Personalized learning tailored to the needs of individual students, coupled with group projects, is taking hold in the nation's schools. “We can’t just line up students in rows and teach everybody the same way, at the same pace,” says Leanne Meyer-Smith, AIA, LEED AP, VP of Architecture with Wight & Company. “That’s not working.”
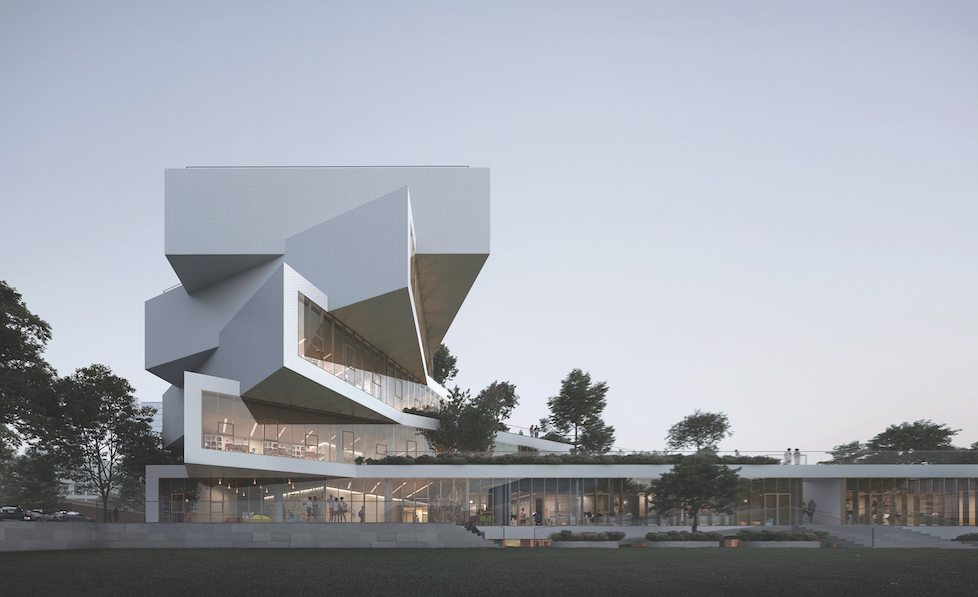
In terms of school design, no single template has taken hold, but one thing is certain: long, double-loaded corridors are a thing of the past.
Improved economic conditions have freed up money for new projects and renovations. There’s a sense of urgency to update facilities to make up for the time lost when the Great Recession stymied many projects. “We’ve been seeing a lot more success with school funding referendums,” says Steve Herr, AIA, Director of Design, Fanning Howey.
See also: Top 150 K-12 Architecture + AE Firms - 2018 Giants 300 rankings
See also: Top 75 K-12 Engineering + EA Firms - 2018 Giants 300 rankings
See also: Top 90 K-12 Construction + CM Firms - 2018 Giants 300 rankings
Designing schools that can accommodate the pedagogy of today and the teaching styles of tomorrow is educated guesswork. “You have to allow for evolving instructional models without forcing tremendous expense to reconfigure spaces,” says Sean O’Donnell, FAIA, LEED AP, Principal and Practice Area Leader, Primary Education, with Perkins Eastman. Providing a little extra room and flexibility is crucial.
Extra space for learning and socializing can be created in common areas, where students can study and collaborate on projects in nooks and crannies around the school. “Interstitial spaces are really important,” says O’Donnell.
The building core at the Wilson School, a new 775-student high school under construction in Arlington, Va., will feature a wide staircase that opens out to the lobby, which will double as a gathering place for students. “We typically see that type of space in a university setting,” says Andrew Graham, AIA, Associate with Leo A Daly, the project’s design architect, along with Bjarke Ingels Group.
Even renovations of old double-loaded corridors can get at least part of the way to a modern design. Provided there's sufficient structural support in place, interior walls can be removed and track-mounted wall systems can be installed. “When you open up the walls, the corridor disappears and becomes a learning space,” says Lance Tritsch, LEED AP, Project Director, Pepper Construction.
