Within the next five years, the AE firm SmithGroup wants to be able to incorporate the highest level of energy efficiency into every project it designs and builds. But the challenge is selecting the right energy model from literally thousands of options.
“The number of buildings we need to touch, and the pace we need to do it, exceed what an individual could do in a lifetime,” says Stet Sanborn, engineering lead in SmithGroup’s San Francisco office.
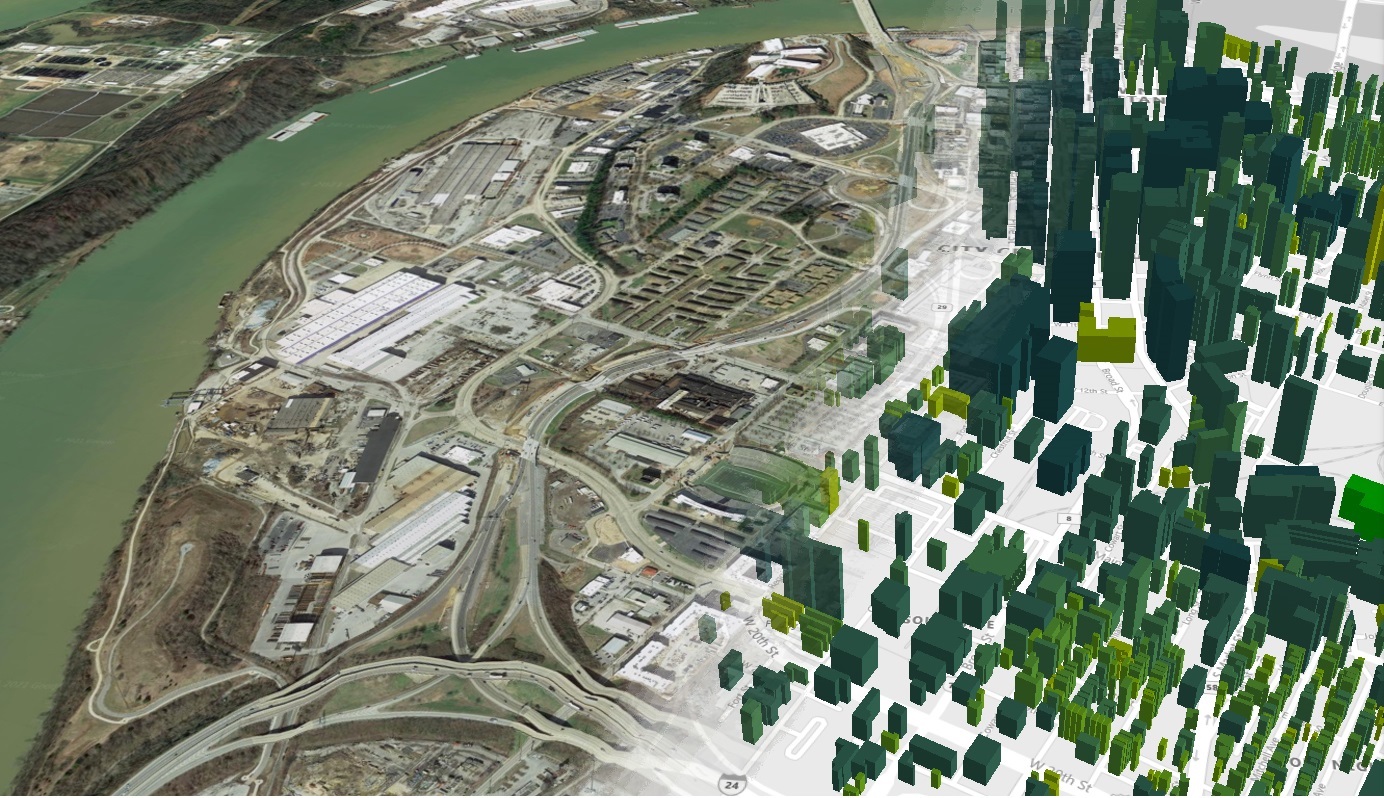
To speed this process, SmithGroup has partnered with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), whose Automated Building Energy Modeling software suite, better known as AutoBEM, has simulated the energy use of 123 million structures, or 98 percent of U.S. Buildings.
