In 2009, we met with Senior Facility Managers of four U.S. national laboratories to discuss a major limitation in the way they summarized their capital needs. As with most large organizations, they expressed capital needs in terms of deferred maintenance projects—things that needed to be fixed as determined by condition assessment (inspection or prescribed schedule). To put these needs in perspective, they computed a facility condition index (FCI), which is the ratio of deferred maintenance (D.M) costs to the replacement value of a building or portfolio.
Several years later, following the acquisition of Whitestone Research by CBRE Inc., it quickly became clear that major healthcare organizations around the world oftentimes employ a similar FCI based approach to their capital planning and prioritization decisions.
FACILITY CONDITION INDEX BREAKDOWN
According to a well-known scale developed initially for educational facilities in 1991, a facility is considered in poor condition if its FCI exceeds 90%. The shortcomings of the FCI approach are well-known, as results are not easily compared with alternative condition assessment approaches, and it does not contemplate methodologies for determining replacement values. These choices can become highly political for an organization that uses, as many do, the FCI as a key policy metric.
The basic concern of the laboratory facility managers was that the FCI did not represent the true condition of the facility in terms of safety, security, mission relevance, and other criteria that actually guide their decisions. FCI is also not a forecast or leading indicator that demonstrates consequences of alternative actions. These concerns led to a series of small projects that would eventually define a new approach to summarizing facility condition and prioritizing capital expenditures.
The new method, Risk Scanning, meets three requirements identified in our original meeting. The process must not rely on expensive inspections, must incorporate multiple (customizable) criteria, and the outcomes must be expressed as a simple monetary value.
This approach has universal applicability for laboratories and for large, corporate occupiers. In addition, we have found this approach to be particularly relevant for healthcare organizations today, given the extraordinary economic and regulatory pressures that have become a reality for the industry.
RISK SCANNING
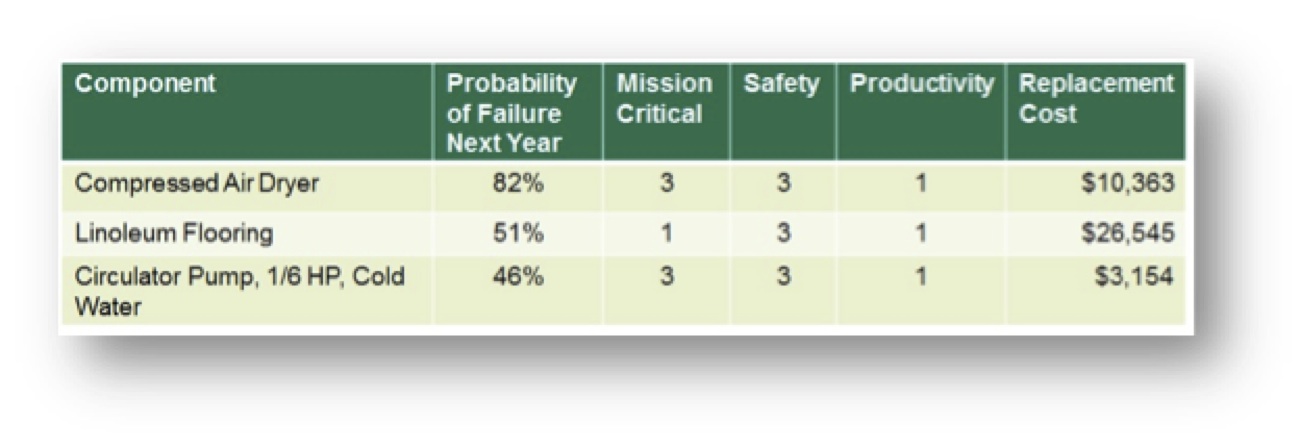
Risk Scanning assumes that buildings or other assets can be reduced to an inventory of components (roof, HVAC equipment, plumbing fixtures, etc.). Each component has a “survivor” curve that relates its age to the likelihood of its failure in the future, little different than an actuarial calculation for an insurance policy. And each component, should it fail, could have consequences for the building operation. Below, Figure 1 illustrates how this data could be used as a simple sort by probability of failure, consequence of failure, or replacement cost.
