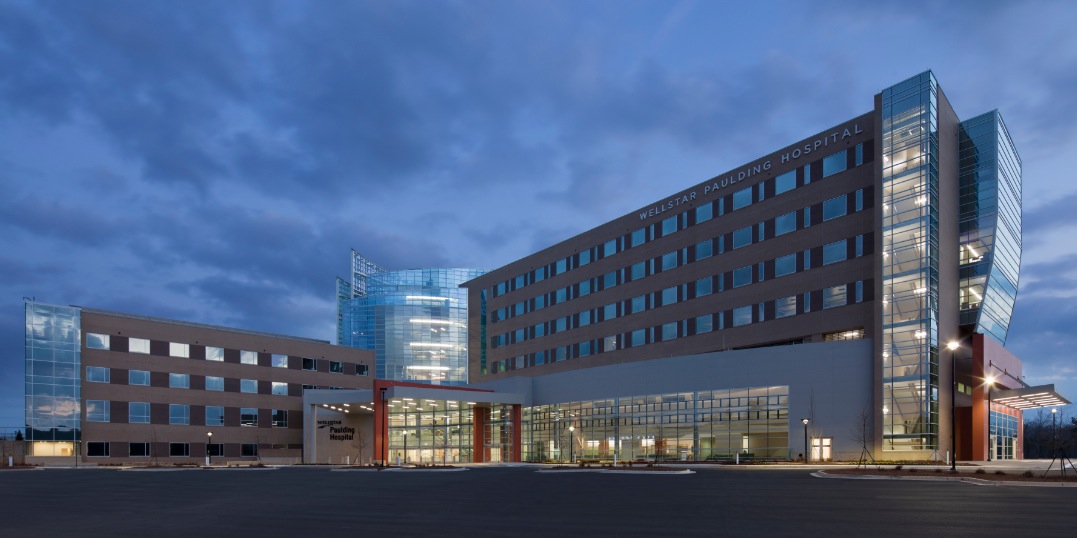
For years we have been told that the benefits of prefabrication often parallel those of building information modeling: increased safety and efficiency, higher quality, and reduced labor and material costs. Contractor Brasfield & Gorrie’s use of BIM and prefabrication on the $94 million WellStar Paulding Hospital in Hiram, Ga., is an excellent case study of how digital tools can inform prefabrication and lead to project savings, a safer work environment, and better-delivered construction.
The 100-bed Wellstar Paulding Hospital is one of the first hospitals in the U.S. to rely almost entirely on geothermal energy. The scope of the 24-month project took in 33 acres of site work, including a one-level, 120,000-sf precast parking deck; site utilities; modular block and concrete retaining walls; an eight-story, 295,700-sf hospital; a four-story, 82,220-sf medical office building; and a seven-story atrium that links the site’s two medical office buildings to the new hospital.
The design of the geothermal system called for 35,000 sf of radiant floor piping to heat and cool the atrium and high-ceiling areas. The ground-source heat pump system utilizes 209 wells, each 400 feet deep, with a total of about 38 miles of piping. The GSHP equipment included six chiller/heat pump modules, each with capacity for 110 tons of cooling and 2,038 MBH of heating.
The system has three sets of pumps: one for hot water, one for chilled water, and one for ground-loop circulation. More than half of the facility’s 700-ton total building cooling load is handled by the GSHP system. The remainder is managed by the air-cooled chillers. The GSHP system also handles the building heating and domestic hot water load of approximately 5,000 MBH.
With such complexity involved, both in the construction of the new hospital and connecting it with the medical office buildings, Brasfield & Gorrie turned to laser scanning and a sophisticated BIM program to inform its construction decisions.
VDC Modeling Starts the Process
Brasfield & Gorrie’s Virtual Design and Construction group created BIM models and collaborated in real time with the design team (including architect CPH Partners and engineering firm PerryCrabb) through more than 23 revision packages. Models were created in Autodesk Revit and reviewed in Autodesk Navisworks.
The BIM process correlated with the construction schedule, and was carefully planned as part of the overall project schedule. Each floor was modeled; each model included every trade and discipline.
