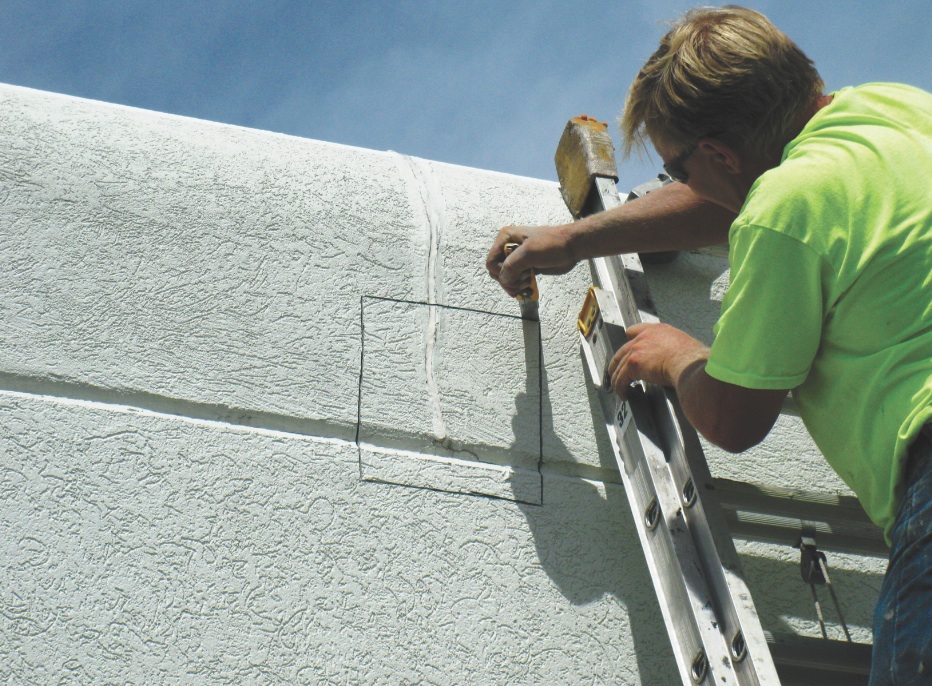
Exterior insulation and finish systems, or EIFS, are proprietary wall cladding assemblies that combine rigid insulation board with a water-resistant exterior coating. EIFS are popular chiefly for their low cost and high insulating values, and they are used in a range of construction types, from hotels to office parks to multifamily housing.
Unlike traditional stucco, which is composed of inorganic cement-bonded sand and water, EIFS uses organic polymeric finishes reinforced with glass mesh. As an energy-efficient, economical wall covering, EIFS can be effective for both new construction and recladding applications.
However, successful use of EIFS is highly dependent on proper design and sound construction practices. Without correct design and detailing, EIFS wall systems have been known to fail dramatically.
This course discusses the six elements of an EIFS wall assembly; common EIFS failures and how to prevent them; and EIFS and sustainability.
After reading this article, you should be able to:
• Describe the components of a typical Exterior Insulation and Finish System (EIFS) and differentiate among the classes of EIFS in terms of materials, properties, and usage, so as to evaluate existing systems and specify EIFS for new construction.
• Identify signs of distress in EIFS wall systems and associated sealant joints, flashings, and accessories, applying principles of EIFS construction to deducing the underlying causes of premature failure.
• Apply green building codes and standards to the design and specification of EIFS, implementing updated energy code requirements for continuous exterior insulation, so as to meet or exceed standards for building envelope thermal regulation and moisture control.
• Implement maintenance and repair practices to address staining, impact damage, punctures, cracks, and other signs of injury, using appropriate strategies that comply with industry standards, manufacturers’ requirements, aesthetic goals, and the client’s restoration objectives.
Take this AIA CES Discovery course at BDCUniversity.com
Related Stories
| Oct 6, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Dow Corning features new silicone weather barrier sealant
Modular Design Architecture >Dow Corning 758 sealant used in GreenZone modular high-performance medical facility.
| Oct 4, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011
Click here for the latest news and products from Greenbuild 2011, Oct. 4-7, in Toronto.
| Oct 4, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Nearly seamless highly insulated glass curtain-wall system introduced
Low insulation value reflects value of entire curtain-wall system.
| Oct 3, 2011
Balance bunker and Phase III projects breaks ground at Mitsubishi Plant in Georgia
The facility, a modification of similar facilities used by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Inc. (MHI) in Japan, was designed by a joint design team of engineers and architects from The Austin Company of Cleveland, Ohio, MPSA and MHI.
| Sep 12, 2011
Living Buildings: Are AEC Firms up to the Challenge?
Modular Architecture > You’ve done a LEED Gold or two, maybe even a LEED Platinum. But are you and your firm ready to take on the Living Building Challenge? Think twice before you say yes.
| Jul 22, 2011
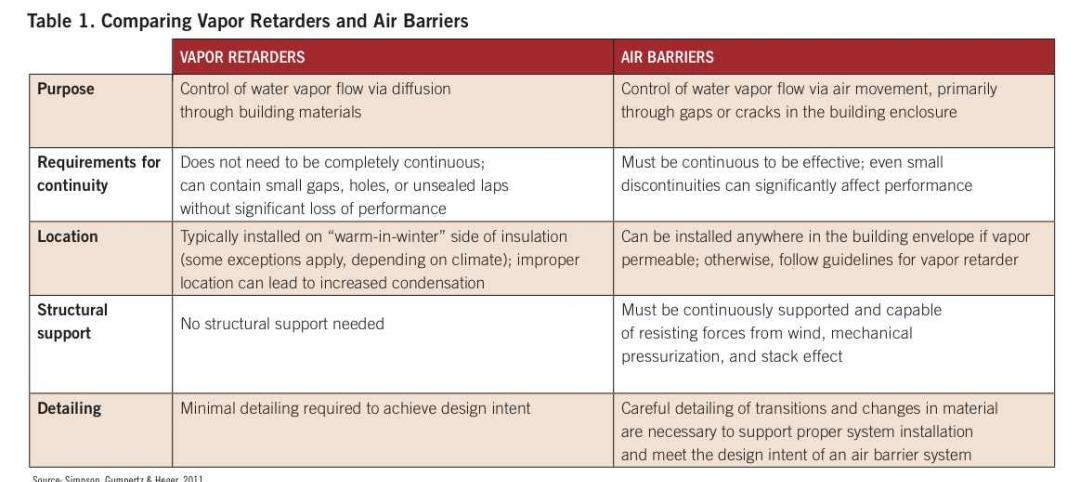
Air barrier systems: Your guide to optimal performance
Expert advice on how to control wasteful air leakage in the building envelope.
| Jul 22, 2011
Five award-winning modular innovations
The Modular Building Institute's 2011 Awards of Distinction highlight fresh ideas in manufactured construction projects.
| Oct 13, 2010
Community college plans new campus building
Construction is moving along on Hudson County Community College’s North Hudson Campus Center in Union City, N.J. The seven-story, 92,000-sf building will be the first higher education facility in the city.