AutoBEM was developed using high-performance computing to process layers of imaging data with information about each building, such as its size, use, construction materials, and HVAC technologies. The goal was to create a digital twin of the nation’s buildings, says Joshua New, ORNL’s project leader.
Sanborn tells BD+C that SmithGroup got involved with this technology collaboration project 18 months ago, after responding to the lab’s request for proposal. After six months of planning, SmithGroup provided information for every building type it handles, including climate zones, footprints, orientation, and envelope construction. The modeling also took into account lighting and HVAC variations.
This project generated more than 200,000 building iterations and 250,000 energy models. The computation, which took less than an hour to complete, was equal to the output of one employee working full time for 365 years.
Using AI to spot trends
AutoBEM’s information was used to train an artificial intelligence tool that will allow SmithGroup to pre-simulate the energy impact of every design possibility for any building.
Sanborn says that these data sets are still pretty rudimentary, so they should benefit from ORNL’s plans to update its information this year. “We’re looking for much better resolution, so we can eventually have real-time and predictive feedback,” he explains.
In 2023, SmithGroup plans to train the AI bots to spot trends and choose the best energy-efficient iteration for a given project. Sanborn says his team has already been surprised by how the data has highlighted “the interaction of things” like glass U-values and wall R-values. More refined data, he predicts, should make these data sets more accessible and actionable. (Sanborn says that SmithGroup already has pre-simulated climate data for every market it builds in.)
The first new designs for which this energy modeling is likely to be applied could be for a civic or higher education building, says Sanborn, where no restrictions to sharing information exist.
ORNL’s partners such as SmithGroup and Google—which is using AutoBEM to improve its free Environmental Insights Explorer tool—have committed to sharing data sets created by using AutoBEM. Some data sets have already been posted, and Sanborn thinks that open-source access is important because “SmithGroup can’t build every building, as much as we’d like to. We don’t want to hold a secret sauce or limit everyone’s ability to drive efficiency in response to what is really a climate emergency.”
SmithGroup participated in the funding of AutoBEM, whose development, expansion and collaborations are also funded by DOE’s Office of Electricity, the Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy’s Building Technologies Office and the National Nuclear Security Administration. The research team leveraged supercomputing resources from Argonne National Laboratory.
Related Stories
| Sep 7, 2014
Building the cladding palette: panels, rainscreens, and veneers [AIA course]
When it comes to cost, performance, and aesthetics—not to mention maintenance and long-term resilience—the evaluation of cladding materials and façade systems is more complex than ever. This course is worth 1.0 AIA CES HSW learning units.
| Aug 11, 2014
New guide for prevention of thermal bridging in commercial buildings
The guide aims to overcome obstacles with respect to mitigating thermal bridging to reduce energy consumption in buildings.
| Aug 4, 2014
Facebook’s prefab data center concept aims to slash construction time in half
Less than a year after opening its ultra-green, hydropowered data center facility in Luleå, Sweden, Facebook is back at it in Mother Svea with yet another novel approach to data center design.
| Jul 30, 2014
German students design rooftop solar panels that double as housing
Students at the Frankfurt University of Applied Sciences designed a solar panel that can double as living space for the Solar Decathlon Europe.
| Jul 25, 2014
Grocery stores choosing Green Globes for building sustainability certification
The Green Building Initiative (GBI) has announced a wave of Green Globes certifications for new grocery stores, including New Seasons Markets, Whole Foods, Price Chopper, Aldi’s, Harris Teeter, Wegmans, and Publix.
| Jul 17, 2014
A harmful trade-off many U.S. green buildings make
The Urban Green Council addresses a concern that many "green" buildings in the U.S. have: poor insulation.
| Jul 11, 2014
Are these LEGO-like blocks the future of construction?
Kite Bricks proposes a more efficient way of building with its newly developed Smart Bricks system.
| May 22, 2014
Facebook, Telus push the limits of energy efficiency with new data centers
Building Teams are employing a range of creative solutions—from evaporative cooling to novel hot/cold-aisle configurations to heat recovery schemes—in an effort to slash energy and water demand.
| May 22, 2014
Big Data meets data centers – What the coming DCIM boom means to owners and Building Teams
The demand for sophisticated facility monitoring solutions has spurred a new market segment—data center infrastructure management (DCIM)—that is likely to impact the way data center projects are planned, designed, built, and operated.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.