A more useful view of this data combines knowledge of the probability of failure and the potential consequences as the Risk Facility Managers implicitly consider when scheduling repairs. For example, a new light bulb in a closet would be low risk (low likelihood of failure, low impact on safety, security, mission, etc.), while a roof or electrical panel, far beyond their expected service life would be a high risk. Individual component risk ratings can be aggregated into risk maps by building, consequence type, or aggregated at the portfolio level.
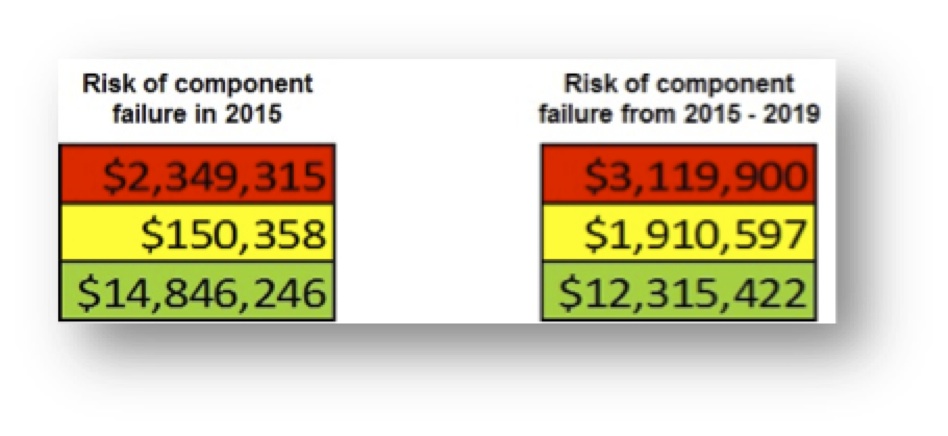
Another example is a risk scan of a data center built in 1980, as shown in Figure 2. Risk is summarized by three consequences or threats of failure – mission, productivity and safety. The “Loss Intensity” is the measure (low, medium, high) of the impact of failure. Each cell in the tables is the sum of the replacement value of each component. For instance, in the first table there are high risk (red) components with replacement values totaling $374,210.
