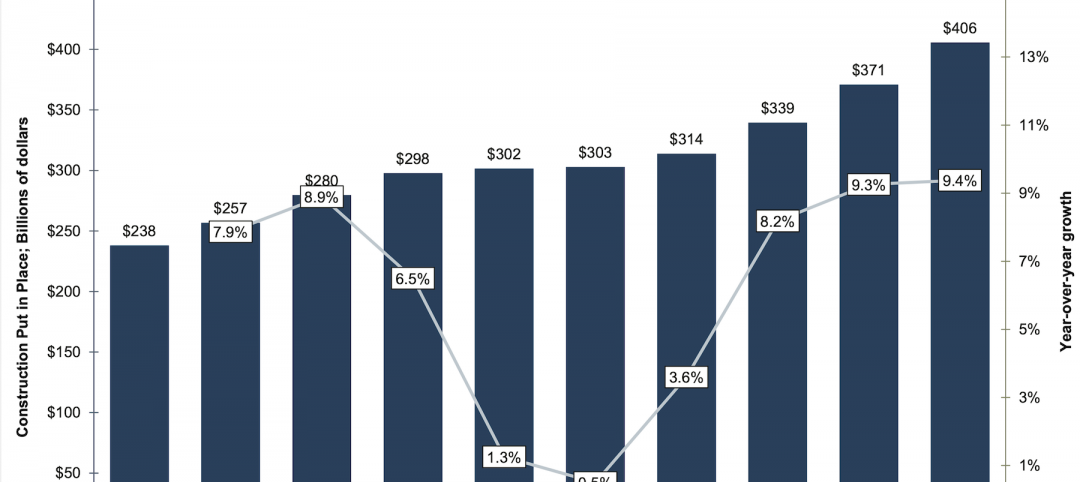
Nonresidential construction spending, which rose by 3.5% in the second half of 2019, is expected to increase in 2020, albeit at a modest 2% clip, with demand projected to weaken as the year goes on.
In its Construction Outlook for the U.S. 2020, JLL attributed last year’s performance mostly to the 10.1% rise in public spending. Construction employment was up 2.1% to 6.44 million, and construction unemployment dipped to 4.5%. Indexed building costs increased 1.5% year-over-year.
In 2020, the dollar value of construction starts (according to Dodge Data & Analytics) is expected to decline by nearly 5%. And JLL expects the disparity between public and private nonres construction spending to continue.
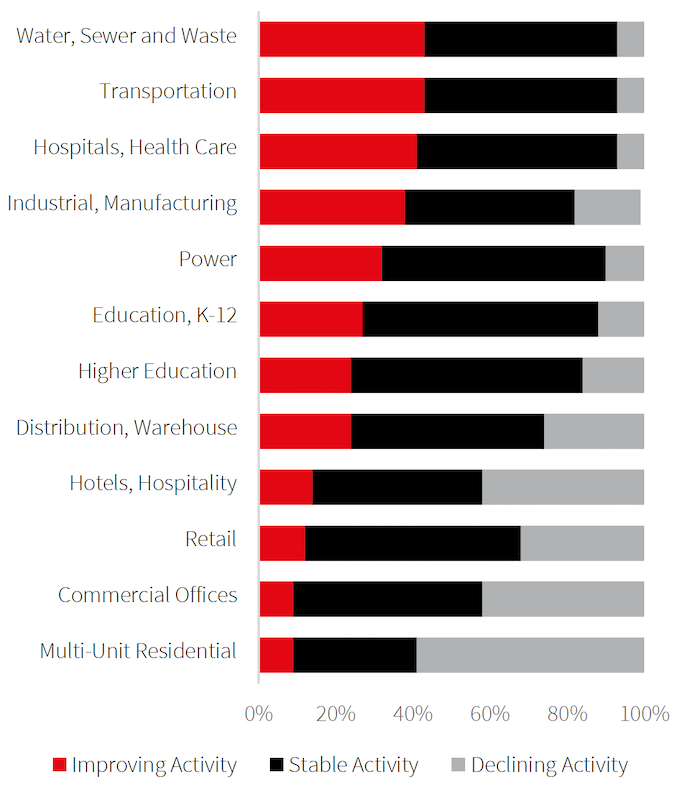
With nearly all growth in construction spending coming from public dollars, the sectors expected to do well this year will be those with the most public investment, such as transportation, education, healthcare and public safety. The reverse will be true about multifamily residential, commercial office, hotels, and retail.
