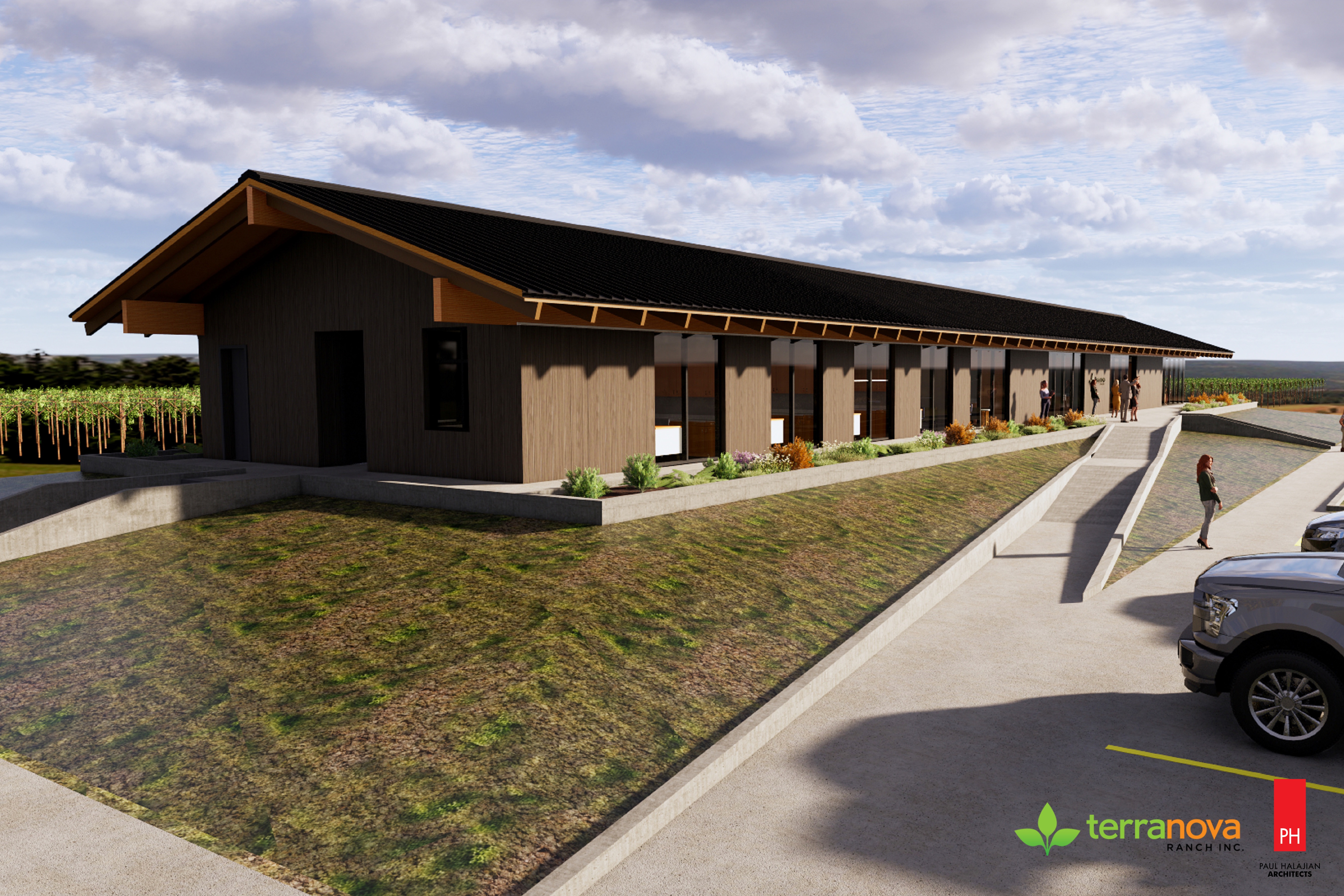
Terranova Ranch in Fresno, Calif., grows more than 25 different crops on 6,000 acres. The company, which started in 1981, has focused its attention lately on methods that keep its soil, water, and air quality as healthy and sustainable as possible.
The design for Terranova Ranch’s new office pavilion is the first net-zero carbon and net positive energy project by Paul Halajian Architects (PHA), and the client’s design choices were informed by the use of cove.tool’s web-based building performance app.
Terranova Ranch’s aimed for a 100 percent reduction in operational carbon emissions, and the architect provided several options toward meeting or exceeding that goal. (Cove.tool shared some of the details of this case study with BD+C.)
