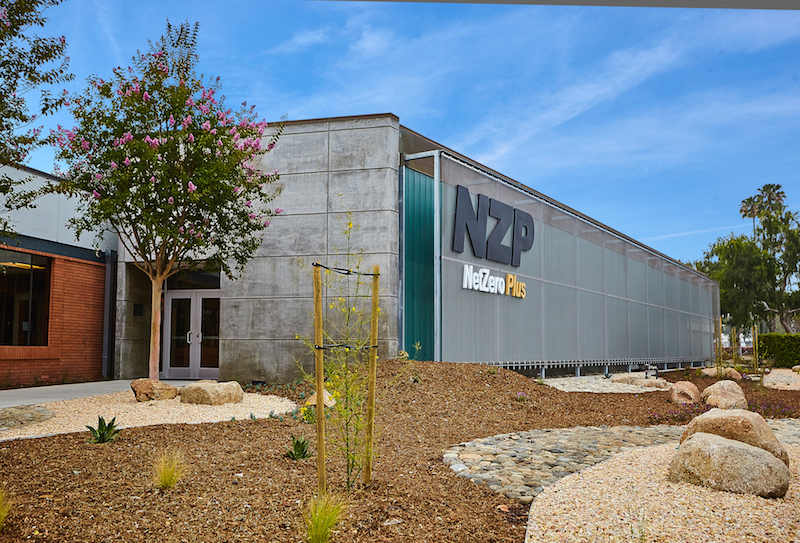
The Net Zero Plus Electrical Training Institute in Los Angeles trains about 1,500 electrical apprentices, journeymen, and contractors annually. It is also a demonstration center and living lab for advanced and energy clean energy technologies.
It seems appropriate, then, that this 144,000-sf building is now the country’s largest Net Zero Plus commercial building retrofit.
Net Zero Plus is a comprehensive set of strategies designed by the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 11 and the Los Angeles National Electrical Contractors Association, which finance the Institute through a Taft-Hartley trust, according to Brett Moss, the Institute’s Training Director.
Those strategies provide building owners and managers, developers, and architects with integrated energy efficiencies and advanced technologies aimed at changing the way buildings use, produce, store, and monitor energy.
The $15.5 million retrofit, which was completed a few months ago, is expected to reduce the building’s annual total energy usage by 51%, and lower its carbon footprint by 520 metric tons per year.
Moss says that one of the goals of this retrofit is for the building to produce 1.25 times the energy it consumes. In the first months since the retrofit was completed, the building has outperformed expectations.
“I think it’s important to point out that this was a retrofit,” says Moss, who spoke with BD+C last week. “A lot of people are under the assumption that the only way to achieve net zero is ground up.” He adds that the building remained operational during the upgrade.
This building, which dates back to the 1960s, had been expanded a number of times. About a dozen years ago a solar array was added.
The retrofit project started, says Moss, with a building audit that focused on the envelope. A new roof with foam insulation was installed. Stainless-steel mesh shades wall windows, letting in plenty of daylight but also reducing the temperature on the inside of the windows by 20%.
Electrochromatic glass was installed into another wall that’s part of the Institute’s classroom space.

Electrochromatic windows help keep classrooms cool. Image courtesy of NZP ETI.
The building is essentially a warehouse with classrooms. Pre-retrofit, the warehouse door usually stayed open all day, letting hot air into common areas that weren't air conditioned to begin with. The retrofit installed an electric sliding door, and doors to the air-conditioned classrooms stay closed to keep them cool.
Moss says the Institute was an early adopter of LED lighting. “But what we had wasn’t tunable,” and were replaced with fixtures and a Lutron lighting system. And on the mechanical side, a series of package units on the roof was replaced by chillers and a cooling tower.
The building's energy storage system has 300 kilowatt-hours worth of energy stored. As the price of energy storage continues to fall—solar panels go for about 85 cents per watt now, compared to $5 per watt in 2002, when the Institute installed its first PV array—Moss says the Institute envisions this building serving as an emergency operations center that “can operate around the clock” by harvesting energy during the day, drawing down on that storage during the evening, and producing more energy than it uses.
“We should have enough energy in our battery to take the building through any catastrophic event,” says Moss.
Commercial buildings account for nearly 65% of L.A.’s energy consumption, and are responsible for huge amounts of CO2 emissions. The NZP ETI, as the Institute’s building is now known, could also serve as a model for transforming other existing buildings, said Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti, who was among the more than 500 dignitaries attending the June 6 dedication ceremony for the building.
California requires all commercial structures in the state to be net zero buildings by 2030.
The development team on the Institute's retrofit included contractors O’Bryant Electric and PDE Total Energy Solutions, as well as stok, Western Allied Mechanical, and SimonGlover Architects.