JLL forecasts construction inflation to fall somewhere between 1% and 3%, and by a bit higher percentages on the labor side.
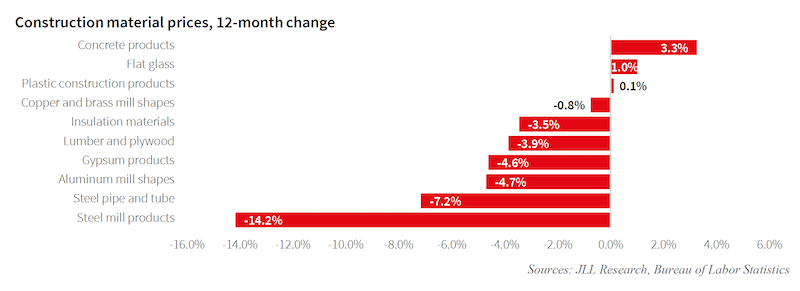
Inflation in the cost of construction materials has been held in check.
JLL was reluctant to speculate on the impact of the coronavirus on construction. But it did note that roughly between one-quarter and one-third of all construction products in the U.S. are sourced from China, so any sustained slowdown in Chinese production due to the spread of COVID 19 may cause material shortages in the U.S.
The Outlook’s projections about the U.S. economy—that it would remain strong enough in 2020 to keep the construction industry on track overall, but would not provide the private investment fuel that would be necessary for robust growth—were made before the economy appeared to be sinking into recession in mid March.
On the plus side, the Outlook points out that the ratified U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement is on track to be fully implemented in 2020. “The agreement brings stability to critical material markets for the construction industry, particularly for lumber, steel and aluminum,” JLL posited. Across the Pacific, the U.S. and China signed a Phase One agreement to roll back a very small portion of the tariffs that were imposed between the two countries over the past few years. Phase One represents the first time under the Trump administration that average tariff rates on Chinese imports have declined.
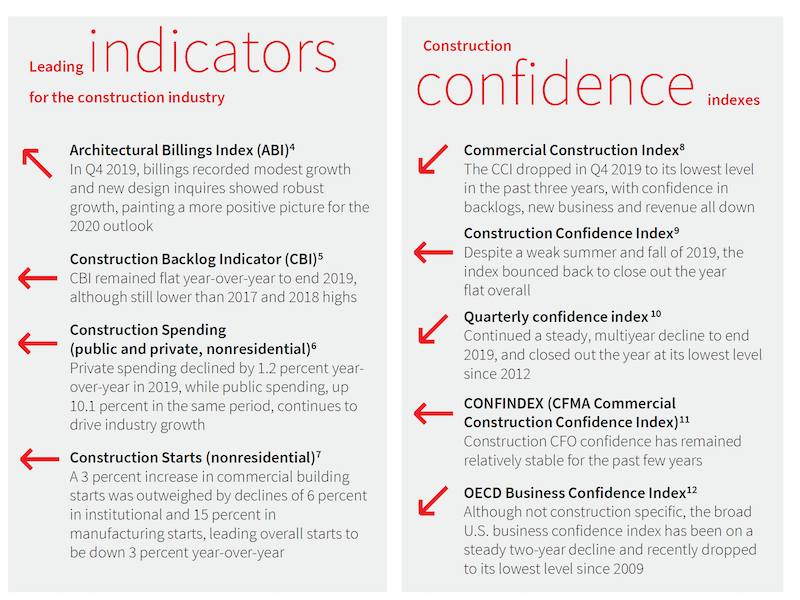
Construction confidence was flat to down in 2019, according to several measurements.
Much of the Outlook was actually devoted to recounting key metrics from last year. It points out, for example, that construction confidence was flat in 2019, while the Commercial Construction Index, as aggregated by the U.S. Chamber of Commerce and USG, dropped in the fourth quarter to its lower level in three years.
Last year, the rate of increase for construction materials eased a bit, to 3%, with most of that increase occurring in the first half of the year. Steel-mill products, in fact, experienced a 14.2% decrease over the 12-month period.