GOING BEYOND CODE MINIMUMS
Initially, the energy model for the 5,800-sf office building was designed to follow code minimum baseline assumptions from California’s Title 24, version 2019, which offered a carbon reduction of 12 percent. PHA’s project architect conducted several analyses on possible improvements to reduce the overall Energy Use Intensity (EUI), which in this model was 42.52 kBtu/sf/year.
These analyses measured the impacts of the building’s HVAC, lighting, equipment, hot water, fans, and pumps. The first proposed design change was an envelope upgrade, from the mandatory minimum of R-19 to R-30 by adding two inches of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam board to the exterior walls; and three inches of foam board insulation to the roof, which increased its R-value from 30 to 41. These changes would increase the building’s overall carbon reduction in base design to 20 percent and reduce the EUI to 38.
GLAZING’S BENEFITS DIDN’T PENCIL
The second option the architect investigated for Terranova Ranch combined the proposed envelope upgrade with improved glazing using Solarban 72 Acuity glass or Starphire glass with a u-value of 0.28 and solar heat coefficient of 0.28. (The baseline requirement is Solarban 60.) However, using cove.tool analysis tool, the architect determined that the whole-building EUI would have only reduced to 37, and only increased the carbon reduction by 2 percent from the first option. There were also cost considerations that made the glazing option less favorable.
The third upgrade option explored introduced 2,200 sf of monocrystalline solar panels, angled at a 15-degree incline atop a shaded parking structure. This option would reduce the building’s carbon emissions by 84 percent (from option No. 2’s 22 percent) and decrease the EUI to 7 form 37. Terranova Ranch was enthusiastic about this option.
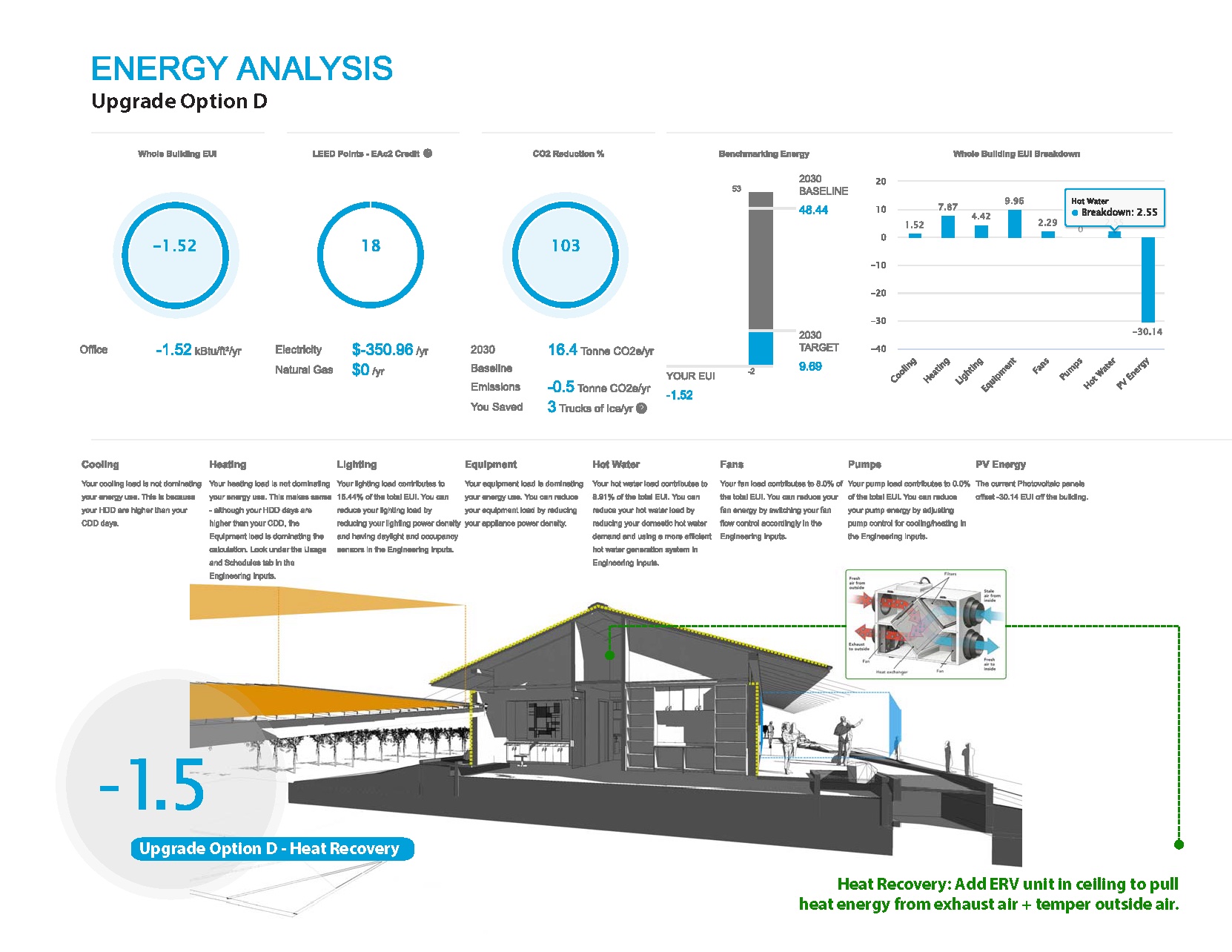
A fourth alternative explored introducing heat recovery by adding an energy recovery ventilator in the ceiling. This option allowed for a carbon reduction of 103 percent and an EUI score of negative 1.5. The client agreed to move forward in the building’s design with each option except the glazing upgrade.