Even when structural alterations are not possible, spaces can still be reconfigured at relatively low cost. “There’s a lot you can do with agile furniture,” says Meyer-Smith. Classrooms can be spruced up with new carpeting, plush pillows, and strategically placed bookshelves as dividers.
K-12 school designers are also using the increasing body of scientific evidence that links the interior environment to student performance as they pitch design ideas to district officials. Daylighting and indoor air quality are always on the front burner in these discussions.
Acoustic clarity within the classroom is also a major consideration. “If students can’t hear the teacher clearly, their ability to learn is impaired,” says Laura Wernick, FAIA, REFP, LEED AP, Senior Principal with HMFH Architects. Reducing noise is especially critical for children with ADHD, a condition exacerbated by excessive stimuli.
HMFH brings in experts at various stages of the project to measure and analyze classroom acoustics. This enables designers and contractors to identify noise problems early, before they get too expensive to fix, says Chin Lin, AIA, LEED AP, Senior Associate with HMFH.
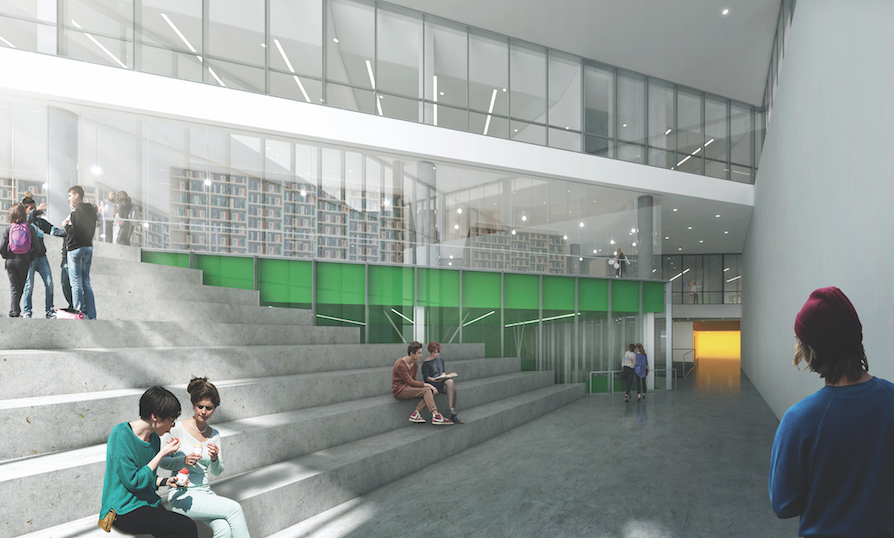

Wilson School, Arlington, Va
Children with ADHD and other conditions that are made worse by excessive stimuli can benefit from the use of tunable LEDs, says Lin. “Dimming and providing warmer tones through lighting is calming,” he says. With color-tunable lighting currently costing about twice as much as standard lighting, schools are likely to use the more expensive options in special needs classrooms where they can do the most good.