Figure 2: Dashboard showing risk by consequence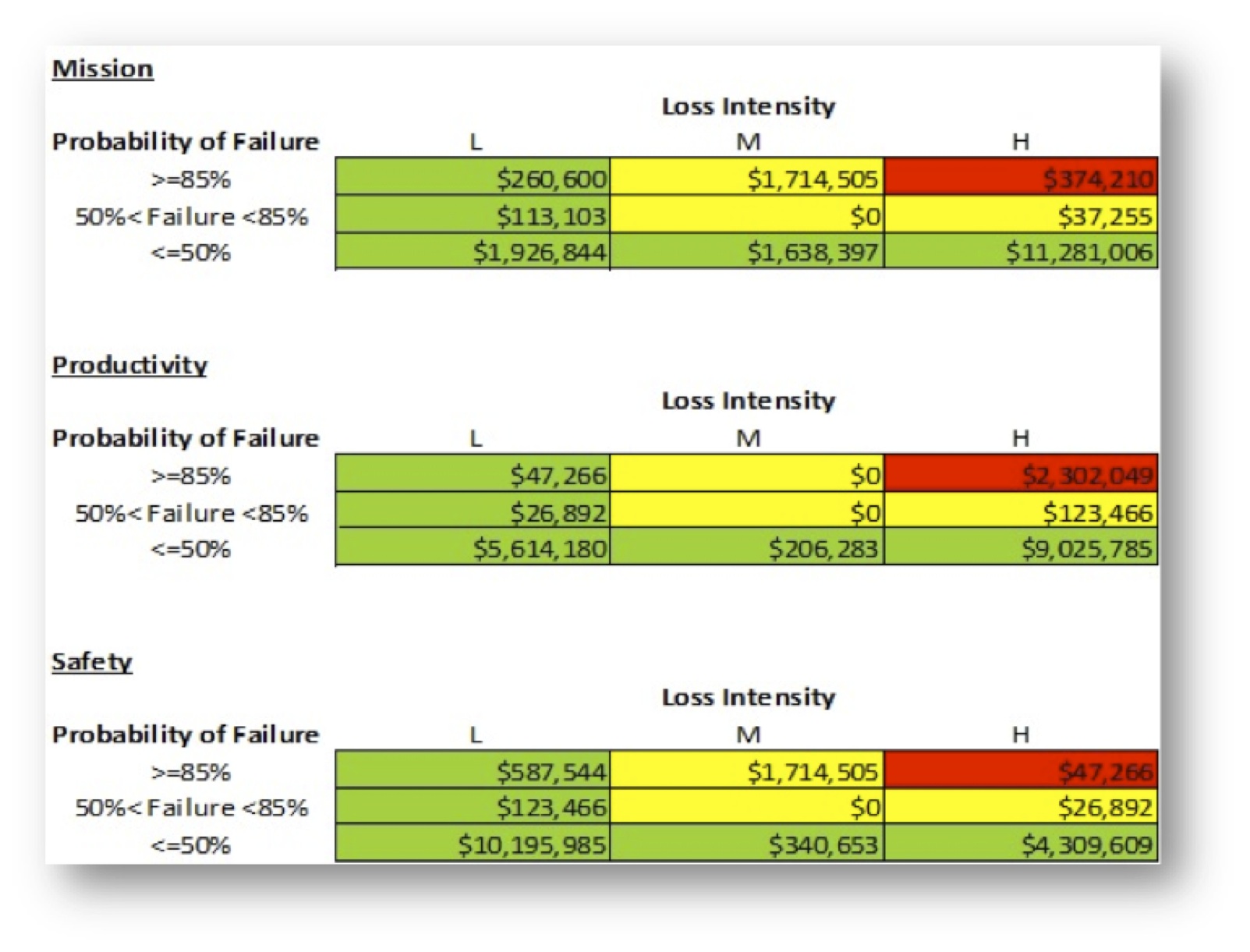
One way to represent overall risk is to sum across the individual tables in Figure 2, by risk category (red = high, yellow = moderate, green = low) to produce a single risk column, as shown in Figure 3. This shows that the costs to replace components rated high risk in 2015 for any reason (mission, productivity, or safety) were $2,349,315. Note that some components are high risk for multiple reasons.
The calculation of the column can be modified for different purposes. The ratings from the dashboard could be weighted to reflect management priorities. The likelihood of failure, and consequent migration of risk ratings, could be estimated for a range of years, as shown for the period 2015-2019.
COMPARING THE FCI WITH RISK SCANNING
The data center example provides a useful comparison of the output from a simple condition assessment with the additional data provided by Risk Scanning.