The most expensive cities with more than 150,000 people to build in last year were the usual suspects: New York, San Francisco, Chicago, Honolulu, and Fairbanks, Alaska. The least expensive were Knoxville, Tenn., Austin, Amarillo, Texas, Little Rock, Ark., and El Paso, Texas.
JLL’s Outlook also provides regional comparisons for the years 2008 through 2019. In that context, for example, warehouses were the strongest construction sector in the Midwest and Northeast, Amusement & Recreation in the West, and Auto Service/Parts in the South. The sectors with the greatest decline over that decade were bank and financial offices (Northeast and South), Multiretail (West), and houses of worship (Midwest).
As for overall growth during this 10-year period. the Northeast, West, and Midwest fell short of the national average in terms of construction backlog, while the South outperformed the country as a whole.
Related Stories
Market Data | Oct 19, 2021
Demand for design services continues to increase
The Architecture Billings Index (ABI) score for September was 56.6.
Market Data | Oct 14, 2021
Climate-related risk could be a major headwind for real estate investment
A new trends report from PwC and ULI picks Nashville as the top metro for CRE prospects.
Market Data | Oct 14, 2021
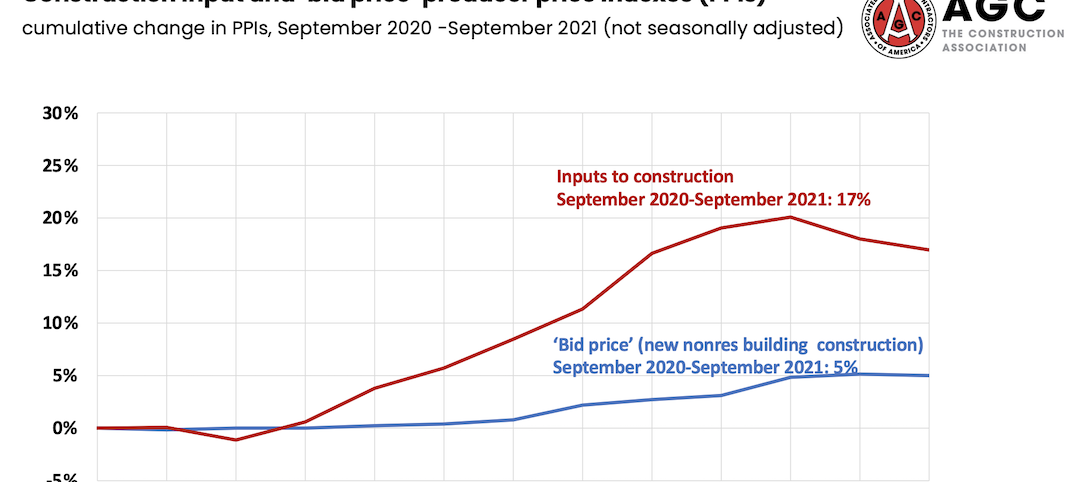
Prices for construction materials continue to outstrip bid prices over 12 months
Construction officials renew push for immediate removal of tariffs on key construction materials.
Market Data | Oct 11, 2021
No decline in construction costs in sight
Construction cost gains are occurring at a time when nonresidential construction spending was down by 9.5 percent for the 12 months through July 2021.
Market Data | Oct 11, 2021
Nonresidential construction sector posts first job gain since March
Has yet to hit pre-pandemic levels amid supply chain disruptions and delays.
Market Data | Oct 4, 2021
Construction spending stalls between July and August
A decrease in nonresidential projects negates ongoing growth in residential work.
Market Data | Oct 1, 2021
Nonresidential construction spending dips in August
Spending declined on a monthly basis in 10 of the 16 nonresidential subcategories.
Market Data | Sep 29, 2021
One-third of metro areas lost construction jobs between August 2020 and 2021
Lawrence-Methuen Town-Salem, Mass. and San Diego-Carlsbad, Calif. top lists of metros with year-over-year employment increases.
Market Data | Sep 28, 2021
Design-Build projects should continue to take bigger shares of construction spending pie over next five years
FMI’s new study finds collaboration and creativity are major reasons why owners and AEC firms prefer this delivery method.
Market Data | Sep 22, 2021
Architecture billings continue to increase
The ABI score for August was 55.6, up from July’s score of 54.6.