slowly filter down from higher to lower rents.” And if construction sates high-end demand, “developers in some areas may turn their attention to middle-market rentals,” the report speculates.
The report acknowledges, however, that high development costs make building new units of affordable or even moderate-income multifamily difficult without government subsidies. And absent of public subsidies, “the cost of a typical market-rate rental unit will remain out of reach for the nation’s lowest-income households.”
The Joint Center concludes that with housing assistance insufficient to help most of those in need, “the limited supply of low-cost units promises to keep the pressure on all renters at the lower end of the income scale.”
It’s still not certain how these dynamics will impact homeownership, even when buying is still more affordable than renting in 58% of U.S. markets, according to RealtyTrac’s 2016 Rental Affordability Analysis.
“Renters in 2016 will be caught between a bit of a rock and a hard place, with rents becoming less affordable as they rise faster than wages, but home prices rising even faster than rents,” said Daren Blomquist, Vice President at RealtyTrac. “In markets where home prices are still relatively affordable, 2016 may be a good time for some renters to take the plunge into homeownership before rising prices and possibly rising interest rates make it increasingly tougher to afford to buy a home.”
Related Stories
MFPRO+ New Projects | Oct 30, 2024
BIG’s One High Line finally reaches completion in New York City’s West Chelsea neighborhood
One High Line, a luxury residential project spanning a full city block in New York’s West Chelsea neighborhood, reached completion this summer following years of delays related to investor lawsuits.
MFPRO+ New Projects | Oct 30, 2024
Luxury waterfront tower in Brooklyn features East River and Manhattan skyline views
Leasing recently began for The Dupont, a 41-story luxury rental property along the Brooklyn, N.Y., waterfront. Located within the 22-acre Greenpoint Landing, where it overlooks the newly constructed Newtown Barge Park, the high-rise features East River and Manhattan skyline views along with 20,000 sf of indoor and outdoor communal space.
Multifamily Housing | Oct 28, 2024
A case for mid-rise: How multifamily housing can reshape our cities
Often referred to as “five-over-ones,” the mid-rise apartment type is typically comprised of five stories of apartments on top of a concrete “podium” of ground-floor retail. The main criticism of the “five-over-one” is that they are often too predictable.
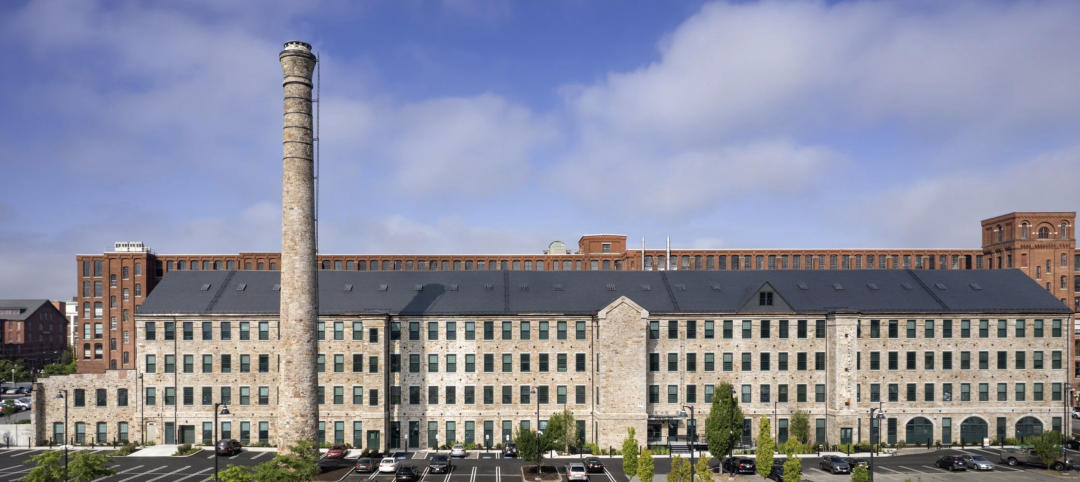
Adaptive Reuse | Oct 22, 2024
Adaptive reuse project transforms 1840s-era mill building into rental housing
A recently opened multifamily property in Lawrence, Mass., is an adaptive reuse of an 1840s-era mill building. Stone Mill Lofts is one of the first all-electric mixed-income multifamily properties in Massachusetts. The all-electric building meets ambitious modern energy codes and stringent National Park Service historic preservation guidelines.
