Empty churches and shuttered parochial schools are scattered throughout neighborhoods in many older U.S. cities, and Chicago is no exception. Meanwhile, many daycare providers, community organizations, and charter schools are desperate for program space. Could this be evidence of divine providence at work?
The story of Concordia Place illuminates both the difficulties and rewards of trying to match empty buildings with social programs. Concordia Lutheran Church, founded by Swedish Lutherans in 1898 and today a member congregation of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America, was seeking to expand its highly successful early childhood program, Concordia Place. That program was started in the early 1980s, when three single mothers pleaded with the small, 60-member congregation to provide low-cost childcare.
Located in Chicago’s North Center neighborhood, about six miles northwest of the Loop, Concordia Place had a long waiting list and no space in which to grow. When a shuttered Catholic church, St. Veronica’s, about a mile southwest of Concordia, came on the market, Concordia’s leaders sprung at the opportunity.
Project summary
CONCORDIA PLACE
Chicago, Ill.Building Team
Owner: Concordia Lutheran Church
Owner’s representative: Cotter Consulting
Project planning and development: LL Consulting
Architect, interior design, SE: Holabird & Root
MEP engineer: EME (now KJWW)
Civil engineer: Terra Engineering
Historic preservation consultant: Harboe Architects
Landscape architect: McKay Landscape Architects
Contractor: Bulley & AndrewsGeneral Information
Project size: 28,000 sf
Construction cost: $5.6 million
Delivery method: Design-bid-build
There was talk about razing the structures in order to build condominiums, but the local community would hear nothing of that: They wanted the buildings preserved and repurposed to serve mounting social demands. Concordia members undertook a multi-year fundraising campaign, doubling their regular contributions, mortgaging existing church facilities, and soliciting donations from businesses, foundations, and government sources
Unravelling a hodgepodge of building uses
The property featured an unusual set of structures. St. Veronica Parish was founded in 1904 and a year later dedicated a combination church-school building. What looked like a three-story brick-and-limestone school actually contained a sanctuary on the ground floor, classrooms on the floor above, and a large community hall on the third. Gone was an old convent in a wood-frame penthouse above it all; it was destroyed by fire years ago.
In contrast to the modest church-school structure, the rectory, built a decade later, was an imposing red brick Tudor design by noted ecclesiastical architect Henry Schlacks. The archdiocese closed both church and school and sold the property to the city of Chicago in 1989. For a time, it was used as overflow space for a nearby public school, but within a few years it was vacant and subject to repeated vandalism.
Such combination church-school buildings may be the most readily adaptable of church properties, as they usually have no bell towers, large rose windows, or tall, voluminous naves. The lack of the typical church basement meant that the main level was just up from the sidewalk, making ADA compliance easier to achieve.
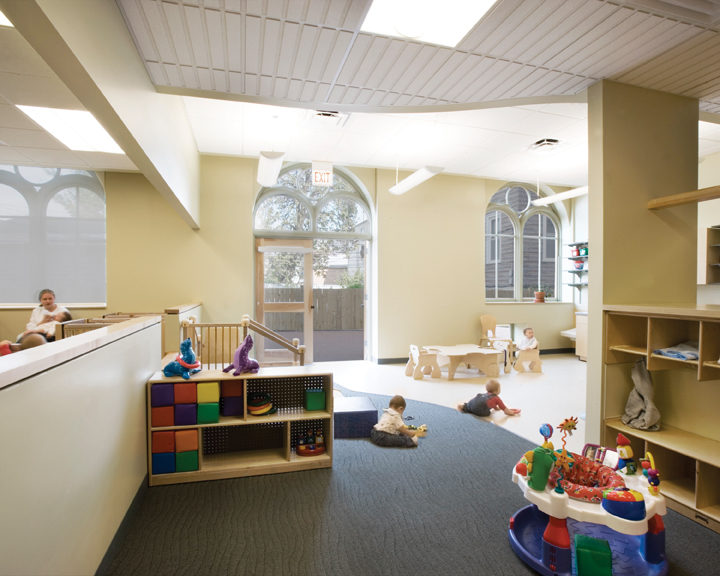
When Concordia Lutheran eventually purchased the property, the first two floors of the church-school building prooved perfect for their early childhood and preschool program. But according to the church’s pastor, Reverend Nicholas J. Zook, the leaders wondered what to do with the cavernous third floor. They surveyed the community and found that, due to heightened gang activity in the neighborhood, teen programs would be welcomed. There was also a large population of seniors and non-English-speaking adults with unmet needs.
