In the race to develop tech tools to make meaningful efficiency gains in the complex, often-messy commercial construction process, the R&D team at Turner Construction Company has remained keenly focused on one goal: simplicity.
New tools and processes must be easy to execute, by almost anyone in the field, and take advantage of readily accessible data—photos, video—to solve real-world problems. Leave the mind-bogglingly complicated data analysis work to computer scientists like Mani Golparvar-Fard.
Turner’s multi-year partnership with Golparvar-Fard, an Assistant Professor of Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and a former Turner field engineer, has led to the development of breakthrough analytics tools that use structure from motion (SfM) algorithms to make sense of a job site, in real time, using high-definition photos and video.
Now, the technology is being piloted in the field, on the Sacramento Kings’ new 17,500-seat Golden 1 Center project, currently under construction in downtown Sacramento, Calif.
“Over the past 10 years, we’ve built these amazing 4D and 5D BIM models to help us plan our large commercial construction projects,” says Lincoln Wood, Regional Manager, Virtual Design and Construction, based in Turner’s Oakland, Calif., office. “But we still face the challenge of knowing what’s happening out in the field in real time.”
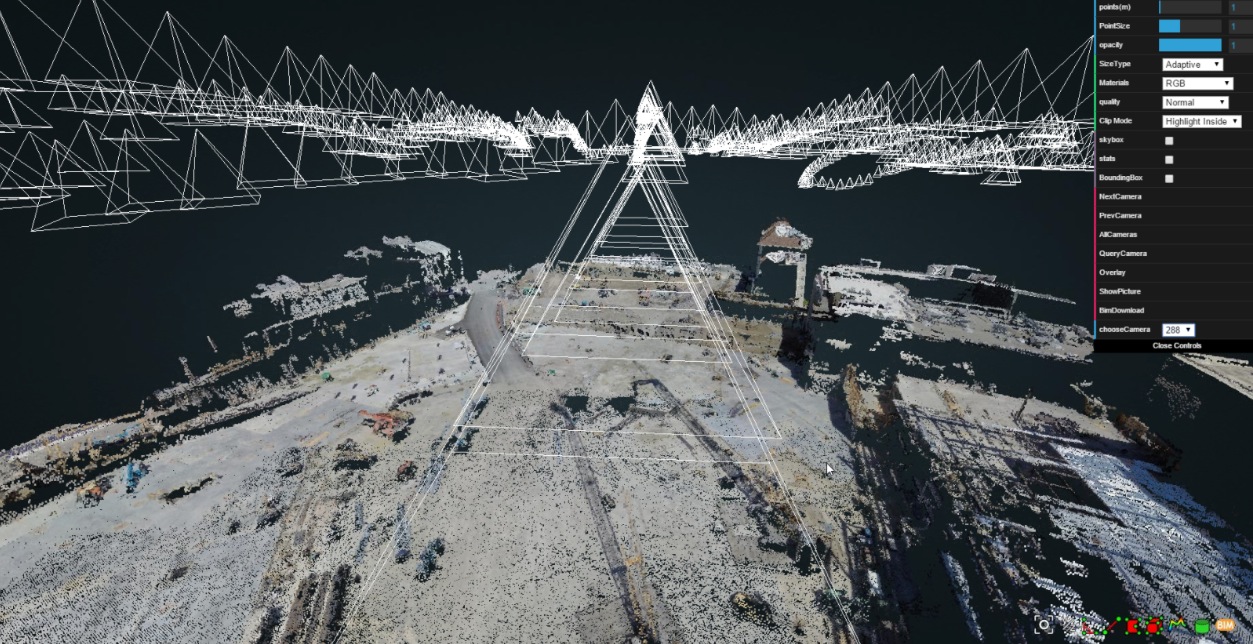
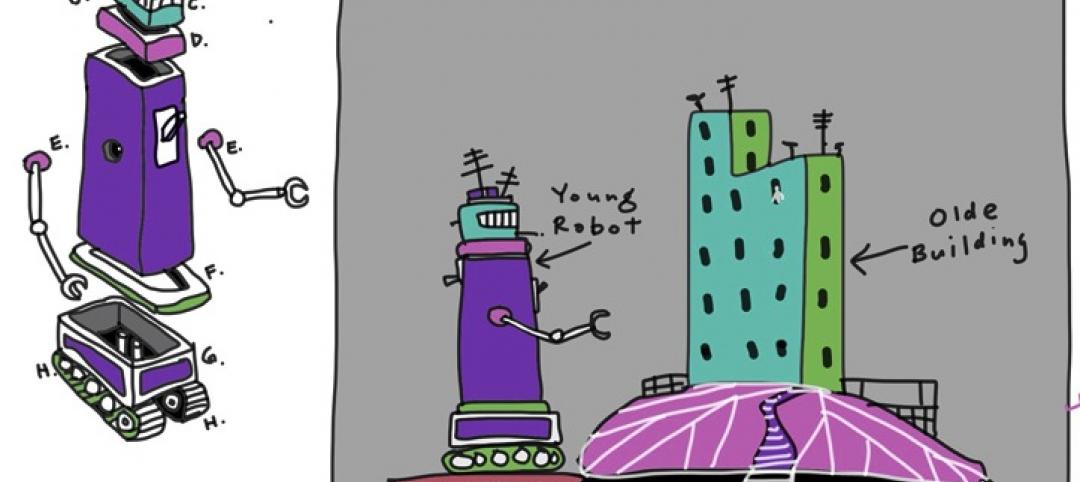
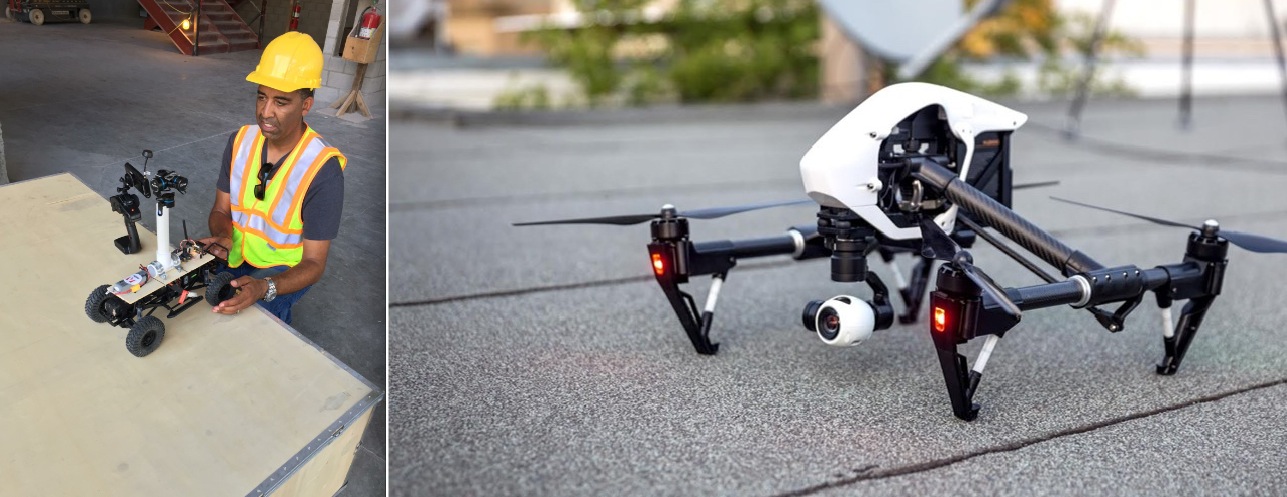 The initial phase of the pilot project involves using aerial drones (right) to document the construction progress. Once the structure goes up, the team will utilize a custom-built rover (left), as well as project engineers, to capture images and video. “The goal is to do this every day,” says Lincoln Wood, Regional Manager, Virtual Design and Construction, with Turner. “With the pilot, we have it down to a week, in time for the weekly work plan.” Courtesy Turner. Click image to enlarge.
The initial phase of the pilot project involves using aerial drones (right) to document the construction progress. Once the structure goes up, the team will utilize a custom-built rover (left), as well as project engineers, to capture images and video. “The goal is to do this every day,” says Lincoln Wood, Regional Manager, Virtual Design and Construction, with Turner. “With the pilot, we have it down to a week, in time for the weekly work plan.” Courtesy Turner. Click image to enlarge.
