Societies continue to move toward megacity cultures, lifestyles, and economies that are becoming more vital, in some cases, than the countries that spawn them.
One result of this trend has been a growing tendency among owners, developers, and their Building Teams to package smaller and multiple commercial projects into large, single megaprojects whose construction costs exceed $1 billion, in spite of such projects’ historically erratic success rates and shortcomings.
“Speed to market has become critical for owners. In addition, construction companies are getting larger, making it more feasible for them to handle bigger projects,” explains Ron Magnus, a founding Principal with the market research firm FMI, which has just come out with a new study titled “Megaprojects: Changing the Conversation.”
FMI’s report, authored by its content director Sabine Hoover, indicates that at least 320 megaprojects have been awarded in the U.S. alone since 2012—at an aggregate investment valued at over $700 billion.
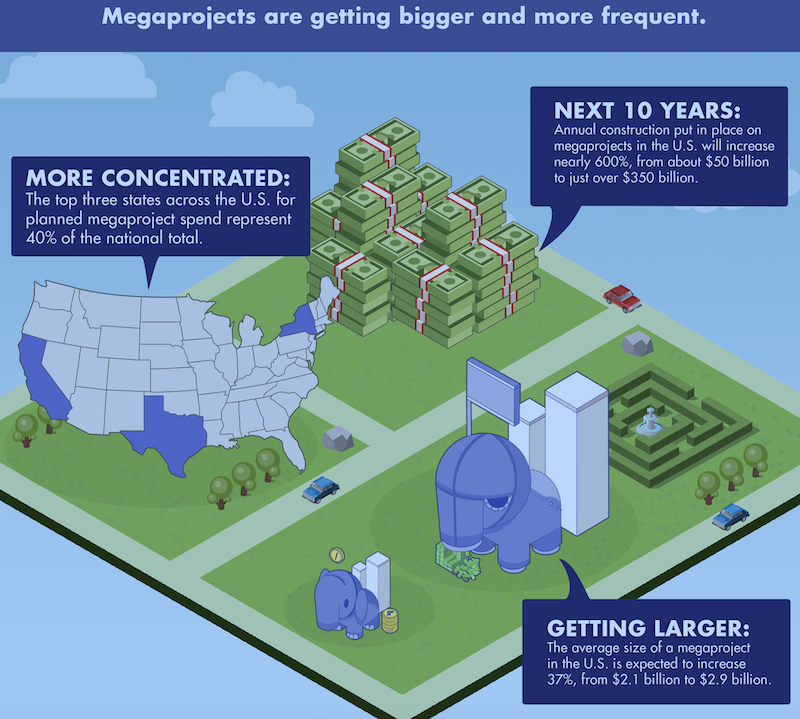
Additionally, more than 670 megaprojects are being planned, a future investment opportunity likely to reach $2 trillion. Most of these planned megaprojects are expected to be built in the South and West, with three states accounting for 40% of the total starts value (New York, 15%; California, 15%; and Texas, 10%).
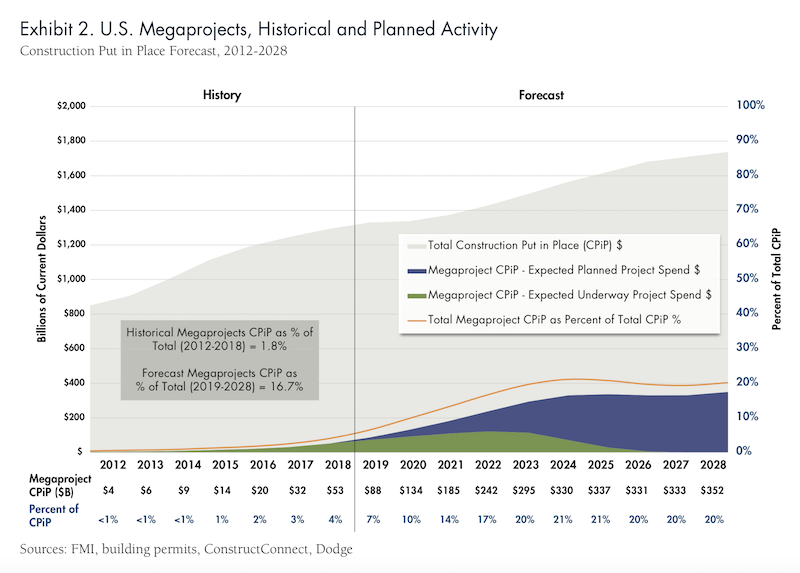
FMI predicts that megaprojects could account for 20% or more of construction spending within the next five years. Chart: FMI
Megaprojects have been expanding in number and value. Between 2013 and 2018, the annual value of U.S. megaproject starts increased from 3% to approximately 33% of all U.S. construction project starts. FMI predicts that, over the next decade, annual construction put in place on megaprojects will explode by nearly 600% to $350 billion.
