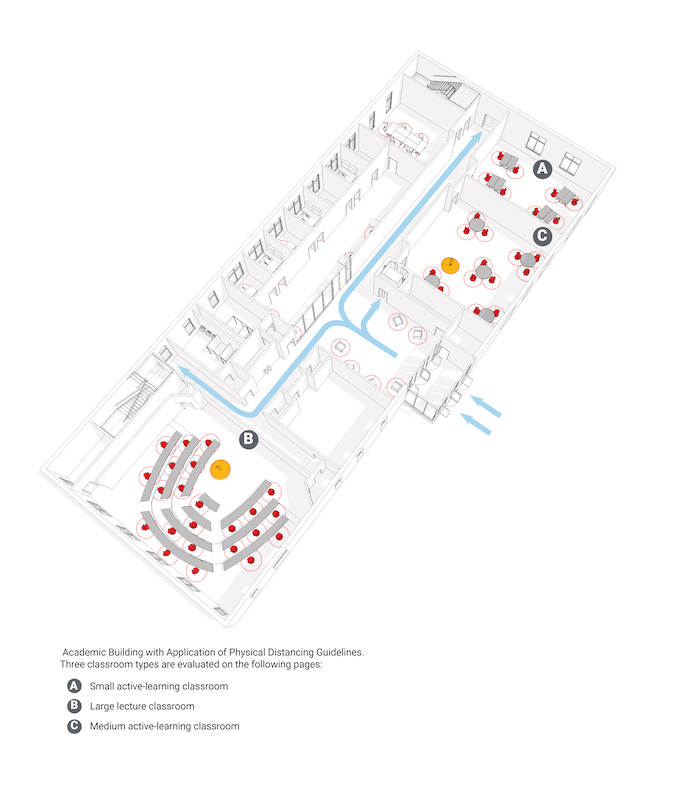
As colleges and universities weigh how to reopen their campuses in the fall, the standard government, health, and academic guidelines—wearing masks, reducing densities, and physical distancing—may not be entirely practical for assembling large numbers of students in one place.
To contribute to this discourse, Leo A Daly recently convened planners, architects, and engineers specializing in higher education to study the facility impacts of physical distancing, and to envision solutions.
This group analyzed available guidelines, and then applied design thinking to three key areas. First, it studied infection dynamics on the campus overall and applied the idea of “cohorts” as a mechanism for limiting exposure. Next, the group conducted a detailed study of two campus building types where students congregate: a general purpose academic building and a “traditional” residence hall with shared toilet and shower facilities. These analyses identified “pinch points,” suggesting the need for behavioral and physical modifications to more closely comply with the intent of the guidelines.
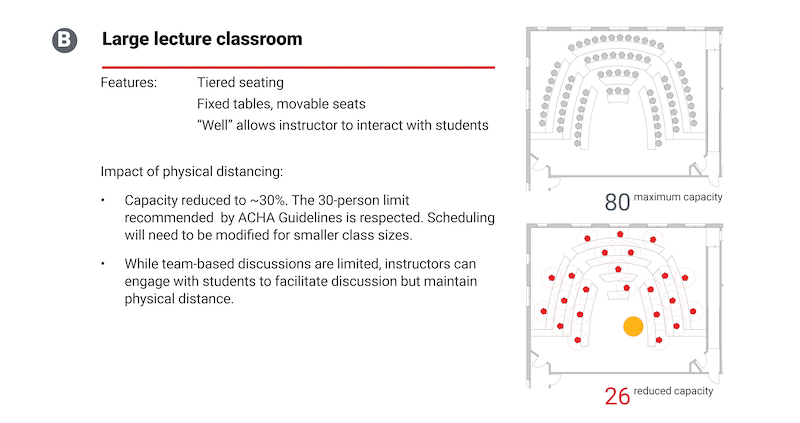 Reducing the number of students in a lecture hall might actually improve instructor engagement.
Reducing the number of students in a lecture hall might actually improve instructor engagement.
A white paper, “Returning to Campus During the Covid-19 Pandemic,” summarizes the group’s findings and recommendations. “The analysis suggests that organizing students into cohorts, and considering rental or toilet and shower facilities, can improve safety where strict compliance of guidelines isn’t feasible,” the report states.
Also see: How to convert college dorms to support the coronavirus crisis
ADDING SAFETY BY DIVIDING STUDENTS INTO SMALL GROUPS
Breaking students into smaller cohorts can help institutions determine roommates and how shared spaces are used. That division can also be extended to academic buildings to create live-learn facilities. The division of students further into micro-communities “would allow students to retain the benefits of social communication while reducing their exposure to pathways of disease common to a large, dense campus,” the white paper’s three authors write.