The first step was to model everything under the basement slab, such as underground plumbing and electrical conduit. This model alone resolved 50 conflicts, including invert tie-in elevations with building and site storm systems and sloping grade beams with underground conduit.
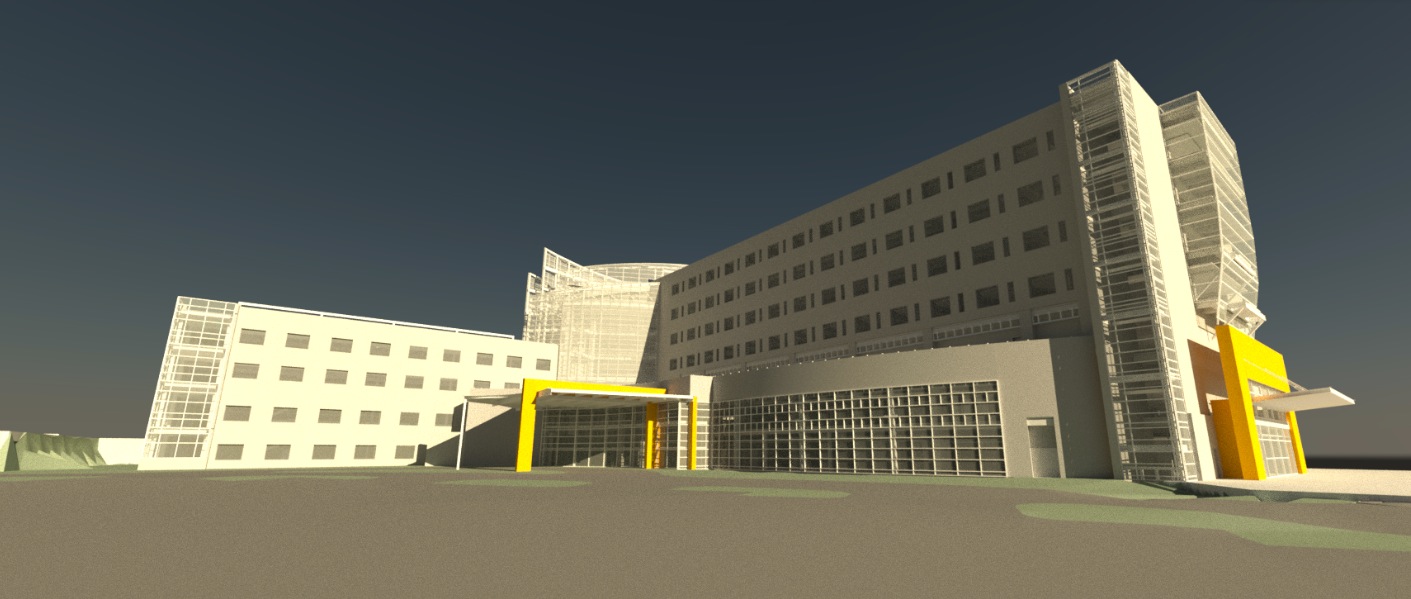 The $94 million WellStar Paulding Hospital in Hiram, Ga., is one of the first hospitals in the U.S. to rely almost entirely on geothermal energy. General contractor Brasfield & Gorrie worked with key subcontractors to create a comprehensive VDC model of the hospital’s systems.
The $94 million WellStar Paulding Hospital in Hiram, Ga., is one of the first hospitals in the U.S. to rely almost entirely on geothermal energy. General contractor Brasfield & Gorrie worked with key subcontractors to create a comprehensive VDC model of the hospital’s systems.
Utilizing existing conditions data imported from Trimble scans, the team was able to streamline the placement and installation of the hangers. “The efficiency in layout for hanger locations was achieved through the use of detailed models showing all locations, or insert points, where the hangers were needed,” says Scott Cloud, Brasfield & Gorrie’s Director of VDC.
