Most older Americans don’t reside in “livable” communities that combine safety, security and affordability with appropriate housing and transportation options, and supportive features and services that enhance personal independence, allow residents to remain in their homes as they age, and foster residents’ engagement in civic, economic, and social life.
In a 33-page paper titled “Which Older Adults Have Access to America’s Most Livable Neighborhoods,” the Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard University and AARP’s Public Policy Institute draw upon information from the 2017 American Communities Survey (ACS)—whose estimates categorize 217,739 Census neighborhood block groups—as a guide to analyze AARP’s 2018 Livability Index, an online interactive source that scores neighborhoods across the U.S. to shed light on the current livability of a given location and to highlight opportunities for improvement.
The Index derives from more than 4,500 questionnaire respondents and 80 in-depth interviews, as well as input from 30 experts in various fields.
The paper also used ACS microdata to examine profiles of older adults residing in neighborhoods with different levels of livability to suggest opportunities for addressing inequality in access to livable communities, and to the specific elements certain populations lack even in the most livable places.
The paper’s goal is to evaluate whether access to livable communities is evenly distributed across the older adult population, to assess how older adults access livability features, and to understand the characteristics of higher performing communities.
DISCONNECT BETWEEN WHERE PEOPLE LIVE AND WHAT THEY NEED
Some key findings:
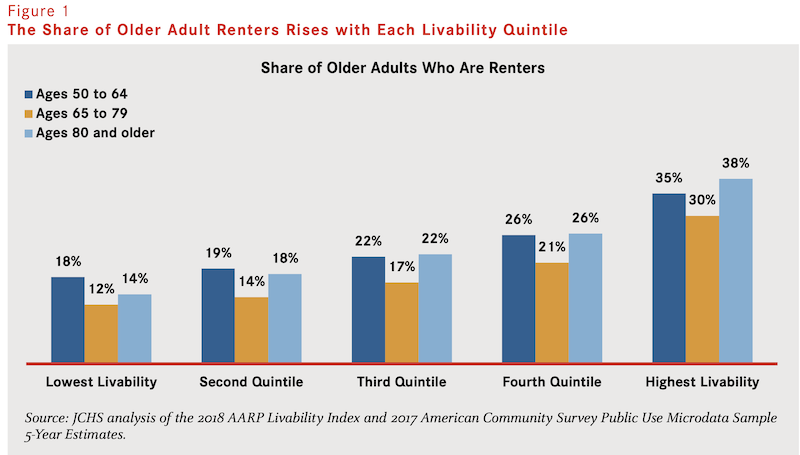
•Nearly 146 million Americans of all ages live in neighborhoods at the bottom two quintiles in terms of livability. And older adults are underrepresented in most livable communities; in the least livable quintile, adults age 55 or older made up near one-third of residents.
•Older adults who move tend to relocate to newer places with similar levels of overall livability as their previous neighborhoods. Only 11% move to more livable locations, and 14% actually move to neighborhoods with lower livability scores.
•There is a relationship between different types of livable neighborhoods and income, race/ethnicity characteristics, and homeownership. “At every level of livability, homeownership and income play important roles in accessing features that contribute to high scores in specific livability categories,” the paper’s authors write.
Certain themes also emerged from this research:
•Livability gap. There is a disconnect between what people have and what they need in communities to age in place.
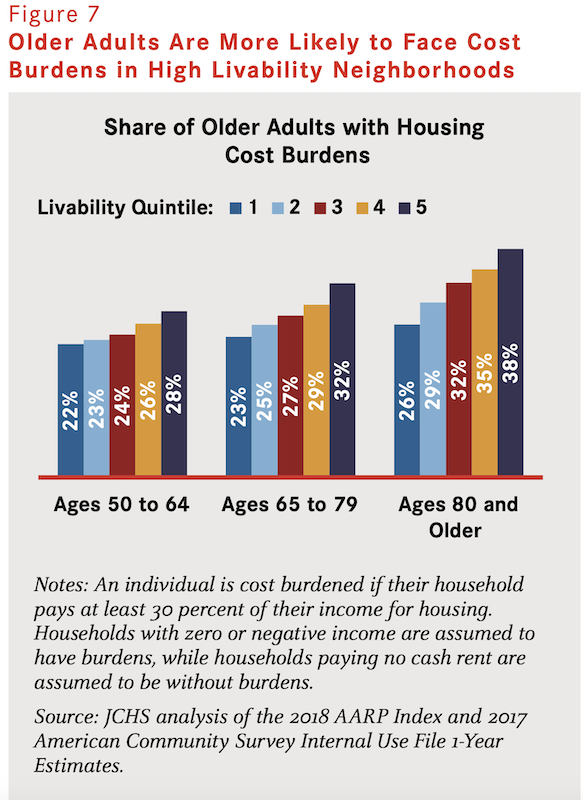
•Housing affordability. Communities that score higher on the Index tend to have higher housing costs. High housing costs can create obstacles to accessing the benefits livable communities can provide.
