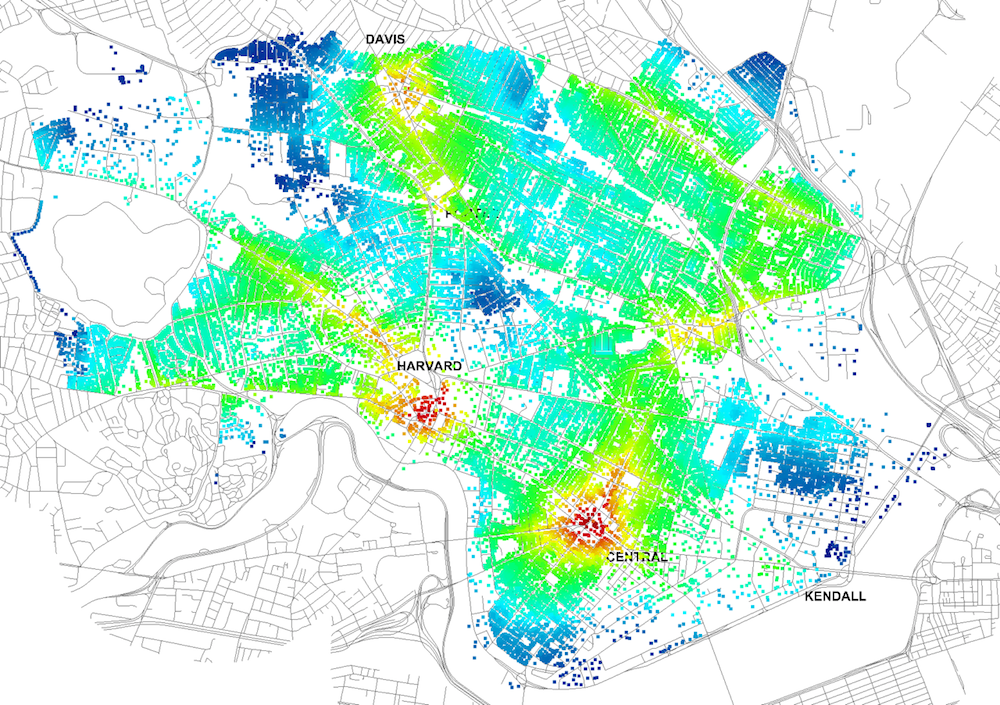
Four years ago, Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s City Form Lab launched Urban Network Analysis (UNA), a city-modeling software that facilitates a mathematical analysis of relationships among elements in a complex system, like a city. The unique feature of UNA is that it incorporates activities within buildings into its analysis.
This toolbox has been popular with planners and geographers, but it requires ArcGIS10 software with an ArcGIS Network Analysis Extension.
In April, City Form Lab expanded this software’s utility by introducing UNA for Rhino 3D, a modeling software for architects, engineers, and designers.
“Our toolbox helps planners and architects analyze these relationships and quantify how intensely different routes are likely to be utilized, how visible or connected public spaces are, or how conveniently one can get from one space to another,” says Andres Sevtsuk, the principal investigator at City Form Lab and developer of the UNA tool.
In layman’s terms, the software predicts where people are likely to go once they’ve decided upon an activity, like, say, going to an ATM machine or a park. The software provides users with some idea about which ATM or park that would be. As for movements to and within buildings, UNA takes into account employee head count, a building’s value, the surrounding population, and so forth.
This app’s toolbox also computes how urban design can affect—or even dictate—pedestrian movement. Sevtsuk notes, too, that the software can be scaled to account for the diversity of movement in different cities and towns.
Sevtsuk is encouraged by the sheer amount of spatial data available about urban areas, particularly in the U.S., where “you can go to any sizable city website and download data that is necessary to calibrate any of these models.” He’s confident that this software can be used to predict movement in public or semi-public spaces such as building lobbies or shopping centers.
Related Stories
| Nov 16, 2010
Calculating office building performance? Yep, there’s an app for that
123 Zero build is a free tool for calculating the performance of a market-ready carbon-neutral office building design. The app estimates the discounted payback for constructing a zero emissions office building in any U.S. location, including the investment needed for photovoltaics to offset annual carbon emissions, payback calculations, estimated first costs for a highly energy efficient building, photovoltaic costs, discount rates, and user-specified fuel escalation rates.
| Nov 9, 2010
12 incredible objects being made with 3D printers today
BD+C has reported on how 3D printers are attracting the attention of AEC firms. Now you can see how other creative types are utilizing this fascinating printing technology. Among the printed items: King Tut’s remains, designer shoes, and the world’s smallest Rubik’s Cube.
| Nov 5, 2010
New Millennium’s Gary Heasley on BIM, LEED, and the nonresidential market
Gary Heasley, president of New Millennium Building Systems, Fort Wayne, Ind., and EVP of its parent company, Steel Dynamics, Inc., tells BD+C’s Robert Cassidy about the Steel Joist Manufacturer’s westward expansion, its push to create BIM tools for its products, LEED, and the outlook for the nonresidential construction market.
| Nov 2, 2010
Energy Analysis No Longer a Luxury
Back in the halcyon days of 2006, energy analysis of building design and performance was a luxury. Sure, many forward-thinking AEC firms ran their designs through services such as Autodesk’s Green Building Studio and IES’s Virtual Environment, and some facility managers used Honeywell’s Energy Manager and other monitoring software. Today, however, knowing exactly how much energy your building will produce and use is survival of the fittest as energy costs and green design requirements demand precision.
| Oct 13, 2010
Test run on the HP Z200 SFF Good Value in a Small Package
Contributing Editor Jeff Yoders tests a new small-form factor, workstation-class desktop in Hewlett-Packard’s line that combines performance of its minitower machine with a smaller chassis and a lower price.
| Oct 13, 2010
Prefab Trailblazer
The $137 million, 12-story, 500,000-sf Miami Valley Hospital cardiac center, Dayton, Ohio, is the first major hospital project in the U.S. to have made extensive use of prefabricated components in its design and construction.