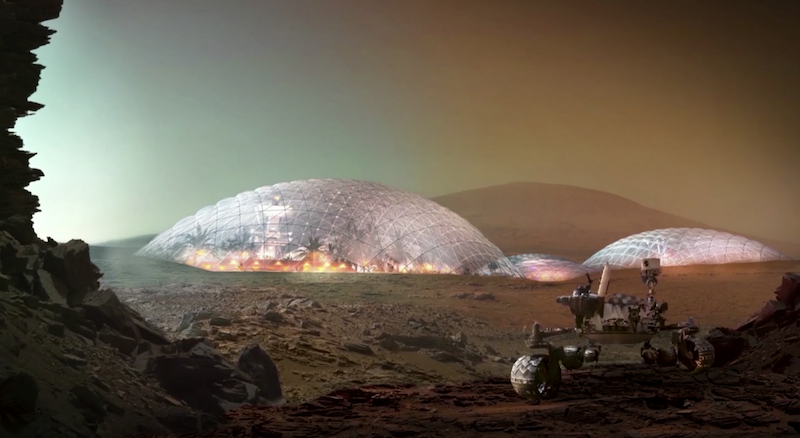
Bjarke Ingels has joined the building-on-Mars party. BIG's prototype Martian city, dubbed Mars Science City, is designed to be an environment dedicated to the knowledge, education, and exhibition of the technologies necessary to inhabit mars.
But what's even the point of this discussion? Especially in times like those which we are currently experiencing, isn't the thought of building a city on Mars a bit quixotic? Perhaps, but as Ingels points out, of the 17 sustainable development goals of the United Nations, eight of them deal with the built environment. And when it comes to the built environment on Mars, sustainability is key.
The purpose of designing for Mars can be summed up in one word: innovation. The solutions architects, designers, scientists, researchers and the like come up with for living on Mars can and will help right here on Earth. Space travel has already given us dozens of innovations and inventions that we now use on an everyday basis; scratch-resistant lenses, shock absorbers for buildings, solar cells, and memory foam were all originally created to help solve a very specific problem associated with space travel.
As Ingels says in his talk, "The exact same principles and the exact same systems that will allow us to live on Mars are the very same that will allow us to be great custodians on earth."
See Also: Designing for the final frontier: Space architecture
Watch the entire presentation from Bjarke Ingels below.
Related Stories
Codes and Standards | Feb 18, 2022
Proposal would make all new buildings in Los Angeles carbon-neutral
Los Angeles may become the next large city to ban fossil fuels from new construction if legislation recently introduced in the city council becomes law.
Sustainability | Feb 7, 2022
Western Washington University will be home to Washington State’s first carbon neutral college building
Perkins&Will is designing the building.
Sponsored | Reconstruction & Renovation | Jan 25, 2022
Concrete buildings: Effective solutions for restorations and major repairs
Architectural concrete as we know it today was invented in the 19th century. It reached new heights in the U.S. after World War II when mid-century modernism was in vogue, following in the footsteps of a European aesthetic that expressed structure and permanent surfaces through this exposed material. Concrete was treated as a monolithic miracle, waterproof and structurally and visually versatile.
Sustainability | Nov 16, 2021
Shanghai’s Starbucks Greener Store Lab is the first RESET-certified store for material circulation in the world
The store is inspired by the city of Shanghai and its waste management goals.
Urban Planning | Nov 11, 2021
Reimagining the concrete and steel jungle, SOM sees buildings that absorb more carbon than they emit
The firm presented its case for a cleaner built environment during the Climate Change conference in Scotland.
Sustainability | Nov 9, 2021
The future of regenerative building is performance-based
Why measuring performance results is so critical, but also easier said than done.
Sustainability | Oct 28, 2021
Reducing embodied carbon in construction, with sustainability leader Sarah King
Sustainability leader Sarah King explains how developers and contractors can use the new EC3 software tool to reduce embodied carbon in their buildings.
| Oct 14, 2021
The future of mass timber construction, with Swinerton's Timberlab
In this exclusive for HorizonTV, BD+C's John Caulfield sat down with three Timberlab leaders to discuss the launch of the firm and what factors will lead to greater mass timber demand.
Green | Oct 6, 2021
My reaction to the UN IPCC Climate Change 2021 report: Ugh!
The recent report of the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change is not a happy read.
Data Centers | Sep 22, 2021
Wasted energy from data centers could power nearby buildings
A Canadian architecture firm comes up with a concept for a community that’s part of a direct-current microgrid.