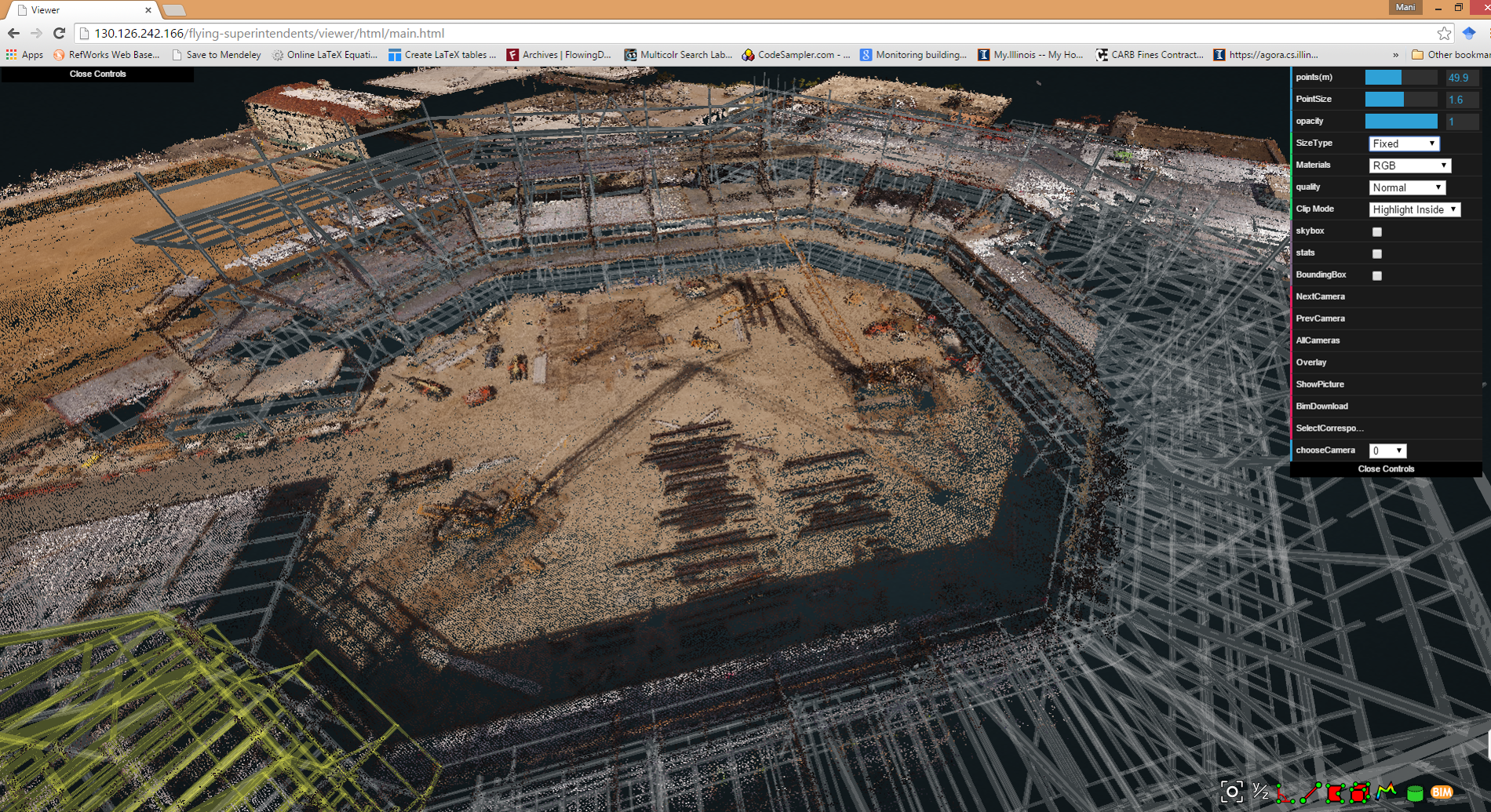
Using proprietary predictive visual data analytics software developed by Golparvar-Fard, the Building Team for the Golden 1 Center project is conducting near-real-time construction progress monitoring using high-resolution photos and video. The initial phase involves reality capture with an aerial drone. As the arena structure goes up, the team will also rely on a camera-equipped land rover (which will be programmed to navigate the interior spaces) and project engineers, who will use smartphones and tablets to gather photos and video.
Once collected, the visual data is stitched together using the SfM algorithm to form a point cloud. The point cloud is then overlaid atop the project’s 4D BIM model to compare and contrast what is happening in the field versus the intended result in the BIM model. (The point cloud creation and BIM overlay work occurs overnight.)
