Related Stories
K-12 Schools | Aug 29, 2024
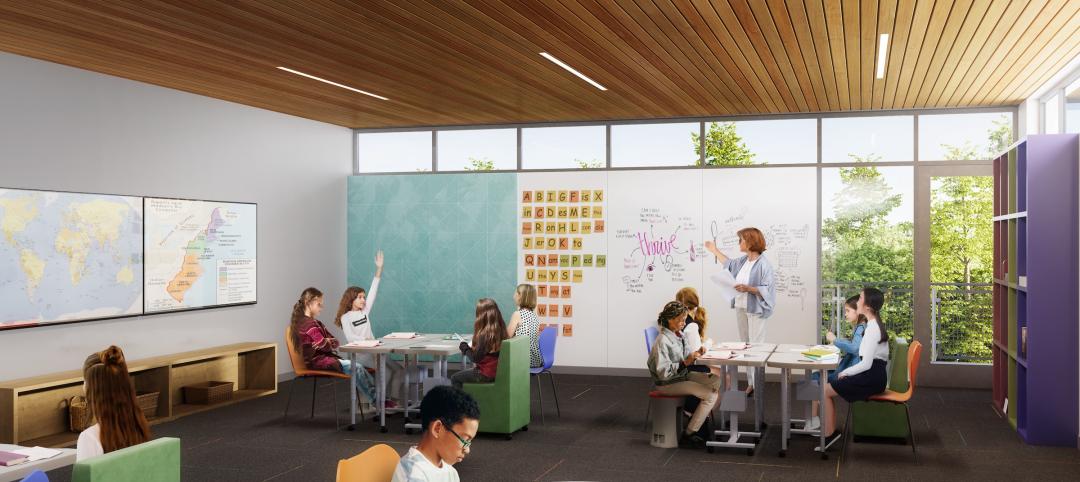
Designing for dyslexia: How architecture can address neurodiversity in K-12 schools
Architects play a critical role in designing school environments that support students with learning differences, particularly dyslexia, by enhancing social and emotional competence and physical comfort. Effective design principles not only benefit students with dyslexia but also improve the learning experience for all students and faculty. This article explores how key design strategies at the campus, classroom, and individual levels can foster confidence, comfort, and resilience, thereby optimizing educational outcomes for students with dyslexia and other learning differences.
Museums | Aug 29, 2024
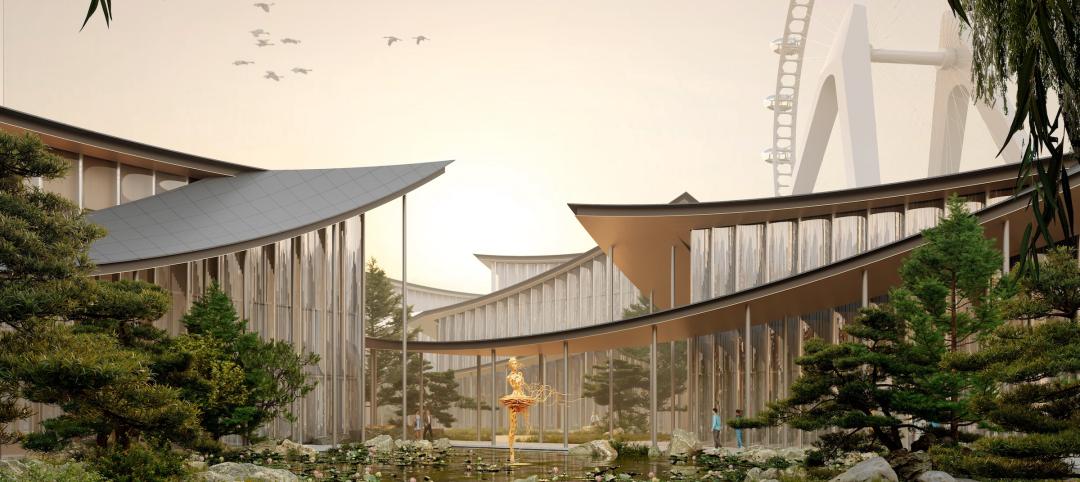
Bjarke Ingels' Suzhou Museum of Contemporary Art conceived as village of 12 pavilions
The 60,000-sm Suzhou Museum of Contemporary Art in Suzhou, Jiangsu, China recently topped out. Designed by Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG), the museum is conceived as a village of 12 pavilions, offering a modern interpretation of the elements that have defined the city’s urbanism, architecture, and landscape for centuries.
Adaptive Reuse | Aug 28, 2024
Cities in Washington State will offer tax breaks for office-to-residential conversions
A law passed earlier this year by the Washington State Legislature allows developers to defer sales and use taxes if they convert existing structures, including office buildings, into affordable housing.