Thus, it was envisioned that the so-called “bonus space” of the third floor could house a community center that would offer after-school and summer camp programs for ages six to 12, leadership development for teens, English classes for adults, and wellness programs for seniors.
Keeping program needs and preservation in mind
Local architects Holabird & Root were charged with meeting the varied programmatic needs of these diverse user groups while preserving the historic exteriors. Careful site planning made use of virtually every square inch of the property. “We wanted to get as much space as possible for the kids to play in, but we also wanted to make a welcoming gesture to the public,” says Maria Segal, RA, then Holabird & Root’s early childhood design specialist. (She is now with Blender Architecture, Chicago.)
General contractor Bulley & Andrews demolished a decrepit 1950s addition and replaced it with a single-story annex. Its colors and materials—soft red and light sage green composite cement panels—mediate between the red brick rectory and the yellow brick church-school building. Siting the annex at the back of the lot created a courtyard that is now used for both school and community events, including a farmers’ market run by the after-school teens.
The high-ceilinged annex is used for children’s large-motor activities as well as banquets, community meetings, and worship services. Extensive glazing provides a visual connection to the outdoors and makes it glow during evening events. A playground for the preschool children is just south of the annex, and a fenced play area for toddlers is tucked into the north part of the site, offering direct access from those classrooms.
Because the church complex was rated orange on the Chicago Historic Resources Survey, the project was able to obtain state funds. That triggered the involvement of the Illinois Historic Preservation Agency, which directed Concordia to preserve all existing window openings. This was at odds with Concordia’s desire to change some of the windows into glass-paned doors for the first floor classrooms.
The IHPA and Concordia reached a compromise: alternating windows were changed into doors, and small square windows were punched into the walls below the sills of the remaining windows. The original wood windows were restored and double-glazed.
Except for a stairway in the southeast corner, the interior of the church-school was gutted. Folding wooden doors that divided a large room on the third floor were reused for the same purpose.
The archdiocese had removed about half of the stained glass windows before selling the property. Those that remained were removed from the first-floor sanctuary and placed in backlit frames in the historic stairwell and in the third-floor teen room, which can also serve as a chapel. The IHPA did not require the stained glass to be preserved, but Reverend Zook insisted that it be done anyway, as a gesture “to show continuity with this place as an anchor in the community.”
The interior materials palette is in neutral, soothing colors with natural materials, such as birch plywood, used wherever possible. “That way the child brings the life and color to the spaces,” Segal says.
Reverend Zook praises the 28,000-sf, $5.6 million project, for its maximization of natural light and for providing and an abundance of storage areas from otherwise useless space, which helps maximize the flexibility of the rooms.
Keeping the scale right
A child-appropriate scale was also achieved despite the high ceilings by breaking down the scale of the classrooms with alcoves, cubbies, and lofts. Activity areas are defined by changes in ceiling and floor treatments. Low, square windows provide views into adjacent classrooms as well as to the outdoors. During construction, a number of cast-iron columns were discovered; these columns had to be reinforced with a secondary set of steel supports.
The third floor has an array of spaces whose flexibility has contributed significantly to the building’s success as a community center. Reverend Zook dreamed of a grand lobby on the first floor, but that space was needed for classrooms. Instead, the project team created a great lobby upstairs, where a pitched-roof skylight structure provides abundant north light, and a café serves as a multipurpose space used throughout the day by seniors, adults, and teens. New doors can close off the corridor to separate the licensed preschool spaces from the community areas
This kind of mixed-use facility is a model for the pooling of community resources that is now often necessitated by tight budgets, especially for nonprofit entities like Concordia.