The Building Team was able to coordinate the hanger locations within the model. Robotic total stations were utilized once formwork was completed and prior to concrete pours. Because the team was able to locate inserts within the concrete slabs as the structure was completed, it eliminated the need to drill/epoxy hangers in the concrete deck, post-shore removal. Not only did this allow for gains in schedule, it supported Brasfield & Gorrie’s ability to prefabricate larger assemblies for MEP overhead utilities and improved overall safety on the job by eliminating extra stockpiles of materials.
Electrical contractor Inglett & Stubbs exported data from the construction model to the company’s prefabrication department so that boxes and conduit could be built and delivered to the site already connected and ready for placement. All prefabricated units—junction boxes, conduit assemblies—and trapeze hanger assemblies were completed off site within Inglett & Stubbs’s shop.
Sheet metal contractor R.F. Knox Co. used the construction model for accurate prefabrication of ductwork and other metal components. The detailed development of the models fully supported material procurement for ductwork, piping, conduit, and even some equipment.
Because the BIM coordination process began nearly four months prior to the start of the elevated structure, the team was able to approve the fabrication design shop drawings and release material fabrication much earlier in the process than usual. As owner changes in the design occurred throughout construction, the detailed models aided in quicker and more accurate response times to pricing changes.
“When one section of the hospital originally designated as clinical office space changed to surgery recovery, we were able to quickly adapt to help complete a design that met design intent,” says Cloud, “but accurately relayed routing paths for utilities that would impact MEP material quantities.”
Sure Shoring with Shotcrete
Brasfield & Gorrie specified a shotcrete wall to hold up the foundation, and used a field survey to model the shotcrete wall virtually and coordinate the material for the slab rebar and penetrations.
A Brasfield & Gorrie field crew surveyed a series of points along the wall. This information was used to develop a 3D model of the wall, which was then incorporated within the composite model to coordinate MEP penetrations and structural dimensions, based on the actual dimensional survey information taken from the field.
Once coordinated in the model, this information was shared with the formwork, rebar, and MEP contractors to support material fabrication, release, deliveries, and installation in the field.
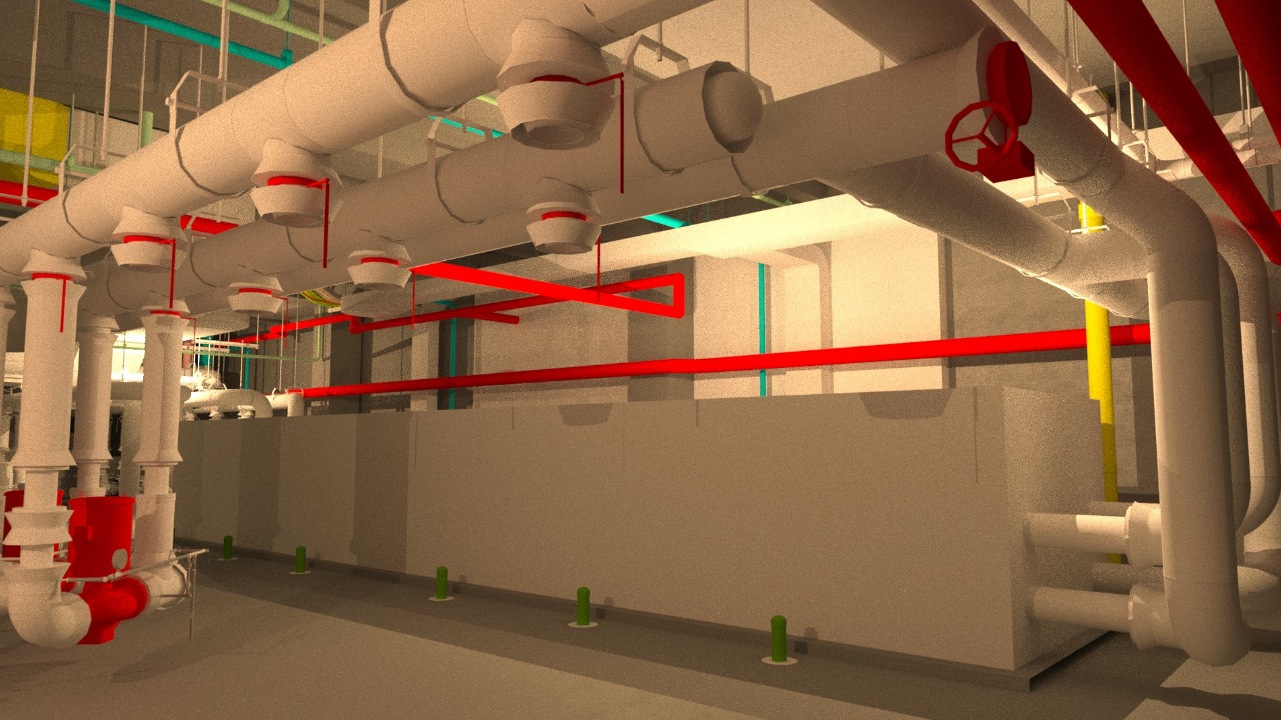 Using existing conditions data collected through laser scanning, the Building Team was able to coordinate the MEP systems hanger locations within the model. Robotic total stations were utilized to locate each hanger insert point within the concrete slabs as the structure was completed.