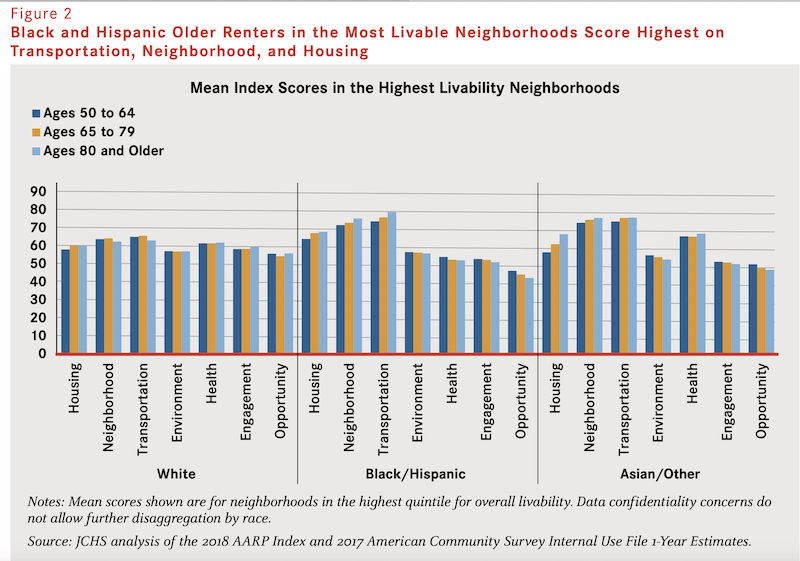
•Disparities in access to specific livability features. People of color, people with disabilities, and people with lower incomes may not have access to amenities and services that support aging. As the analysis shows, even when living in high scoring communities these groups may not have access to amenities and services related to health, engagement, and opportunity.
•Mobility. People tend to move to places with similar livability levels as their previous neighborhood.
•Neighborhood preferences and location choice. Individual preferences, barriers, and available community amenities may impact people’s decisions on where to live.
POLICY SUGGESTIONS INCLUDE PROMOTING HEALTHIER ENVIRONMENTS
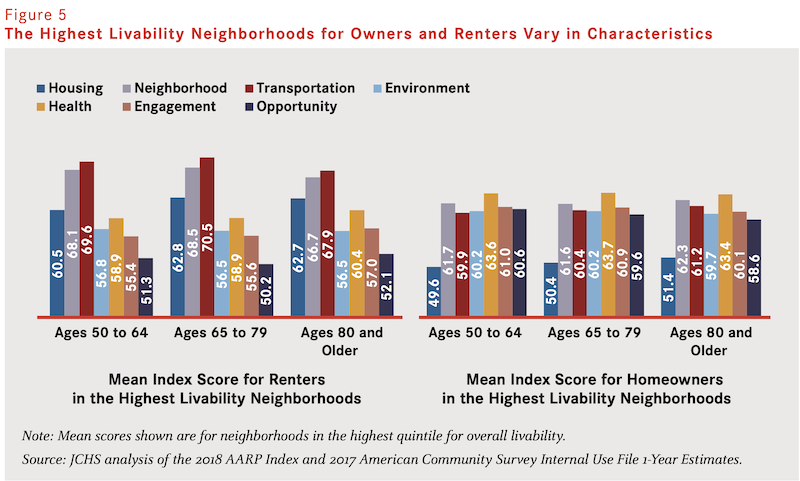
Livable communities tend to have diverse housing types that include more single-person households, where older adults are more likely to reside. This factor might explain why, on average, older renters live in more livable places than do older owners.
The likelihood of living in livable communities shifts somewhat with the person’s age. Among older adults, those ages 50 to 64 as well as those ages 80 and older have a slightly better chance of living in a high livability neighborhood than do those ages 65 to 79. Among those ages 80 and older, 18 percent reside in the top quintile neighborhoods but only 16 percent of those ages 65 to 79 do. In contrast, those ages 65 to 79 are more likely than other age groups to live in lower-livability neighborhoods.
The paper offers policy recommendations that focus on housing affordability and access, creating save neighborhoods that have ample food and culture available, environments that promote healthy, clean and natural places to live; and communities that supporting resident well-being and social lives, and enable economic and educational pursuits.
“By analyzing the Index in conjunction with Census block group data from the ACS, we have revealed specific areas that warrant focused attention,” the paper states. “Housing stock, tenure, and affordability have particular influences on the access older adults have to the most livable communities.” While this analysis could not reveal if the most vulnerable older people residing in livable communities have equal access to every feature, service, and amenity, “one expects they do not.”
Related Stories
Market Data | Apr 4, 2016
ABC: Nonresidential spending slip in February no cause for alarm
Spending in the nonresidential sector totaled $690.3 billion on a seasonally adjusted, annualized basis in February. The figure is a step back but still significantly higher than one year ago.
Market Data | Mar 30, 2016
10 trends for commercial real estate: JLL report
The report looks at global threats and opportunities, and how CRE firms are managing their expectations for growth.
Market Data | Mar 23, 2016
AIA: Modest expansion for Architecture Billings Index
Business conditions softening most in Midwest in recent months.
Retail Centers | Mar 16, 2016
Food and technology will help tomorrow’s malls survive, says CallisonRTKL
CallisonRTKL foresees future retail centers as hubs with live/work/play components.
Market Data | Mar 6, 2016
Real estate execs measure success by how well they manage ‘talent,’ costs, and growth
A new CBRE survey finds more companies leaning toward “smarter” workspaces.
Market Data | Mar 1, 2016
ABC: Nonresidential spending regains momentum in January
Nonresidential construction spending expanded 2.5% on a monthly basis and 12.3% on a yearly basis, totaling $701.9 billion. Spending increased in January in 10 of 16 nonresidential construction sectors.
Market Data | Mar 1, 2016
Leopardo releases 2016 Construction Economics Report
This year’s report shows that spending in 2015 reached the highest level since the Great Recession. Total spending on U.S. construction grew 10.5% to $1.1 trillion, the largest year-over-year gain since 2007.
Market Data | Feb 26, 2016
JLL upbeat about construction through 2016
Its latest report cautions about ongoing cost increases related to finding skilled laborers.
Market Data | Feb 17, 2016
AIA reports slight contraction in Architecture Billings Index
Multifamily residential sector improving after sluggish 2015.
Market Data | Feb 11, 2016
AIA: Continued growth expected in nonresidential construction
The American Institute of Architects’ semi-annual Consensus Construction Forecast indicates a growth of 8% in construction spending in 2016, and 6.7% the following year.