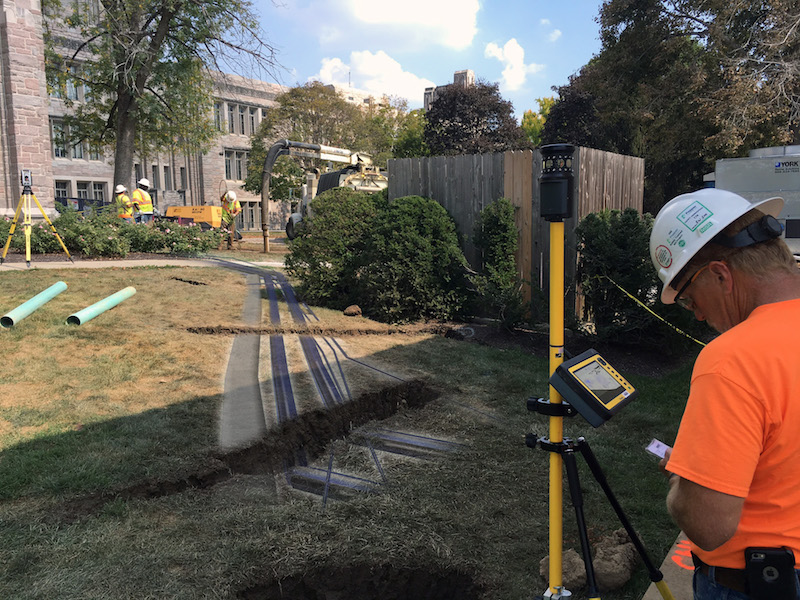
Over the years, Pepper Construction, like most general contractors, has hit its share of underground utilities installed beneath jobsites. “That’s not a phone call the CEO of our company wants to get,” says Mike Alder, Virtual Construction Manager at Pepper’s office in Indianapolis.
These breaches have occurred despite standards and protocols that have been in place for decades to identify and avoid underground pipes, wiring, and cables. Pepper typically hires a public or private locating company—depending on who owns the land—that relies on a combination of schematics on record, what’s visible above ground, and what’s underground that can be tracked by certain equipment. Sometimes, excavation is required.
But a few years ago, Pepper started asking itself whether there was a better way to locate and avoid hitting utilities. This is particularly important for hospital projects, says Alder, “where you don’t want to disrupt service and what might be on the other side of that service.”
In conversations with its field crews and subs, Pepper heard over and over again that the lack of communication and subpar information were the culprits behind these collisions. “We walked out of those meetings with the notion that everyone had a victim mentality,” says Alder.
At one of those meetings, Pepper’s safety director, Dave Murphy, made what Alder recalls as an “obvious but profound” observation that “we hit underground utilities because we can’t see them.” Soon after, in 2017, Murphy and Alder started working together to create underground 3D models. “Civil drawings just weren’t enough anymore,” says Alder.
Their first step was to gather site drawings, and then overlay them with the new utilities and building that were being installed. Using those images as guides, Pepper then went to the site with a Vac truck, which Alder describes as a giant dirt vacuum, to further locate the buried utilities and to mark them by putting six-inch pipes into the ground.
Pepper had been doing all of this before. But now, it was also surveying the site, and bringing those survey points into modeling software. Alder says his company also creates 3D models for the project’s new utilities. “The benefit of this is that we were finding places where there were clashes between the old and new utilities.”
Pepper shares this information with its field crews, giving them better reconnaissance.