MFPRO+ News | Oct 22, 2024
Project financing tempers robust demand for multifamily housing
AEC Giants with multifamily practices report that the sector has been struggling over the past year, despite the high demand for housing, especially affordable products.
Products and Materials | Oct 17, 2024
5 multifamily tech products for your next project
Multifamily housing and technological upgrades go hand-in-hand. From the rise in electric vehicle charging needs to the sophistication of smart home accessories, tech products are abound in the multifamily space.
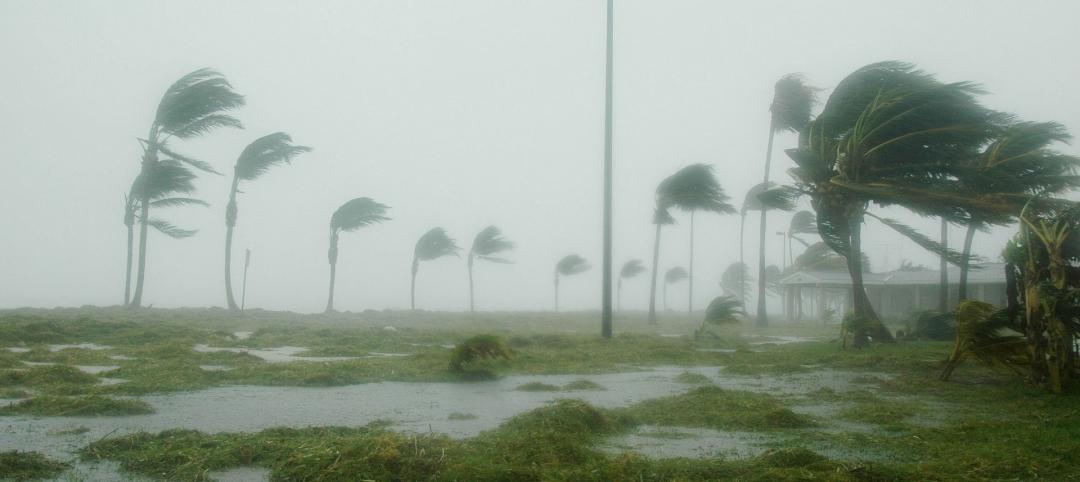
Codes and Standards | Oct 16, 2024
North Carolina’s code policies likely worsened damage caused by Hurricane Helene
The North Carolina Legislature’s rejection of building code updates likely worsened the damage caused by Hurricane Helene, code experts say. Over the past 15 years, lawmakers rejected limits on construction on steep slopes, which might have reduced the number of homes destroyed by landslides.
MFPRO+ News | Oct 16, 2024
One-third of young adults say hurricanes like Helene and Milton will impact where they choose to live
Nearly one-third of U.S. residents between 18 and 34 years old say they are reconsidering where they want to move after seeing the damage wrought by Hurricane Helene, according to a Redfin report. About 15% of those over age 35 echoed their younger cohort’s sentiment.
Student Housing | Oct 9, 2024
University of Maryland begins work on $148 million graduate student housing development
The University of Maryland, in partnership with Campus Apartments and Mosaic Development Partners, has broken ground on a $148.75 million graduate student housing project on the university’s flagship College Park campus. The project will add 741 beds in 465 fully furnished apartments.
MFPRO+ News | Oct 9, 2024
San Francisco unveils guidelines to streamline office-to-residential conversions
The San Francisco Department of Building Inspection announced a series of new building code guidelines clarifying adaptive reuse code provisions and exceptions for converting office-to-residential buildings. Developed in response to the Commercial to Residential Adaptive Reuse program established in July 2023, the guidelines aim to increase the viability of converting underutilized office buildings into housing by reducing regulatory barriers in specific zoning districts downtown.

