The paper stresses one-way circulation in academic buildings that would also have a single point of entry, directional signage, and multiple exits. To minimize disease transmission in restrooms, measures might include using alternating stalls and sings, no-touch fixtures and hardware, and frequent cleaning and disinfection. To reduce pinch points, the paper recommends adding toilet capacity by installing temporary trailers with single-use facilities inside trailers adjacent to the building.
The report provides guidelines for small and medium active-learning classrooms, large lecture classrooms (in which it recommends a 30% capacity reduction to a 30-person maximum).
MAKING RESIDENCE HALLS (AND THEIR BATHROOMS) SAFER
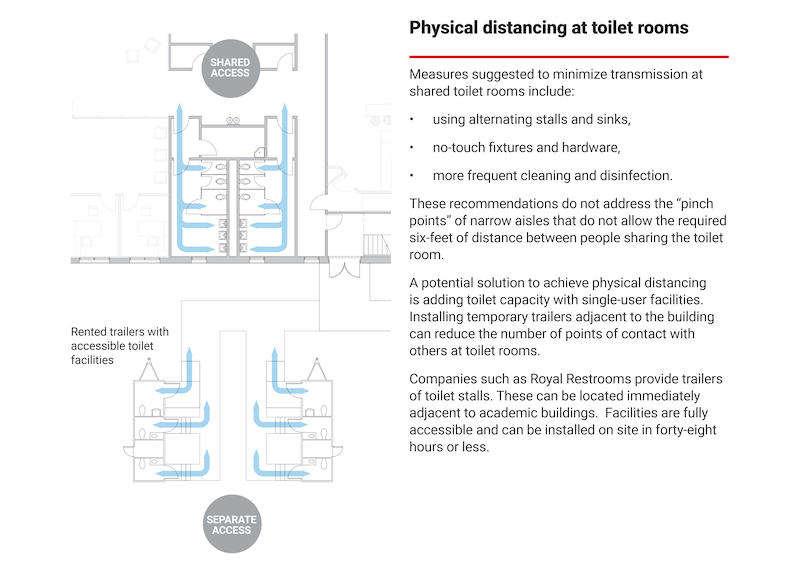 Extending restroom access by installing temporary facilities near academic and residence buildings would minimize disease transmission.
Extending restroom access by installing temporary facilities near academic and residence buildings would minimize disease transmission.
For residence halls, the report thinks that toilets and showers can still be shared, albeit with some changes that include the installation of automatic openings at common doors, assigning student rooms as single occupancy, and converting shower rooms to function as single-occupancy rooms by adding a door and restricting access.
The report suggests that assigning a shower stall to just two living units would reduce the potential for cross contamination among student residents. (Such separations could be achieved by color-coding the stalls.) At shared toilet sites, no-touch or at least reduced-touch fixtures should be standard.
Schools should treat existing shared bathrooms as single use, and reserve them for select students. Other students can be provided bathrooms in the form of temporary facilities adjacent to the resident hall and accessible by a covered hallway. (The report states that a three-unit combined shower, toilet, and lavatory can be rented for $5,500 per month, to start.)
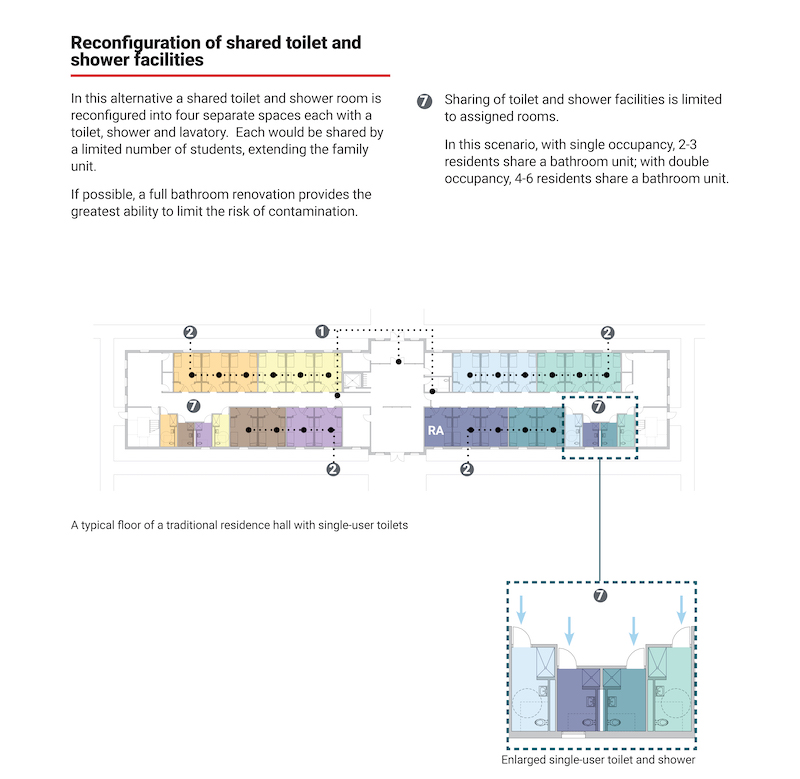
As an alternative, shared toilet and shower rooms can be reconfigured into four separate spaces, each shared by a limited number of students and assigned rooms.