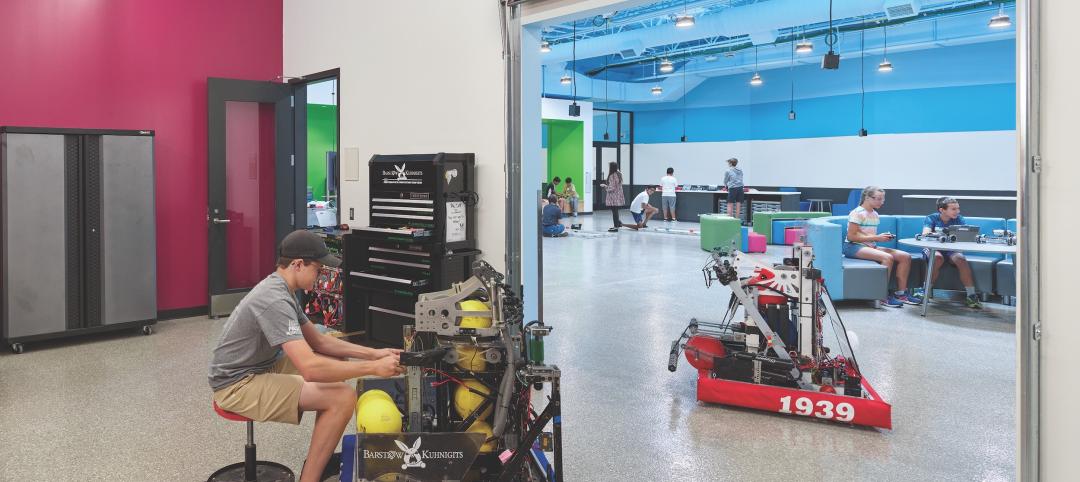
The trend toward more hands-on learning remains strong. STEAM and STREAM (the “R” is for robotics) curricula often include maker spaces equipped with 3D printers. O’Donnell says “flight lounges"—areas adjacent to maker spaces, where teachers from different subject areas can get together to devise interdisciplinary teaching strategies and hands-on student projects—are coming into vogue.
getting students out into the world
High schools are also experimenting with giving students real-world business experience. The new Carmel (Ind.) High School has a 2,000-sf space for a student-run coffee shop and retail outlet featuring school-themed clothing and gear. Students perform all the managerial, accounting, marketing, graphics, and communication tasks to run the business. There's even a “Shark Tank,” where students can pitch ideas using whiteboards and high-end presentation tools.
A 30,000-sf space in a repurposed warehouse at the Brooklyn (N.Y.) Navy Yard is dedicated to the STEAM Center, where 11th and 12th graders from Brooklyn schools spend half of each day learning vocational and technical skills such as engineering, design, construction, film and media, and culinary arts.
“Students are introduced to companies in the Navy Yard and have the opportunity to participate in internships,” says Christine Schlendorf, AIA, Principal with Perkins Eastman.
Related Stories
K-12 Schools | Jun 5, 2023
How to achieve cost-effective kindergarten classrooms
Educational architect Robin Randall shares realistic advice about the challenges of adding developmentally appropriate, play-based kindergarten classrooms while respecting budget limitations.
K-12 Schools | May 30, 2023
K-12 school sector trends for 2023
Budgeting and political pressures aside, the K-12 school building sector continues to evolve. Security remains a primary objective, as does offering students more varied career options.
K-12 Schools | May 25, 2023
From net zero to net positive in K-12 schools
Perkins Eastman’s pursuit of healthy, net positive schools goes beyond environmental health; it targets all who work, teach, and learn inside them.
K-12 Schools | May 22, 2023
The revival of single-building K-12 schools
Schools that combine grades PK through 12 are suddenly not so uncommon. Education sector experts explain why.
K-12 Schools | May 17, 2023
Designing K-12 schools for students and safety
While bullying, mental health, and other acts of violence are all too common in schools today, designers have shown that smart and subtle preventive steps can make a big difference. Clark Nexsen’s Becky Brady shares how prevention and taking action at the design level can create safe and engaging learning environments.
