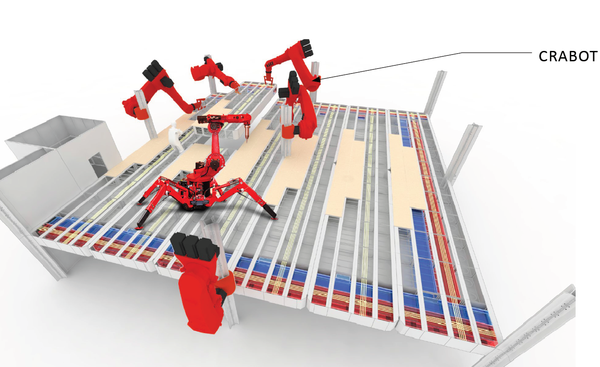
Google’s plans for its new headquarters in Mountain View, Calif., include using small cranes and robotic machines that are capable of reconfiguring interior modular spaces, as needs change, within hours.
According to its development application, the search-engine giant envisions a headquarters with four large structures, built on 3 million sf of land. Each would be scaled as an entire city block and draped with glass canopies. The first site, called The Landings, would start construction by 2020, with the other structures to be started within the following four years.
Each structure’s floors, walls, ceilings, and other interior elements would be attachable to and detachable from permanent steel frames, so that whole new workspaces could be formed and manipulated, not unlike moving around office furniture.

The Silicon Valley Business Journal reports that Google intends to install cranes and robots, known as “crabots,” within these buildings to lift and move around the modular components. The Business Journal could not ascertain whether the crabots are still on the drawing board or exist as practical tools. And Google, in its documents, isn’t revealing much, as it only suggests that a specialized crabot could be developed and manufactured by combining the latest crane and robot technology.
It’s worth remembering, though, that Google bought eight robotics companies in 2012 and 2013, including Boston Dynamics, which has designed research robots for the Pentagon. Google has also been testing self-driving cars since 2009.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Apr 15, 2016
Should architects learn to code?
Even if learning to code does not personally interest you, the growing demand for having these capabilities in an architectural business cannot be overlooked, writes computational design expert Nathan Miller.
Building Tech | Apr 12, 2016
Should we be worried about a tech slowdown?
Is the U.S. in an innovative funk, or is this just the calm before the storm?
BIM and Information Technology | Apr 8, 2016
Turner streamlines construction progress tracking using predictive visual data analytics
The construction giant teams with a computer science and engineering professor to develop a clever drone- and rover-based construction monitoring tool.
BIM and Information Technology | Apr 5, 2016
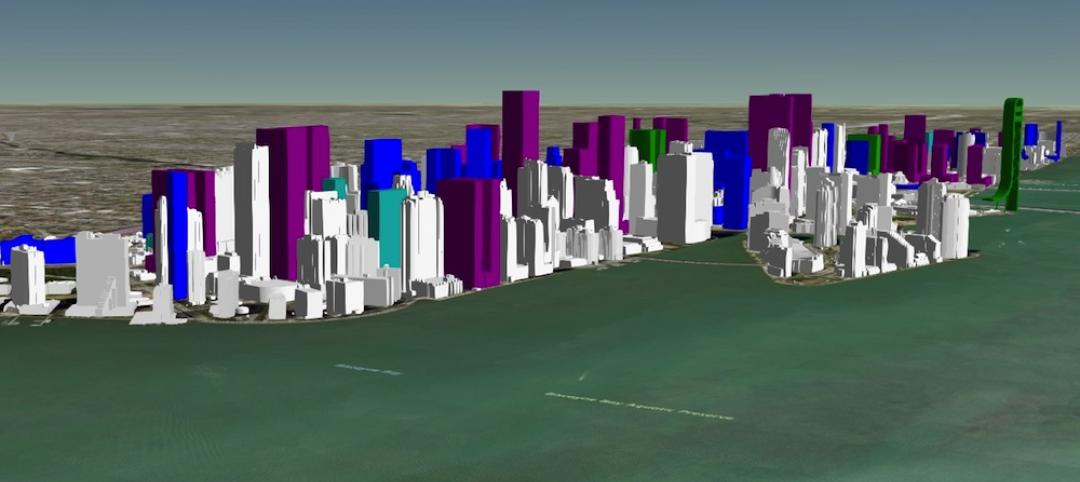
Interactive 3D map shows present and future Miami skyline
The Downtown Miami Interactive 3-D Skyline Map lets users see the status of every downtown office, retail, residential, and hotel project.
AEC Tech | Mar 31, 2016
Deep Learning + AI: How machines are becoming master problem solvers
Besides revolutionary changes to the world’s workforce, artificial intelligence could have a profound impact on the built environment and the AEC industry.
Big Data | Mar 28, 2016
Predictive analytics: How design firms can benefit from using data to find patterns, trends, and relationships
Branden Collingsworth, HDR’s new Director of Predictive Analytics, clarifies what his team does and how architecture projects can benefit from predictive analytics.
BIM and Information Technology | Mar 21, 2016
Latest tech devices simplify the leap from BIM to virtual reality
Faster conversion times and higher-quality graphics are enabling VR to make the jump from novelty to necessity in the AEC world.
AEC Tech | Mar 15, 2016
Two to tango: Project Tango isn’t just for entertainment, it also has a wide range of possibilities relating to the professional world
Making things like augmented reality, precise measurements of indoor spaces, and indoor wayfinding possible, Google’s Project Tango has all the makings to become a useful and ubiquitous tool in the AEC market.
BIM and Information Technology | Mar 14, 2016
Visual estimating, generative design, and component construction push the limits of BIM/VDC
DPR Construction, JE Dunn, and The Living advance the AEC industry with three clever tech solutions.
Drones | Mar 9, 2016
A new image-capturing platform mediates drone and cloud technologies
3DRobotics, Autodesk, and Sony launch Site Scan to speed the process of making models from field data.