Industrial Facilities | Aug 28, 2024
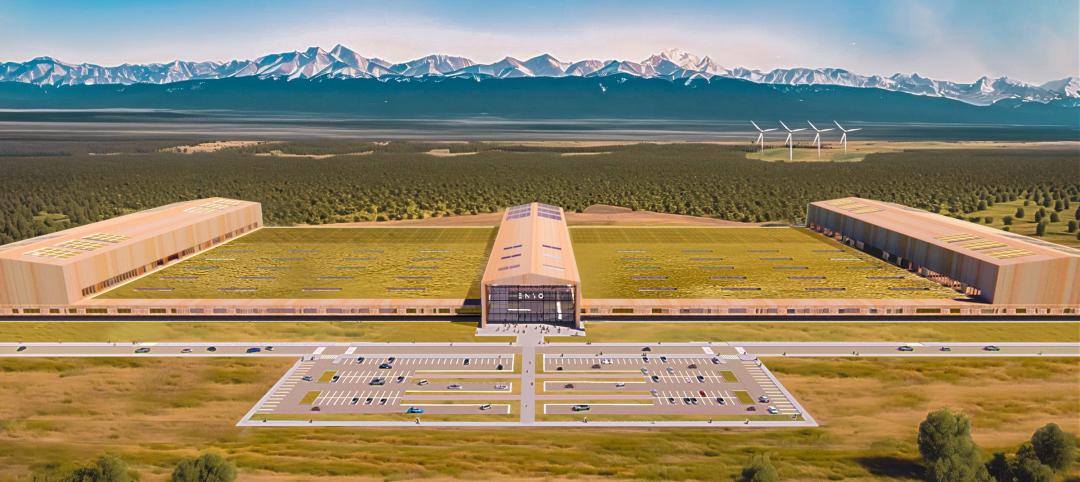
UK-based tire company plans to build the first carbon-neutral tire factory in the U.S.
ENSO, a U.K.-based company that makes tires for electric vehicles, has announced plans to build the first carbon-neutral tire factory in the U.S. The $500 million ENSO technology campus will be powered entirely by renewable energy. The first-of-its-kind tire factory aims to be carbon neutral without purchased offsets, using carbon-neutral raw materials and building materials.
Architects | Aug 28, 2024
KTGY acquires residential high-rise specialist GDA Architects
KTGY, an award-winning design firm focused on architecture, interior design, branded environments and urban design, announced that it has acquired GDA Architects, a Dallas-based architectural firm specializing in high rise residential, hospitality and industrial design.
K-12 Schools | Aug 26, 2024
Windows in K-12 classrooms provide opportunities, not distractions
On a knee-jerk level, a window seems like a built-in distraction, guaranteed to promote wandering minds in any classroom or workspace. Yet, a steady stream of studies has found the opposite to be true.
Building Technology | Aug 23, 2024
Top-down construction: Streamlining the building process | BD+C
Learn why top-down construction is becoming popular again for urban projects and how it can benefit your construction process in this comprehensive blog.
Airports | Aug 22, 2024
Portland opens $2 billion mass timber expansion and renovation to its international airport
This month, the Portland International Airport (PDX) main terminal expansion opened to passengers. Designed by ZGF for the Port of Portland, the 1 million-sf project doubles the capacity of PDX and enables the airport to welcome 35 million passengers per year by 2045.
Adaptive Reuse | Aug 22, 2024
6 key fire and life safety considerations for office-to-residential conversions
Office-to-residential conversions may be fraught with fire and life safety challenges, from egress requirements to fire protection system gaps. Here are six important considerations to consider.
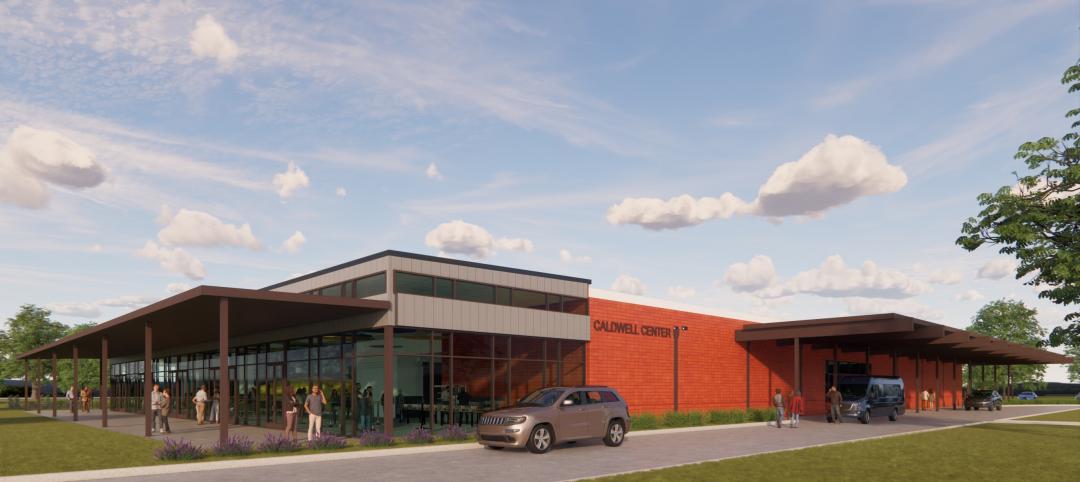
Resiliency | Aug 22, 2024
Austin area evacuation center will double as events venue
A new 45,000 sf FEMA-operated evacuation shelter in the Greater Austin metropolitan area will begin construction this fall. The center will be available to house people in the event of a disaster such as a major hurricane and double as an events venue when not needed for emergency shelter.