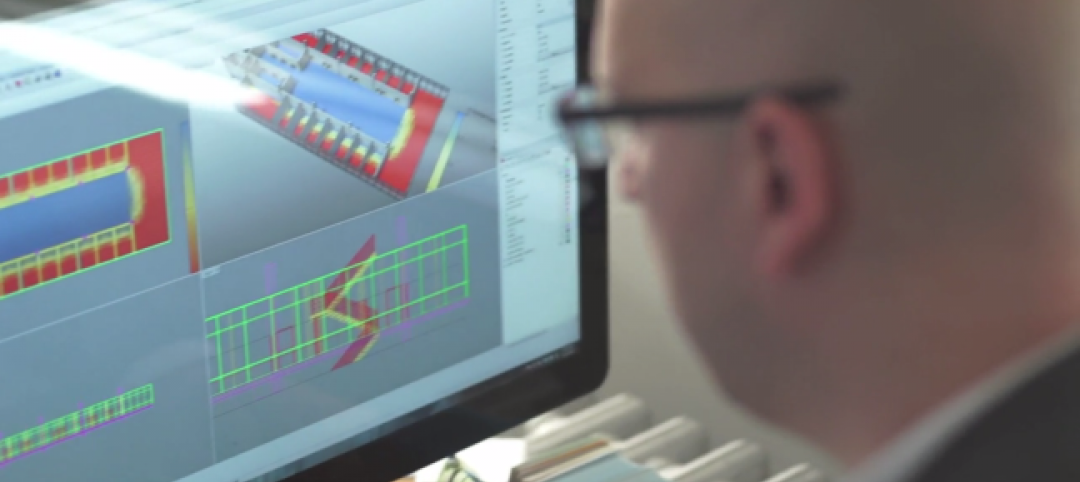
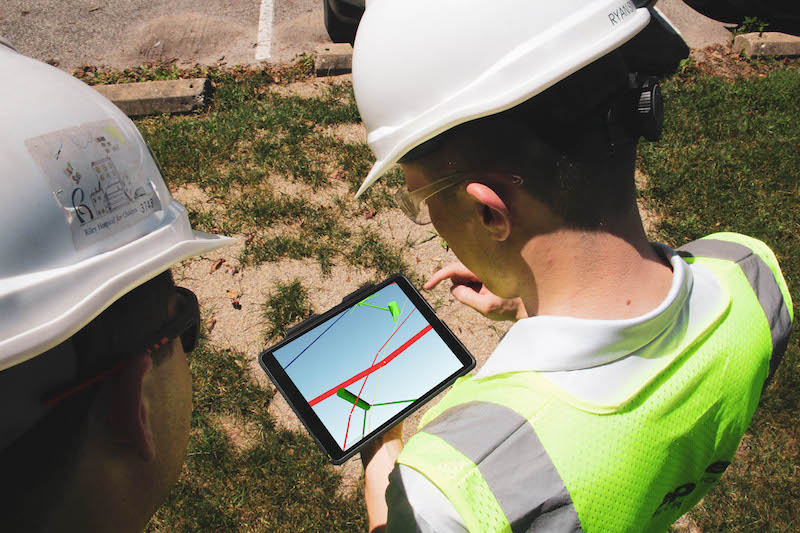 Crew members look at models showing where underground utlities are located on jobsites. Image: Pepper Construction.
Crew members look at models showing where underground utlities are located on jobsites. Image: Pepper Construction.
The firm has done underground 3D models for more than a dozen projects, and over time has made some tweaks to its process. For one thing, it’s been trying to get Civil Engineers on projects more involved upfront in the drawings and surveying during the design phase.
Pepper also flies drones over its jobsites to capture imagery that can be used to create 2D maps of the site, which Alder says gives the underground 3D models more perspective.
The modeling of underground utilities is now standard operating procedure for Pepper’s Indiana office. (Alder couldn’t say whether the firm’s other offices were following suit.). “If we had waited for the process to be perfect, we probably wouldn’t have rolled this out yet.”
Pepper is looking attempting to leveraging technology to create better models faster, and to produce a more dynamic deliverable, which will mean getting crews in the field more involved in up-to-the-minute the data collection.
“It’s important to realize that this has been a big endeavor for us,” says Alder. “It’s like flipping the industry on its head.” He notes, though, that the biggest obstacle to more widespread underground 3D modeling continues to be the cost it adds to the project, and the potential for adding more time, too, if it’s not scheduled properly.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Feb 28, 2018
Nine tips to bridge the cybernetic design gap
Unlike other technologies we have seen, augmented and virtual reality are looking to have staying power in a truly disruptive way.