SUNLIGHT EXPOSURE WILL REDUCE BUILDING’S LIGHTING NEEDS
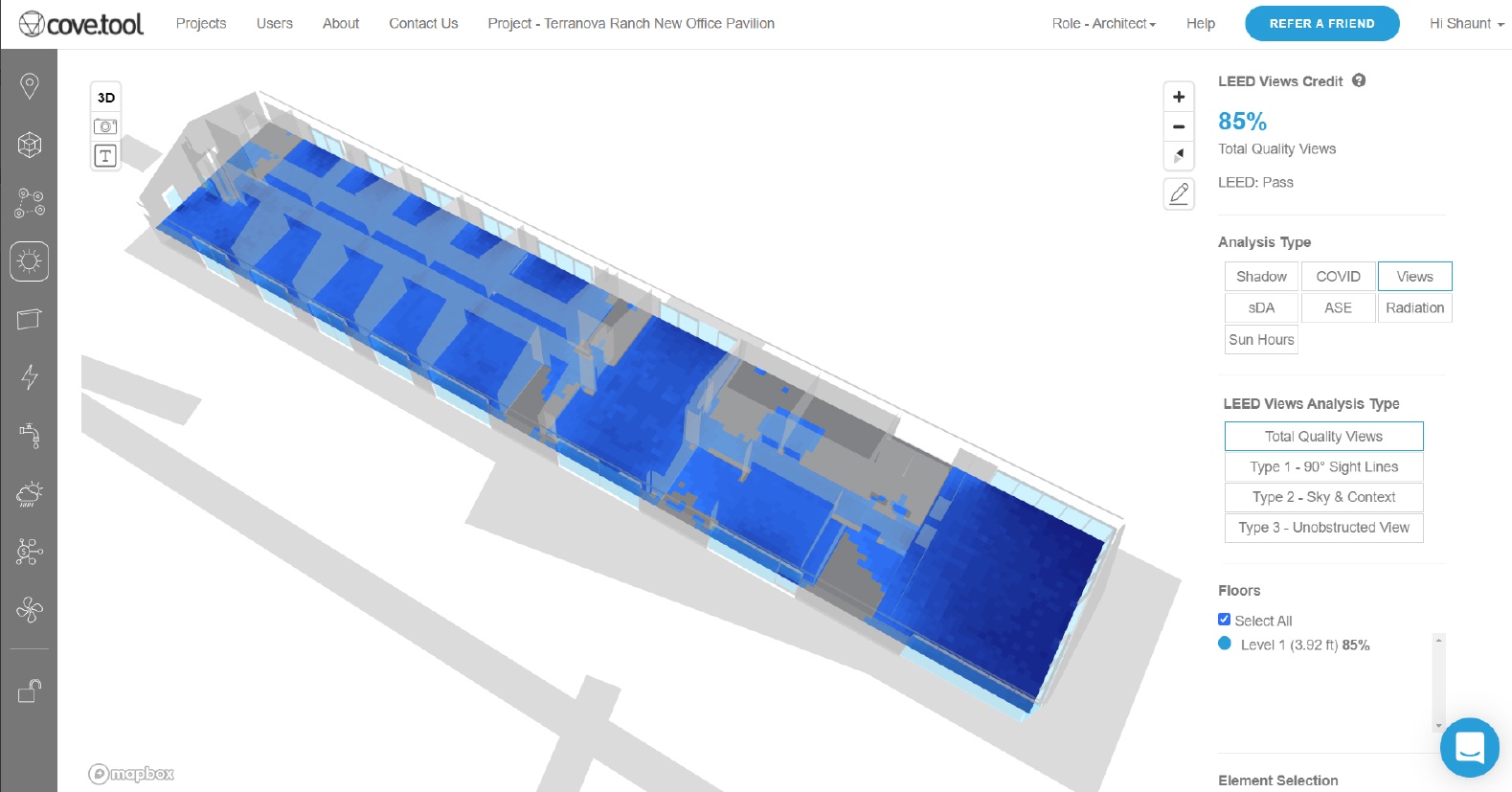
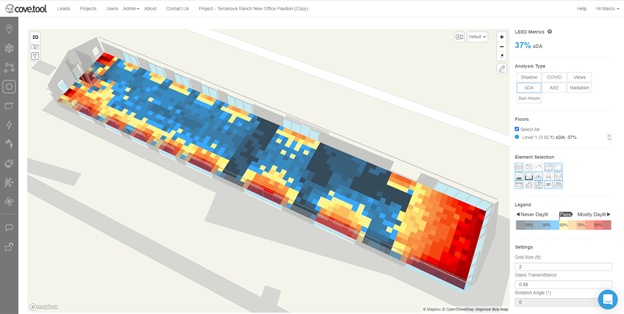
Along with the energy study, the architect conducted other analyses. Using cove.tool software, the architect observed that 85 percent of the office building’s interior would have access to “quality exterior views,” which in turn would earn the product LEED Views Credit. A daylight analysis of the architect’s design also showed that the building would be exposed to up to 12 hours of sunlight per day, reducing the design’s artificial lighting requirement.
While most clients might not be as sustainably inclined as Terranova Ranch, conducting data-driven analyses can be fruitful as a