K-12 Schools | May 12, 2023
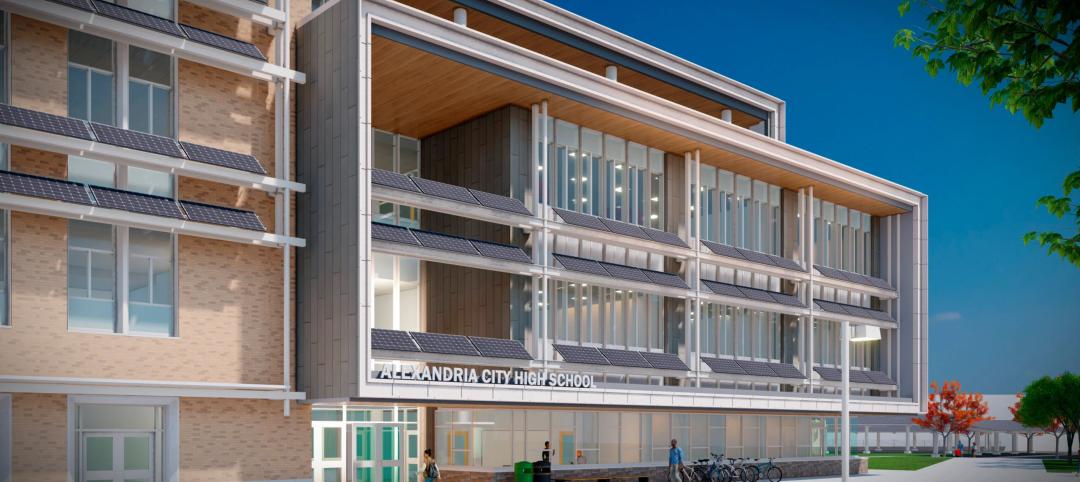
In Virginia, a new high school building helps reimagine the experience for 1,600 students
In Virginia, the City of Alexandria recently celebrated the topping out of a new building for Alexandria City High School. When complete in 2025, the high-performance structure will accommodate 1,600 students.
Sustainability | Apr 20, 2023
13 trends, technologies, and strategies to expect in 2023
Biophilic design, microgrids, and decarbonization—these are three of the trends, technologies, and strategies IMEG’s market and service leaders believe are poised to have a growing impact on the built environment.
K-12 Schools | Apr 18, 2023
ASHRAE offers indoor air quality guide for schools
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) has released a guide for educators, administrators, and school districts on indoor air quality. The guide can be used as a tool to discuss options to improve indoor air quality based on existing HVAC equipment, regional objectives, and available funding.
K-12 Schools | Apr 13, 2023
Creating a sense of place with multipurpose K-12 school buildings
Multipurpose buildings serve multiple program and functional requirements. The issue with many of these spaces is that they tend not to do any one thing well.
Market Data | Apr 11, 2023
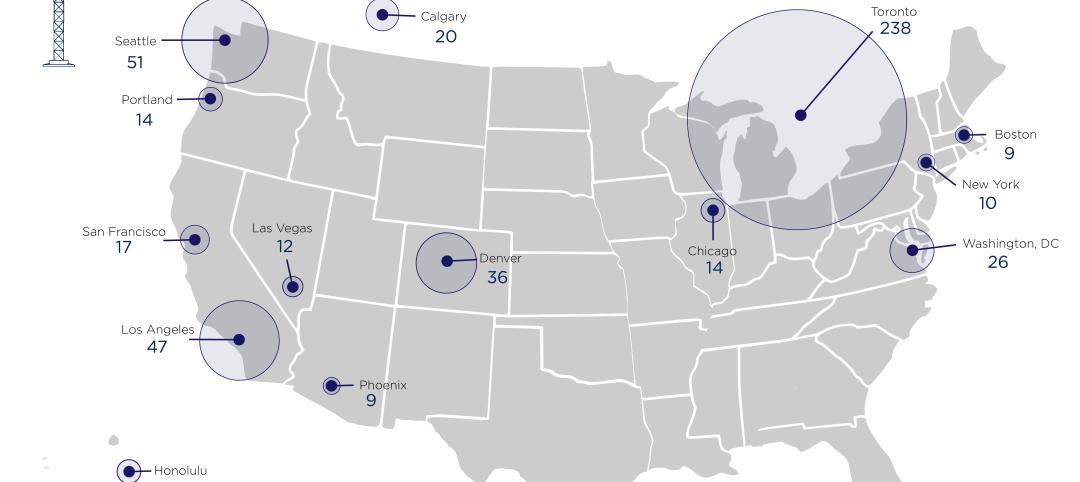
Construction crane count reaches all-time high in Q1 2023
Toronto, Seattle, Los Angeles, and Denver top the list of U.S/Canadian cities with the greatest number of fixed cranes on construction sites, according to Rider Levett Bucknall's RLB Crane Index for North America for Q1 2023.