“Innovation” was the byword as 175 healthcare designers gathered in Chicago for the American College of Healthcare Architects/AIA Academy of Architecture for Health Summer Leadership Summit.
Experts from Kaiser Permanente, Cleveland Clinic, Mayo Clinic, Massachusetts General Hospital, and other healthcare institutions and think tanks described various models they’re using to spur innovation and improve the quality of care for their patients.
That’s a topic of mounting importance under the Affordable Care Act, which can penalize a hospital with a poor record of patient satisfaction and outcomes.
KAISER PERMANENTE. Jennifer Liebermann, Co-founder of Kaiser Permanente’s 37,000-sf Garfield Innovation Center, described a typical problem such in-house innovation facilities tackle: how to reduce medication errors. “Nurses get interrupted all the time when they’re trying to give patients their meds,” she said. That leads to medication errors and injury to patients.
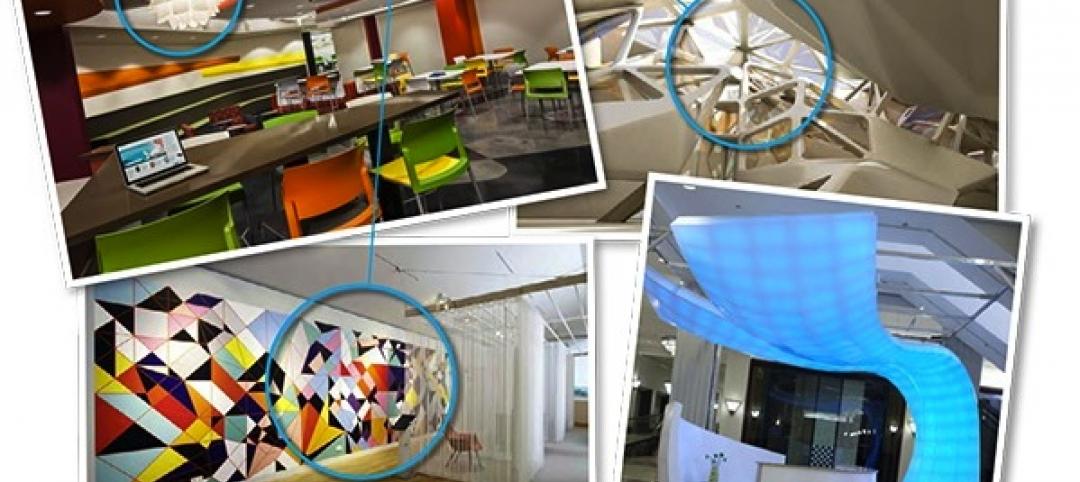
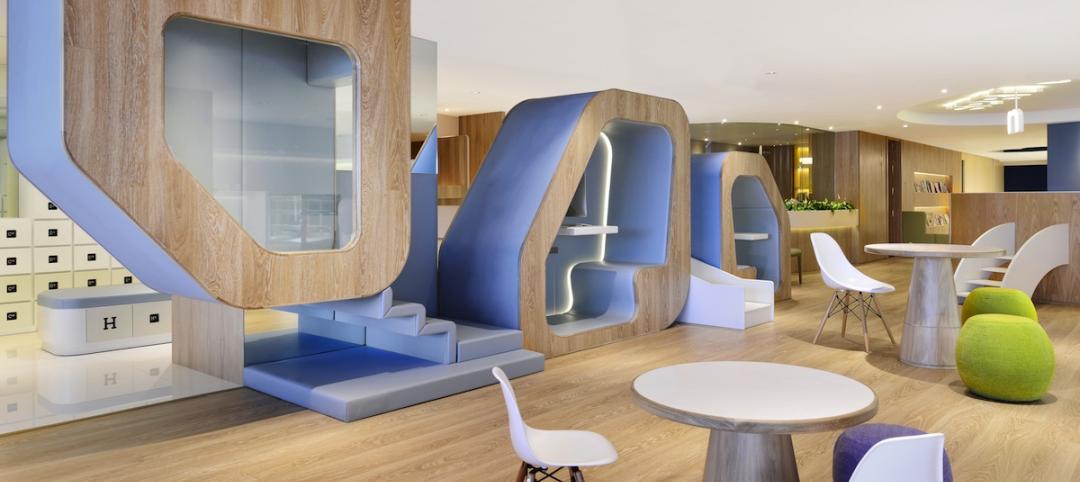
HOW TO DESIGN A HEALTHCARE INNOVATION CENTER
Larry Stofko, EVP of the Innovation Institute, provided ACHA/AAH summiteers with advice on designing physical spaces to enable innovation:
1. Make the space flexible, with movable walls and furnishings.
2. Make it inspiring, with whimsical artwork and “creative” colors (orange and blue seem to work best).
3. Make it collaborative, with lots of whiteboards, wall space, and glass to write on.
4. Make it social, with a working kitchen, comfy couches, springboard chairs.
5. Make it hard-working, by providing the right tools and hardware (e.g., 3D printers).
6. Make sure it reflects the institution’s culture and brand.
7. Provide a dedicated showcase to display your innovation successes.
The Garfield Center team tried several ideas, even something that looked like a hazmat suit (“We tested it on nurses, and they said they’d never wear that thing,” said Liebermann). The solution: a bright yellow sash that the nurse wears over her shoulder when dispensing prescriptions.
“That sash lets everyone know, ‘Don’t interrupt me, I’m dispensing meds,’” said Liebermann. A simple and inexpensive solution, but so effective that it’s being rolled out through the entire 32-hospital Kaiser Permanente system.
“We borrow ideas from other healthcare organizations, but some of our most powerful inspiration comes from outside healthcare,” said Liebermann. KP is working with Walmart on telemedicine and with NASA on improving safety in operating rooms. “NASA has a lot of experience with its people working in tight spaces,” she said.
CLEVELAND CLINIC is an institution with a long history of innovation in healthcare—2,600 patent applications, 450 royalty licenses, 71 spinoffs, $799 million in equity investments, according to Brian Kolonick, General Manager of Cleveland Clinic Innovations’ Global Healthcare Innovations Alliance. The alliance includes MedStar Health, North Shore–LIJ, Promedica, the University of Notre Dame, and Marshfield Clinic.
Half (50%) of the clinic’s inventions have been medical devices, along with IT solutions (23%) and therapeutic/diagnostic systems (22%). The remaining 5% were healthcare delivery solutions. “Delivery solutions are our secret sauce,” said Kolonick. Cleveland Clinic excels at coming up with new ways to improve patient outcomes and then outsourcing those capabilities to other institutions.
Cleveland Clinic is not modest about collaborating with the private sector and government agencies. It’s working with NASA Glenn Research Center to see how lessons from space medicine can be applied to terrestrial healthcare. They’re consulting with Parker Hannifan (“They know a lot about tubes, and we use a lot of tubes in healthcare,” said Kolonick) and Lubrizol, for its expertise in polymers.
“We’re also involved with Cox Communications, to see how they can help us work with patients from inside the home, or via healthcare pods at the grocery store,” he said.
MAYO CLINIC’s Center for Innovation was founded in 2008. “We’re a shared service for innovation across Mayo,” said Barbara Spurrier, MHA, CMPE, the CFI’s Administrative Director. Its staff of 60 includes scientists, designers, programmers, analysts, bioethicists, nurses, and lawyers.
The CFI has 47 projects in the works, most of which have to be completed in 12 months. “There are a lot of things that don’t work out,” Spurrier said. “Sometimes we get all the way to a prototype and it doesn’t work, and we have to put it on the shelf.”
Mayo is looking at developing smartphone apps, such as one that teenage asthma patients could use to monitor their condition without having to go to the clinic.