Moss notes that NZP ETI will be on the building tour during Greenbuild, which will be held in Los Angeles this fall.
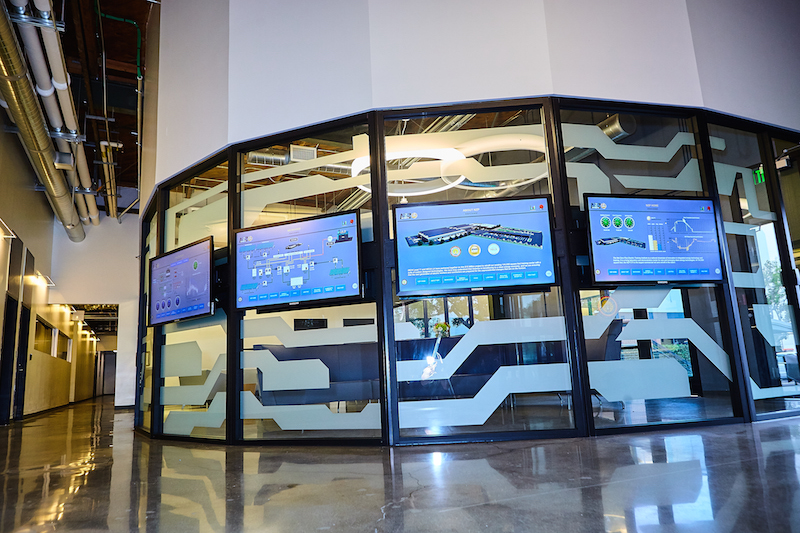

Glass walls surround the Institute's lobby area. A electric sliding glass door was installed to keep the inside of the building, which is mostly warehouse and common areas that aren't air conditioned, cooler. Image courtesy of NZP ETI.
Related Stories
| Feb 22, 2011
Military tests show copper increases HVAC efficiency, reduces odors
Recent testing, which is being funded by the Department of Defense, is taking place in military barracks at Fort Jackson, South Carolina. Side-by-side comparisons demonstrate that air conditioning units made with copper suppress the growth of bacteria, mold, and mildew that cause odors and reduce system energy efficiency.
| Feb 10, 2011
Zero Energy Buildings: When Do They Pay Off in a Hot and Humid Climate?
There’s lots of talk about zero energy as the next big milestone in green building. Realistically, how close are we to this ambitious goal? At this point, the strategies required to get to zero energy are relatively expensive. Only a few buildings, most of them 6,000 sf or less, mostly located in California and similar moderate climates, have hit the mark. What about larger buildings, commercial buildings, more problematic climates? Given the constraints of current technology and the comfort demands of building users, is zero energy a worthwhile investment for buildings in, for example, a warm, humid climate?
| Feb 9, 2011
Fortune 1000: Despite moral obligation to sustainability, cash is still king
Eighty-eight percent of Fortune 1000 senior executives feel business has a moral responsibility, beyond regulatory requirements, to make their companies more energy efficient, according to a new poll released today by Harris Interactive and commissioned by Schneider Electric. At the same time, the vast majority (61%) of respondents say that potential cost savings are their biggest motivator to save energy at the enterprise-level, outranking environmental concerns (13%) or government regulations (2%).
| Feb 4, 2011
U.S. Green Building Council applauds President Obama’s Green Building Initiative
The U.S. Green Building Council applauded a key element of President Obama’s plan to “win the future” by making America’s commercial buildings more energy- and resource-efficient over the next decade. The President’s plan, entitled Better Buildings Initiative, catalyzes private-sector investment through a series of incentives to upgrade offices, stores, schools and universities, hospitals and other commercial and municipal buildings.
| Feb 4, 2011
President Obama: 20% improvement in energy efficiency will save $40 billion
President Obama’s Better Buildings Initiative, announced February 3, 2011, aims to achieve a 20% improvement in energy efficiency in commercial buildings by 2020, improvements that will save American businesses $40 billion a year.
| Jan 25, 2011
Bloomberg launches NYC Urban Tech Innovation Center
To promote the development and commercialization of green building technologies in New York City, Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg has launched the NYC Urban Technology Innovation Center. This initiative will connect academic institutions conducting underlying research, companies creating the associated products, and building owners who will use those technologies.
| Jan 25, 2011
Chicago invented the skyscraper; can it pioneer sustainable-energy strategies as well?
Chicago’s skyline has always been a source of pride. And while few new buildings are currently going up, building owners have developed a plan to capitalize on the latest advances: Smart-grid technologies that will convert the city’s iconic skyline into what backers call a “virtual green generator” by retrofitting high-rise buildings and the existing electrical grid to a new hyper-connected intelligent-communications backbone.