Using existing conditions data collected through laser scanning, the Building Team was able to coordinate the MEP systems hanger locations within the model. Robotic total stations were utilized to locate each hanger insert point within the concrete slabs as the structure was completed.
Related Stories
| Feb 24, 2014
White Paper: Using social media to build your business
This white paper from Benjamin Moore provides practical guidance for building and sustaining an effective online presence, with the ultimate goal of helping your painting business become more successful.
Sponsored | | Feb 20, 2014
Chicago’s historic Wrigley Building renovated to attract tech companies
Purchased in 2011 by a consortium of investors led by BDT Capital Partners, the building’s new owners have recently renovated and reimagined the next life for this architectural landmark—as a hub for tech firms.
| Feb 19, 2014
Sefaira Adds Daylighting Analysis to Performance Based Design Platform
Sefaira, the leader in software for high performance building design, today announced that its performance based design platform now includes daylighting analysis. With the addition of daylighting, Sefaira combines two critical design metrics in the same tool.
| Feb 19, 2014
Harvard's 'termite robots' can build any thing, any way [video]
The robots build by observing thier environment and then obeying a set of traffic rules programmed by researchers.
| Feb 14, 2014
The Technology Report 2014: Top tech tools and trends for AEC professionals
In this special five-part report, Building Design+Construction explores how Building Teams throughout the world are utilizing advanced robotics, 3D printers, drones, data-driven design, and breakthroughs in building information modeling to gain efficiencies and create better buildings.
| Feb 14, 2014
Crowdsourced Placemaking: How people will help shape architecture
The rise of mobile devices and social media, coupled with the use of advanced survey tools and interactive mapping apps, has created a powerful conduit through which Building Teams can capture real-time data on the public. For the first time, the masses can have a real say in how the built environment around them is formed—that is, if Building Teams are willing to listen.
| Feb 11, 2014
Adobe Photoshop update features new 3D printing capabilities
Available as part of an update to Photoshop Creative Cloud, the tool enables users to easily and reliably build, refine, preview, prepare, and print 3D designs.
| Feb 7, 2014
DOE, Autodesk team to overhaul the EnergyPlus simulation program
The update will allow a larger ecosystem of developers to contribute updates to the code in order to improve performance and decrease the time required to run energy model simulations.
| Feb 6, 2014
Bluebeam Software Invests in the Advancement of Design and Construction Education at the Associated Schools of Construction 27th Annual Student Competition
This week, Bluebeam® Software, leading developer of PDF-based markup, measurement and collaboration solutions for design, construction and other technical professionals, is exhibiting at the 27th Annual Associated Schools of Construction (ASC) Student Competition and Construction Management Conference in Sparks, NV.
| Feb 5, 2014
PPG creates new BIM library, adds custom BIM file creation to tool
PPG Industries announced that it has created a new library of building information and modeling (BIM) files, and that architects and specifiers can now use PPG Glass eVIEW to generate custom BIM files for any conceivable PPG glass configuration.