Colleges and universities might also consider building systems that are more focused on occupant health, and incorporating UV-C lighting, which has been shown to kill pathogens.
Related Stories
Coronavirus | Jun 30, 2020
The great reset and our new work life
As many countries begin to return to the office, it’s a chance to ask ourselves: what do we truly value?
Coronavirus | Jun 26, 2020
Infection control in buildings in the age of the coronavirus
Controlling future infection spreads could become job one for most buildings and spaces.
Coronavirus | Jun 26, 2020
ICYMI The Weekly show: The hotel sector's 'competition for cleanliness' and workplace design amid COVID-19
This week on The Weekly (June 25 episode), BD+C editors spoke with leaders from Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Henderson Engineers, and Shawmut Design & Construction on three timely topics.
Coronavirus | Jun 23, 2020
A look back at design standard shifts: ADA vs. COVID-19
The short story is official design guidelines are slow to be developed and made into law.
Coronavirus | Jun 23, 2020
WATG designs solution for isolating without sacrificing social connectivity
The design was inspired by oriel bay windows.
Coronavirus | Jun 22, 2020
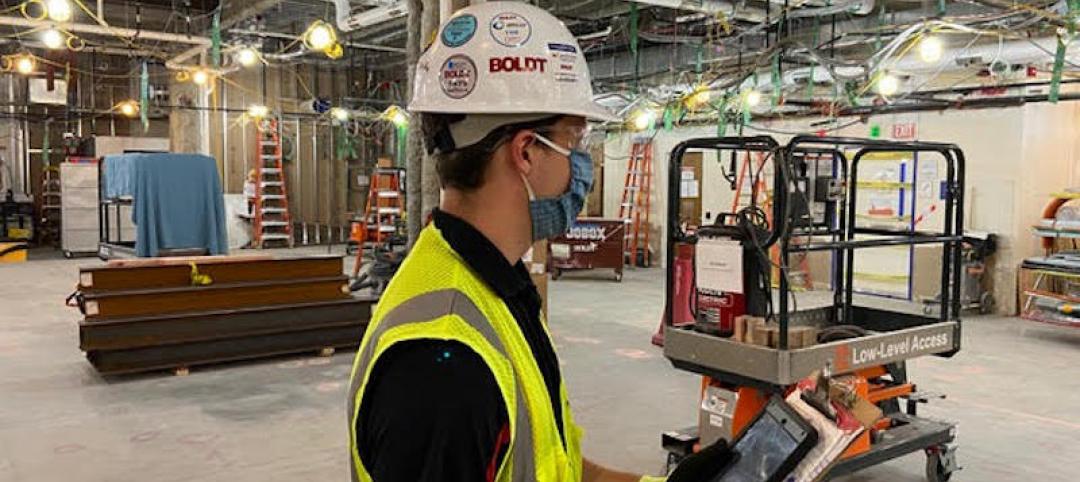
Boldt creates an innovation task force to speed up safe opening of jobsites, 14 offices
Boldt creates an innovation task force to speed up safe opening of jobsites, 14 offices
Coronavirus | Jun 19, 2020
Experts address COVID-19's impact on nursing homes and schools on The Weekly
The June 18 episode of BD+C's "The Weekly" is available for viewing on demand.
Coronavirus | Jun 18, 2020
Brown University tops off first housing building in three decades
The facility, scheduled for completion next April, will combine a residence hall with student health services.
Coronavirus | Jun 17, 2020
HOK and Germfree partner to design mobile COVID-19 testing lab
Access to quick, reliable, and repeated testing has been one of the greatest challenges for businesses, institutions and individuals during the COVID-19 crisis.
Coronavirus | Jun 17, 2020
Guiding changes in the workplace: Past, present, and future
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, many companies are managing sudden change as they assess the impact on workplace design and how people use spaces.