Measured another way, megaproject construction put in place accounted for only 1.8% of total CPiP between 2012 and 2018. FMI estimates that within the next decade—and possibly within the next five or six years—annual megaproject spending could equal around 20% of total construction spending.
While FMI acknowledges that industrial and infrastructure starts have accounted for the bulk of megaproject starts (61% in 2018), it also sees more evidence of this trend in nonresidential building.
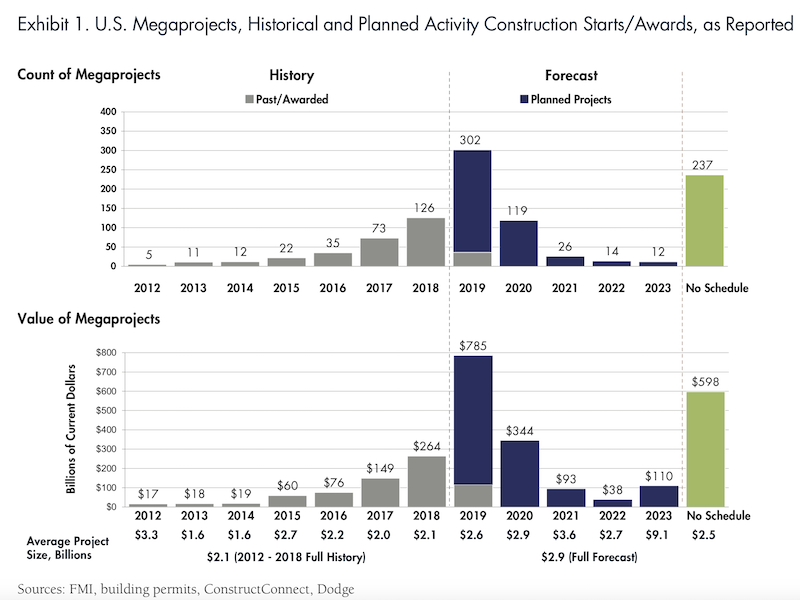
The value of megaproject starts could rise at an especially brisk clip over the next two years. Chart: FMI
The big question, though, is whether the industry is ready to meet this demand. Part of FMI’s research for this report included input from a roundtable of 22 stakeholders—AEC firms, owners, academics—that have engaged megaprojects in the past. From that discussion FMI gleaned five key success factors:
•Trust. Stakeholders on successful megaprojects invest a lot of time upfront in building trust through off-site meetings, getting to know each other on a personal basis. “Trust is the cornerstone, the basic building block,” says Jim Whitaker, FAIA, FDBIA, Principal and Senior Vice President with HKS Inc.
•Culture of Cohesion and Collaboration. DPR Construction on one megaproject spent two weeks with the owner and architect charting the work and setting up its organizational structure. By doing so, the team reduced that project’s budget by $200 million without yielding functionality, square footage, or quality.
Keith Molenaar, associate dean for research at the University of Colorado Boulder, in collaboration with the Pankow Foundation, has studied more than 200 different building projects and found that early collaboration was key to success. The delivery method chosen, on the other hand, had far less impact.
