Over the years, Pepper Construction, like most general contractors, has hit its share of underground utilities installed beneath jobsites. “That’s not a phone call the CEO of our company wants to get,” says Mike Alder, Virtual Construction Manager at Pepper’s office in Indianapolis.
These breaches have occurred despite standards and protocols that have been in place for decades to identify and avoid underground pipes, wiring, and cables. Pepper typically hires a public or private locating company—depending on who owns the land—that relies on a combination of schematics on record, what’s visible above ground, and what’s underground that can be tracked by certain equipment. Sometimes, excavation is required.
But a few years ago, Pepper started asking itself whether there was a better way to locate and avoid hitting utilities. This is particularly important for hospital projects, says Alder, “where you don’t want to disrupt service and what might be on the other side of that service.”
In conversations with its field crews and subs, Pepper heard over and over again that the lack of communication and subpar information were the culprits behind these collisions. “We walked out of those meetings with the notion that everyone had a victim mentality,” says Alder.
At one of those meetings, Pepper’s safety director, Dave Murphy, made what Alder recalls as an “obvious but profound” observation that “we hit underground utilities because we can’t see them.” Soon after, in 2017, Murphy and Alder started working together to create underground 3D models. “Civil drawings just weren’t enough anymore,” says Alder.
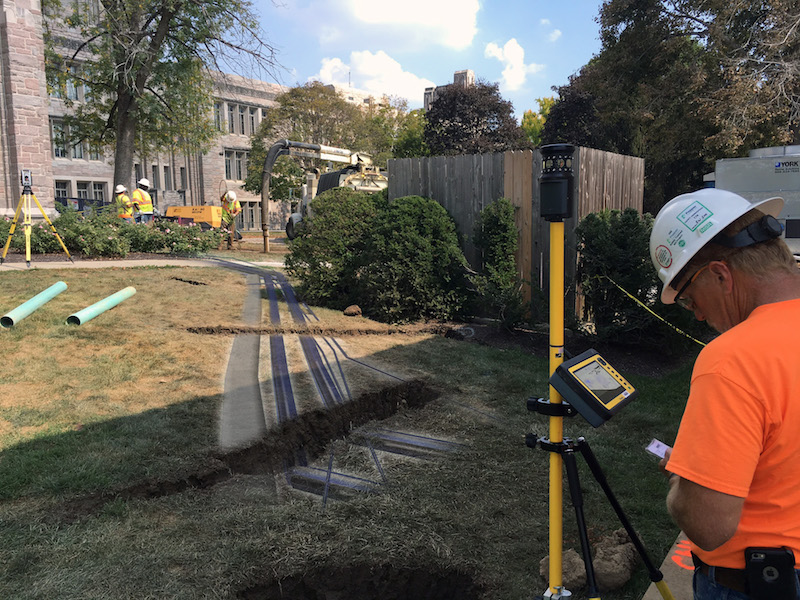
Their first step was to gather site drawings, and then overlay them with the new utilities and building that were being installed. Using those images as guides, Pepper then went to the site with a Vac truck, which Alder describes as a giant dirt vacuum, to further locate the buried utilities and to mark them by putting six-inch pipes into the ground.
Pepper had been doing all of this before. But now, it was also surveying the site, and bringing those survey points into modeling software. Alder says his company also creates 3D models for the project’s new utilities. “The benefit of this is that we were finding places where there were clashes between the old and new utilities.”
Pepper shares this information with its field crews, giving them better reconnaissance.