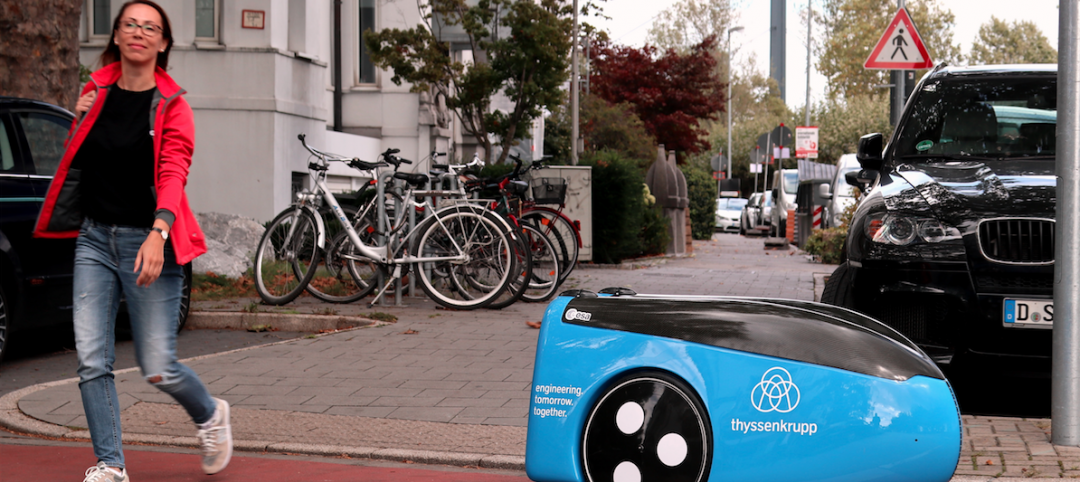
AEC Tech | Jan 29, 2018
thyssenkrupp tests self-driving robot for ‘last mile’ delivery of elevator parts
“With driverless delivery robots, we could fill a gap and get spare parts from our warehouses to the jobsite faster,” said thyssenkrupp SVP Ivo Siebers.
AEC Tech | Jan 25, 2018
Four high-tech solutions to mitigate theft on the jobsite
Geo-fencing and drone surveillance are among the tech solutions for protecting jobsites from asset loss.
BD+C University Course | Jan 2, 2018
The art and science of rendering: Visualization that sells architecture [AIA course]
3D artist Ramy Hanna offers guidelines and tricks-of-the-trade to ensure that project artwork is a stunning depiction of the unbuilt space.
Reconstruction & Renovation | Dec 21, 2017
Interactive map includes detailed information on historic New York City buildings
The New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission launched a new, enhanced version of its interactive map, Discover NYC Landmarks.
AEC Tech | Dec 20, 2017
6 CFD post-processing tips to improve visualization productivity and quality
Southland Engineering’s Abdullah Karimi offers helpful tips for making computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models more productive.
Sponsored | Building Team | Nov 3, 2017
4 strategies for marketing your AEC firm
Having a clearly defined competitive brand and a fine-tuned marketing approach can give your firm a significant competitive advantage.
Sponsored | AEC Tech | Oct 19, 2017
3 reasons why your firm needs cloud software
For firms looking to propel their architectural design services to new heights and levels of sophistication, a consolidated cloud-based platform is a valuable asset.
AEC Tech | Oct 6, 2017
How professional bias can sabotage industry transformation
Professional bias can take the form of change-resistant thinking that can keep transformational or innovative ambitions at bay. Tech consultant Nate Miller presents three kinds of bias that often emerge when a professional is confronted with new technology.
AEC Tech | Aug 25, 2017
Software cornucopia: Jacksonville Jaguars’ new practice facility showcases the power of computational design
The project team employed Revit, Rhino, Grasshopper, Kangaroo, and a host of other software applications to design and build this uber-complex sports and entertainment facility.