Video medical visits, perhaps via Skype, are of keen interest to Mayo, especially for use with older patients. “How can we help seniors thrive in place?” asked Spurrier. “We know that 85% of them can get their care at home. What conditions need to be in place so that we can serve them right in their homes?”
“The Garage” is another Mayo innovation initiative—an incubator for products and services with commercialization potential. There’s also CoDE, which provides as much as $50,000 each to up to 10 teams a year for what Spurrier called “open innovation.” Mayo’s “Transform” international symposium recently attracted 850 innovators from 16 countries.
Mayo’s newest project: the 7,000-sf Well Living Lab, in collaboration with its home city of Rochester, Minn. “We’ll be looking at the intersection of medical and scientific research as related to the built environment,” said Spurrier.
MASS GENERAL. James A. Gordon, MD, MPA, Director of the Learning Laboratory at Massachusetts General Hospital and the Gilbert Program in Medical Simulation at Harvard Medical School, emphasized the need for simulation tools and labs at teaching hospitals. He said simulation training was crucial to improving patient safety and accelerating and assuring physician expertise.
“In medicine, every day is game day,” said Gordon, an emergency medicine specialist. To his fellow physicians, he posed this rhetorical question: “Can you continue to maintain your standards without allocating time for being offline to train?” Gordon didn’t say so outright, but it was clear he didn’t think so.
Related Stories
| Jan 30, 2014
The evolving workplace: One designer's inspiration board
"Open office" has been a major buzzword for decades, and like any buzzword, some of the novelty has worn off. I don't believe we will abandon the open office, but I do think we need to focus on providing a dynamic mix of open and closed spaces.
| Jan 30, 2014
What's in store for healthcare capital markets in 2014?
Despite the shake up stemming from the Affordable Care Act, 2014 will be an active year in healthcare capital markets, according to real estate experts from CBRE Healthcare.
| Jan 28, 2014
16 awe-inspiring interior designs from around the world [slideshow]
The International Interior Design Association released the winners of its 4th Annual Global Excellence Awards. Here's a recap of the winning projects.
| Jan 13, 2014
Custom exterior fabricator A. Zahner unveils free façade design software for architects
The web-based tool uses the company's factory floor like "a massive rapid prototype machine,” allowing designers to manipulate designs on the fly based on cost and other factors, according to CEO/President Bill Zahner.
| Jan 11, 2014
Getting to net-zero energy with brick masonry construction [AIA course]
When targeting net-zero energy performance, AEC professionals are advised to tackle energy demand first. This AIA course covers brick masonry's role in reducing energy consumption in buildings.
| Jan 9, 2014
Harley Ellis Devereaux, BFHL Architects announce merger
Effective January 1, 2014, Ralph Lotito and Brett Paloutzian have merged BFHL, comprising 15 healthcare architects, with Harley Ellis Devereaux. A national architecture and engineering firm in practice since 1908, Harley Ellis Devereaux has offices in Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, San Diego and San Francisco, CA.
Smart Buildings | Jan 7, 2014
9 mega redevelopments poised to transform the urban landscape
Slowed by the recession—and often by protracted negotiations—some big redevelopment plans are now moving ahead. Here’s a sampling of nine major mixed-use projects throughout the country.
| Dec 20, 2013
Top healthcare sector trends for 2014 (and beyond)
Despite the lack of clarity regarding many elements of healthcare reform, there are several core tenets that will likely continue to drive transition within the healthcare industry.
| Dec 17, 2013
IBM's five tech-driven innovation predictions for the next five years [infographics]
Smart classrooms, DNA-based medical care, and wired cities are among the technology-related innovations identified by IBM researchers for the company's 5 in 5 report.
| Dec 17, 2013
CBRE's Chris Bodnar and Lee Asher named Healthcare Real Estate Executives of the Year
CBRE Group, Inc. announced today that two of its senior executives, Chris Bodnar and Lee Asher, have been named Healthcare Real Estate Executives of the Year by Healthcare Real Estate Insights.