common practice that allows the design team and client to delve into different design scenarios to achieve an intended performance goal.
Construction on the office pavilion was scheduled to begin in late spring. The architect and client did not disclose construction costs.
Related Stories
Resiliency | Apr 18, 2023
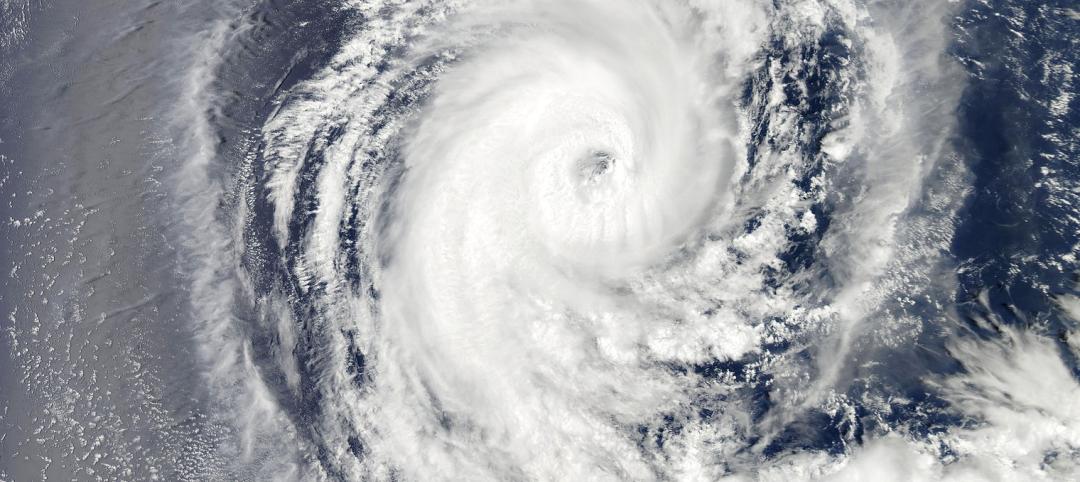
AI-simulated hurricanes could aid in designing more resilient buildings
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have devised a new method of digitally simulating hurricanes in an effort to create more resilient buildings. A recent study asserts that the simulations can accurately represent the trajectory and wind speeds of a collection of actual storms.