Two campuses, one mission
Renovating the buildings and constructing the annex resulted in a dramatic expansion of Concordia’s mission and program. Concordia Place’s two campuses now serve a multi-age population from babies to senior citizens, providing more than 300 children (95% of whom are not Lutheran) with childcare and after-school programs. Seventy percent of the children in the new program come from minority families, nearly half of which are headed by single parents.
Reverend Zook feels that the marginal added costs of preservation were a demonstration of Concordia’s “good-faith relationship to the community.” Instead of being lost to the wrecking ball, this former church serves a new organization’s mission as a place where, in the minister’s words, “The church’s witness of outreach is grounded in her service to the larger community of neighbors in which she lives.” +
--
Laurie Petersen is a regular contributor to Chicago Architect, the official publication of AIA Chicago, from which this article was adapted.
Related Stories
| Jan 25, 2011
Bloomberg launches NYC Urban Tech Innovation Center
To promote the development and commercialization of green building technologies in New York City, Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg has launched the NYC Urban Technology Innovation Center. This initiative will connect academic institutions conducting underlying research, companies creating the associated products, and building owners who will use those technologies.
| Jan 25, 2011
Top 10 rules of green project finance
Since the bottom fell out of the economy, finding investors and financial institutions willing to fund building projects—sustainable or otherwise—has been close to impossible. Real estate finance prognosticators, however, indicate that 2011 will be a year to buy back into the real estate market.
| Jan 25, 2011
Chicago invented the skyscraper; can it pioneer sustainable-energy strategies as well?
Chicago’s skyline has always been a source of pride. And while few new buildings are currently going up, building owners have developed a plan to capitalize on the latest advances: Smart-grid technologies that will convert the city’s iconic skyline into what backers call a “virtual green generator” by retrofitting high-rise buildings and the existing electrical grid to a new hyper-connected intelligent-communications backbone.
| Jan 25, 2011
AIA reports: Hotels, retail to lead U.S. construction recovery
U.S. nonresidential construction activity will decline this year but recover in 2012, led by hotel and retail sectors, according to a twice-yearly forecast by the American Institute of Architects. Overall nonresidential construction spending is expected to fall by 2% this year before rising by 5% in 2012, adjusted for inflation. The projected decline marks a deteriorating outlook compared to the prior survey in July 2010, when a 2011 recovery was expected.
| Jan 25, 2011
Jester Jones Schifer Architects, Ltd. Joins GPD Group
GPD Group is excited to announce that Jester Jones Schifer Architects, a Marion-based architectural firm, has joined our firm, now enabling GPD Group to provide architectural services to the Central-Ohio market.
| Jan 21, 2011
Combination credit union and USO center earns LEED Silver
After the Army announced plans to expand Fort Bliss, in Texas, by up to 30,000 troops, FirstLight Federal Credit Union contracted NewGround (as CM) to build a new 16,000-sf facility, allocating 6,000 sf for a USO center with an Internet café, gaming stations, and theater.
| Jan 21, 2011
Manufacturing plant transformed into LEED Platinum Clif Bar headquarters
Clif Bar & Co.’s new 115,000-sf headquarters in Emeryville, Calif., is one of the first buildings in the state to meet the 2008 California Building Energy Efficiency Standards. The structure has the largest smart solar array in North America, which will provide nearly all of its electrical energy needs.
| Jan 21, 2011
Primate research facility at Duke improves life for lemurs
Dozens of lemurs have new homes in two new facilities at the Duke Lemur Center in Raleigh, N.C. The Releasable Building connects to a 69-acre fenced forest for free-ranging lemurs, while the Semi-Releasable Building is for lemurs with limited-range privileges.
| Jan 21, 2011
Harlem facility combines social services with retail, office space
Harlem is one of the first neighborhoods in New York City to combine retail with assisted living. The six-story, 50,000-sf building provides assisted living for residents with disabilities and a nonprofit group offering services to minority groups, plus retail and office space.