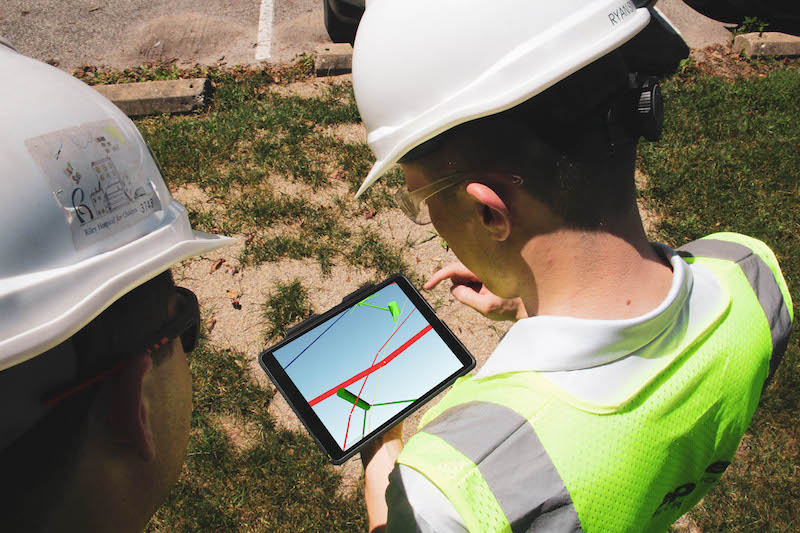 Crew members look at models showing where underground utlities are located on jobsites. Image: Pepper Construction.
Crew members look at models showing where underground utlities are located on jobsites. Image: Pepper Construction.
The firm has done underground 3D models for more than a dozen projects, and over time has made some tweaks to its process. For one thing, it’s been trying to get Civil Engineers on projects more involved upfront in the drawings and surveying during the design phase.
Pepper also flies drones over its jobsites to capture imagery that can be used to create 2D maps of the site, which Alder says gives the underground 3D models more perspective.
The modeling of underground utilities is now standard operating procedure for Pepper’s Indiana office. (Alder couldn’t say whether the firm’s other offices were following suit.). “If we had waited for the process to be perfect, we probably wouldn’t have rolled this out yet.”
Pepper is looking attempting to leveraging technology to create better models faster, and to produce a more dynamic deliverable, which will mean getting crews in the field more involved in up-to-the-minute the data collection.
“It’s important to realize that this has been a big endeavor for us,” says Alder. “It’s like flipping the industry on its head.” He notes, though, that the biggest obstacle to more widespread underground 3D modeling continues to be the cost it adds to the project, and the potential for adding more time, too, if it’s not scheduled properly.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Mar 26, 2019
Embracing collaboration tools from outside the AEC industry
Let's take a look at the available technologies from outside AEC that are seeing greater adoption within the industry.
AEC Tech | Mar 24, 2019
5 ways designers and builders can use business intelligence with data they already have
Tricky construction budgets, large project teams, and unique designs needing extensive coordination are all problems increasingly being handled with new software tools and data.
AEC Tech | Feb 8, 2019
BI(m): BIM data without models
A new breed of data tools creates a valuable opportunity for the next wave of BIM and facilities management, one where “pure data” is at the center, writes John Tobin of SMRT Architects.
AEC Tech | Jan 9, 2019
Our robotic future: Assessing AI's impact on the AEC profession and the built environment
This is the first in a series by Lance Hosey, FAIA, on how automation is disrupting design and construction.
3D Printing | Dec 7, 2018
Additive manufacturing heads to the jobsite
Prototype mobile 3D printing shop aims to identify additive manufacturing applications for construction jobsites.
AEC Tech | Sep 27, 2018
BD+C editors want your input on AEC technology
Please help us improve our editorial coverage by taking this brief survey.
Sponsored | AEC Tech | Sep 14, 2018
Sponsored webinar: Benefits of traceable construction
In this free 60-minute webinar, Keith Alcorn of FARO Technologies will talk about the concept of traceable construction and how 3D reality capture solutions provide portable, efficient, secure, and forward-looking solutions for data collection, pre-processing, and evaluation in the design, build and operating phase. September 18, 2:00 EST.
AEC Tech | Jul 24, 2018
Weidt Group’s Net Energy Optimizer now available as software as a service
The proprietary energy analysis tool is open for use by the public.
Accelerate Live! | Jul 17, 2018
Call for speakers: Accelerate AEC! innovation conference, May 2019
This high-energy forum will deliver 20 game-changing business and technology innovations from the Giants of the AEC market.
Accelerate Live! | Jun 24, 2018
Watch all 19 Accelerate Live! talks on demand
BD+C’s second annual Accelerate Live! AEC innovation conference (May 10, 2018, Chicago) featured talks on AI for construction scheduling, regenerative design, the micro-buildings movement, post-occupancy evaluation, predictive visual data analytics, digital fabrication, and more. Take in all 19 talks on demand.