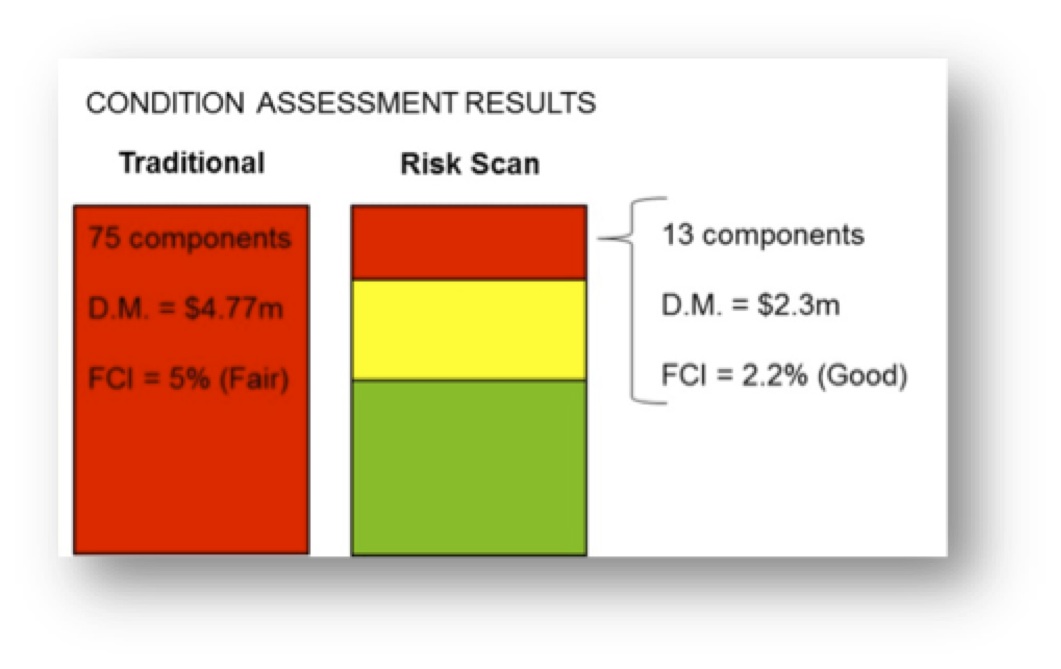
A conventional facility condition assessment using a life cycle cost model indicated that 75 components had exceeded their service life. The costs of replacing these would be $4,771,159. Considering this amount to be deferred maintenance (D.M.), the FCI would be 5% (given $100 million replacement value). This would be summarized as a building in “fair” condition.
A Risk Scan of the component inventory indicates that 13 components are at high risk, and the costs of replacing these would be $2,349,315. This is less than half the costs of replacements by a simple service life-assessment. An FCI based on high risk components would be 2.2%, indicating a building in “good” condition.
In this case, with the additional information provided by Risk Scanning, the facility would be considered in better condition than with the simple condition assessment. Moreover, the risk scan would provide a rating for all components—including those not yet considered as deferred maintenance—as a basis for anticipating future needs and prioritization.
CONCLUSION
The Risk Scanning approach uses well-known risk analytics applied to pre-existing facility data to provide a richer view of facility condition more consistent with actual management decision making. In practice, limited funding is directed to those repairs and replacements that address corporate priorities, such as safety, security, and mission achievement. For healthcare systems, this approach can provide critical insight for decision-making about capital deployment where actionable criteria are not established or where data is limited.
About the Authors
Peter Lufkin is Senior Managing Director and Luca Romani is Senior Analyst with CBRE Whitestone.
Related Stories
MFPRO+ New Projects | Oct 30, 2024
BIG’s One High Line finally reaches completion in New York City’s West Chelsea neighborhood
One High Line, a luxury residential project spanning a full city block in New York’s West Chelsea neighborhood, reached completion this summer following years of delays related to investor lawsuits.
Urban Planning | Oct 30, 2024
Bridging the gap: How early architect involvement can revolutionize a city’s capital improvement plans
Capital Improvement Plans (CIPs) typically span three to five years and outline future city projects and their costs. While they set the stage, the design and construction of these projects often extend beyond the CIP window, leading to a disconnect between the initial budget and evolving project scope. This can result in financial shortfalls, forcing cities to cut back on critical project features.
MFPRO+ New Projects | Oct 30, 2024
Luxury waterfront tower in Brooklyn features East River and Manhattan skyline views
Leasing recently began for The Dupont, a 41-story luxury rental property along the Brooklyn, N.Y., waterfront. Located within the 22-acre Greenpoint Landing, where it overlooks the newly constructed Newtown Barge Park, the high-rise features East River and Manhattan skyline views along with 20,000 sf of indoor and outdoor communal space.