•Transparent and authentic leadership. Effective megaproject leaders, says FMI, are experts in developing a team environment that fosters emotional engagement, shared purpose and accountability.
•Nimble and autonomous teams. Successful megaproject teams are getting away from centralized management and are setting up smaller, more nimble project teams that can move quickly. “Like the platoon model for marines, these teams enjoy a certain degree of autonomy and are empowered to make decisions without approval from the top, and at each decision point,” says FMI.
•Educated and experienced owners. The report quotes Darin Daskarolis, senior director of Global Construction-Data Centers at Facebook, who notes that since commercial construction is largely a relationship-based business, “we knew we had to form strong bonds with our contractors to develop a common and realistic view of the challenges ahead. This common view informed sensible budgets and guided strategic staffing decisions.
The global strategist Parag Khanna sees a world that is becoming more connected by buildings and structures. So where global defense budgets and military spending total about $2 trillion per year, infrastructure spending is expected to increase from $3 trillion today to $9 trillion annually by 2030.
For the U.S., FMI forecasts that half of all megaproject spending over the next three to five years could occur in just 20 metros, and just five of these markets—New York, Los Angeles, Dallas, Houston, and Washington D.C.—will account for one-fifth of total construction in the country. But FMI also ends its report with a cautionary warning for the construction industry. “We have no choice but to completely change our mindsets. Should megaprojects continue to fail just as their spending is expected to reach new heights, the impacts could be devastating to the framework of the E&C industry.”
Related Stories
Industry Research | Dec 28, 2022
Following a strong year, design and construction firms view 2023 cautiously
The economy and inflation are the biggest concerns for U.S. architecture, construction, and engineering firms in 2023, according to a recent survey of AEC professionals by the editors of Building Design+Construction.
Self-Storage Facilities | Dec 16, 2022
Self-storage development booms in high multifamily construction areas
A 2022 RentCafe analysis finds that self-storage units swelled in conjunction with metros’ growth in apartment complexes.
Market Data | Dec 13, 2022
Contractors' backlog of work reaches three-year high
U.S. construction firms have, on average, 9.2 months of work in the pipeline, according to ABC's latest Construction Backlog Indicator.
Contractors | Dec 6, 2022
Slow payments cost the construction industry $208 billion in 2022
The cost of floating payments for wages and invoices represents $208 billion in excess cost to the construction industry, a 53% increase from 2021, according to a survey by Rabbet, a provider of construction finance software.
Mass Timber | Dec 1, 2022
Cross laminated timber market forecast to more than triple by end of decade
Cross laminated timber (CLT) is gaining acceptance as an eco-friendly building material, a trend that will propel its growth through the end of the 2020s. The CLT market is projected to more than triple from $1.11 billion in 2021 to $3.72 billion by 2030, according to a report from Polaris Market Research.
Market Data | Nov 15, 2022
Construction demand will be a double-edged sword in 2023
Skanska’s latest forecast sees shorter lead times and receding inflation, but the industry isn’t out of the woods yet.
Reconstruction & Renovation | Nov 8, 2022
Renovation work outpaces new construction for first time in two decades
Renovations of older buildings in U.S. cities recently hit a record high as reflected in architecture firm billings, according to the American Institute of Architects (AIA).
Market Data | Nov 3, 2022
Building material prices have become the calm in America’s economic storm
Linesight’s latest quarterly report predicts stability (mostly) through the first half of 2023
Building Team | Nov 1, 2022
Nonresidential construction spending increases slightly in September, says ABC
National nonresidential construction spending was up by 0.5% in September, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of data published today by the U.S. Census Bureau.
Hotel Facilities | Oct 31, 2022
These three hoteliers make up two-thirds of all new hotel development in the U.S.
With a combined 3,523 projects and 400,490 rooms in the pipeline, Marriott, Hilton, and InterContinental dominate the U.S. hotel construction sector.