Green | Apr 18, 2023
USGBC and IWBI unveil streamlined certification pathway for LEED and WELL green building programs
The U.S. Green Building Council, Green Business Certification Inc., and the International WELL Building Institute released a streamlined process for projects pursuing certifications for the LEED green building rating system and the WELL Building Standard. The new protocol simplifies documentation for projects that are pursuing both certifications at the same time or that have already earned one certification and are looking to add the other.
Sustainability | Apr 10, 2023
4 ways designers can help chief heat officers reduce climate change risks
Eric Corey Freed, Director of Sustainability, CannonDesign, shares how established designers and recently-emerged chief heat officers (CHO) can collaborate on solutions for alleviating climate change risks.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Apr 5, 2023
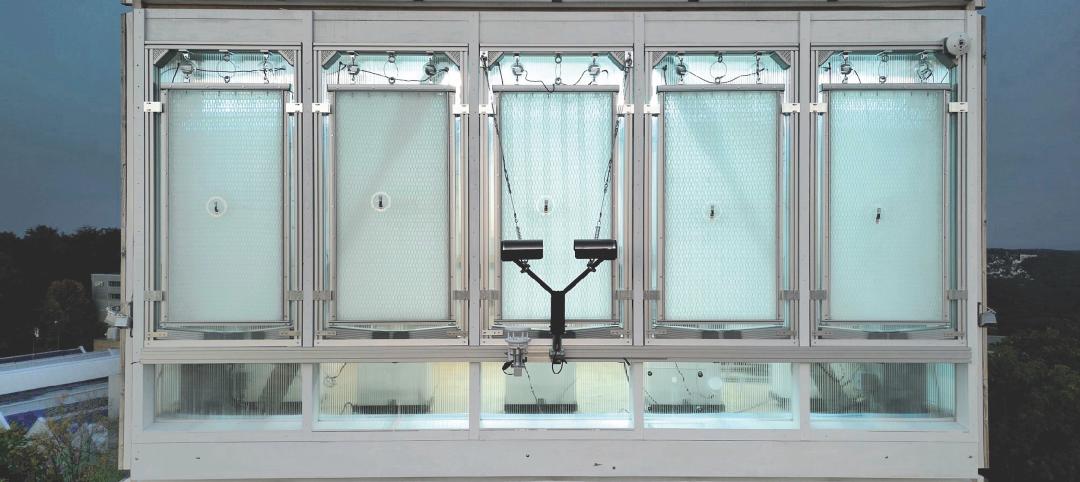
Façade innovation: University of Stuttgart tests a ‘saturated building skin’ for lessening heat islands
HydroSKIN is a façade made with textiles that stores rainwater and uses it later to cool hot building exteriors. The façade innovation consists of an external, multilayered 3D textile that acts as a water collector and evaporator.
Sustainability | Apr 4, 2023
ASHRAE releases Building Performance Standards Guide
Building Performance Standards (BPS): A Technical Resource Guide was created to provide a technical basis for policymakers, building owners, practitioners and other stakeholders interested in developing and implementing a BPS policy. The publication is the first in a series of seven guidebooks by ASHRAE on building decarbonization.
Sustainability | Apr 4, 2023
NIBS report: Decarbonizing the U.S. building sector will require massive, coordinated effort
Decarbonizing the building sector will require a massive, strategic, and coordinated effort by the public and private sectors, according to a report by the National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS).
Geothermal Technology | Mar 22, 2023
Lendlease secures grants for New York’s largest geothermal residential building
Lendlease and joint venture partner Aware Super, one of Australia’s largest superannuation funds, have acquired $4 million in support from the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority to build a geoexchange system at 1 Java Street in Brooklyn. Once completed, the all-electric property will be the largest residential project in New York State to use a geothermal heat exchange system.
Modular Building | Mar 20, 2023
3 ways prefabrication doubles as a sustainability strategy
Corie Baker, AIA, shares three modular Gresham Smith projects that found sustainability benefits from the use of prefabrication.
Sustainability | Mar 16, 2023
Lack of standards for carbon accounting hamper emissions reduction
A lack of universally accepted standards for collecting, managing, and storing greenhouse gas emissions data (i.e., carbon accounting) is holding back carbon reduction efforts, according to an essay published by the Rocky Mountain Institute.
Affordable Housing | Mar 14, 2023
3 affordable housing projects that overcame building obstacles
These three developments faced certain obstacles during their building processes—from surrounding noise suppression to construction methodology.

