Libraries | Oct 30, 2024
Reasons to reinvent the Midcentury academic library
DLR Group's Interior Design Leader Gretchen Holy, Assoc. IIDA, shares the idea that a designer's responsibility to embrace a library’s history, respect its past, and create an environment that will serve student populations for the next 100 years.
Resiliency | Oct 29, 2024
Climate change degrades buildings slowly but steadily
While natural disasters such as hurricanes and wildfires can destroy buildings in minutes, other factors exacerbated by climate change degrade buildings more slowly but still cause costly damage.
Office Buildings | Oct 29, 2024
Editorial call for Office Building project case studies
BD+C editors are looking to feature a roundup of office building projects for 2024, including office-to-residential conversions. Deadline for submission: December 6, 2024.
Healthcare Facilities | Oct 28, 2024
New surgical tower is largest addition to UNC Health campus in Chapel Hill
Construction on UNC Health’s North Carolina Surgical Hospital, the largest addition to the Chapel Hill campus since it was built in 1952, was recently completed. The seven-story, 375,000-sf structure houses 26 operating rooms, four of which are hybrid size to accommodate additional equipment and technology for newly developed procedures.
Multifamily Housing | Oct 28, 2024
A case for mid-rise: How multifamily housing can reshape our cities
Often referred to as “five-over-ones,” the mid-rise apartment type is typically comprised of five stories of apartments on top of a concrete “podium” of ground-floor retail. The main criticism of the “five-over-one” is that they are often too predictable.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Oct 24, 2024
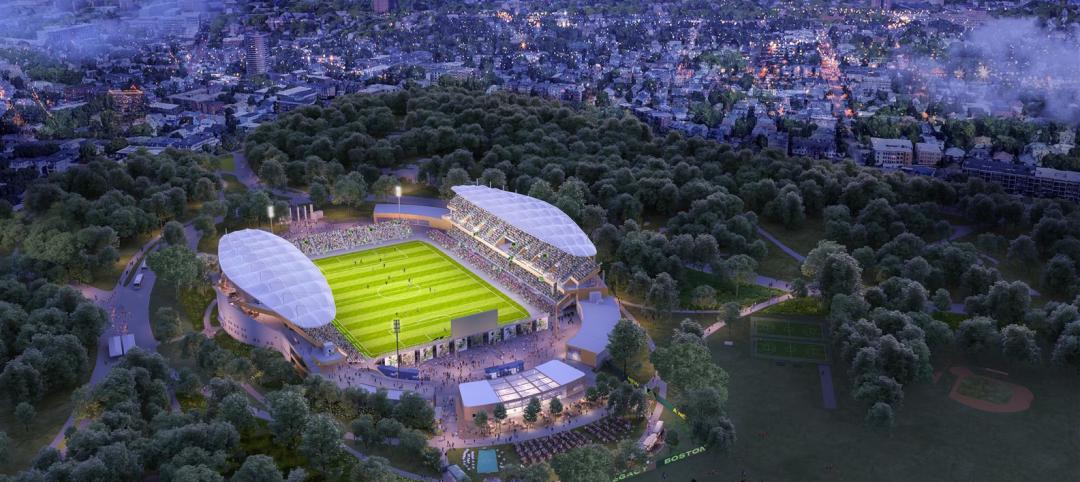
Stadium renovation plans unveiled for Boston’s National Women’s Soccer League
A city-owned 75-year-old stadium in Boston’s historic Franklin Park will be renovated for a new National Women’s Soccer League team. The park, designed by Fredrick Law Olmsted in the 1880s, is the home of White Stadium, which was built in 1949 and has since fallen into disrepair.
Laboratories | Oct 23, 2024
From sterile to stimulating: The rise of community-centric life sciences campuses
To distinguish their life sciences campuses, developers are partnering with architectural and design firms to reimagine life sciences facilities as vibrant, welcoming destinations. By emphasizing four key elements—wellness, collaboration, biophilic design, and community integration—they are setting their properties apart.