The resulting report is a color-coded 3D visual production model that provides the Building Team with a snapshot of the construction progress, and, most importantly, the areas of the job site that are at risk of falling behind schedule.
By streamlining construction progress monitoring, and providing timely reporting, Wood says the project team has a much deeper level of transparency and improved communication.
“A really good superintendent can see everything in their head; they don’t need a BIM model—it’s in their brain,” says Wood. “Unfortunately, the whole project team does not have that brain. This is a great way for the entire team to see where we are and show what we need to do in order to get back on track and improve the schedule.”
Based on the results of the job site scan and analysis, custom reports are generated for each member of the project management team, including key subcontractors, for the weekly planning meetings.
“The goal is to do this every day,” says Wood. “With the pilot, we have it down to a week, in time for the weekly work plan. We give this report to the team, showing the problem areas and the top-10 risks to the job site. It allows us to visualize and mitigate potential risks to our schedule before they happen.”
Wood says that the enhanced construction progress data may eventually be used for faster and more accurate subcontractor payments, “by removing a lot of the administrative work that happens by having to go back and forth between the job site and the office.”
It also equips the Building Team and owner with “smarter” and more-comprehensive visual documentation of the construction work, by automatically organizing and cataloging thousands of photos and video clips.
“With most jobs, the project engineers are asked to take a bunch of photographs when they’re out in the field, if they have time after their RFIs and submittals are completed for the day,” says Wood. Those images then must be uploaded to the project server, where they are stored with a random code and remain largely unorganized.
“Because our images are stitched together to create a point cloud, we have a better sense of a record of time,” says Wood.
Related Stories
| Dec 1, 2014
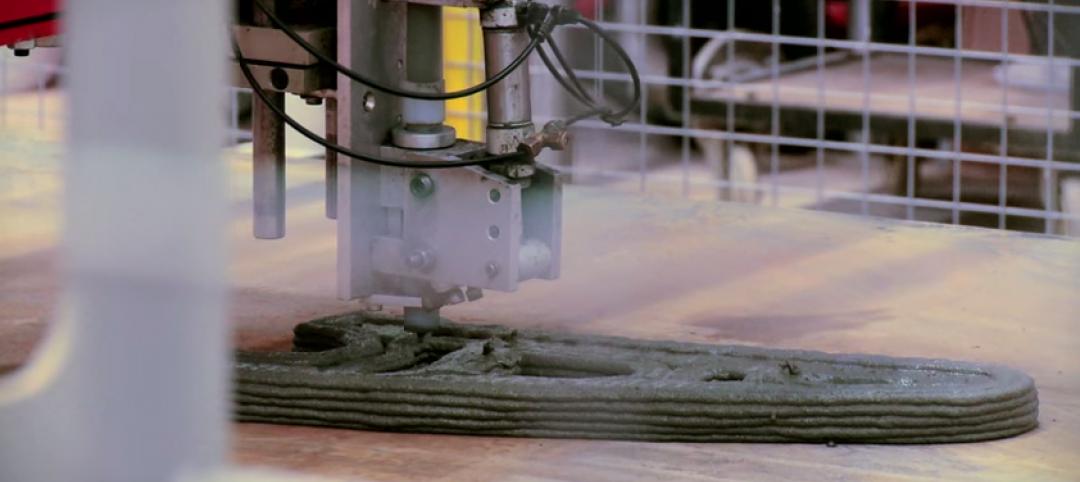
Skanska, Foster + Partners team up on development of first commercial 3D concrete printing robot
Skanska will participate in an 18-month program with a consortium of partners to develop a robot capable of printing complex structural components with concrete.
| Nov 26, 2014
How the 'maker culture' brings the power of design to life
Most people affiliate the maker culture with metal working, welding, ceramics, glass blowing, painting, and soldering. But it also includes coding and online content creation, writes Gensler’s Douglas Wittnebel.
Sponsored | | Nov 26, 2014
Virtual reality in 3D models, iPhone thermal imaging: Inside one very cool tech toybox
A little over a year ago, I embarked on a search to find individuals in the AEC space who were putting new hardware to work in the field.
| Nov 18, 2014
New tool helps developers, contractors identify geographic risk for construction
The new interactive tool from Aon Risk Solutions provides real-time updates pertaining to the risk climate of municipalities across the U.S.
Sponsored | | Nov 12, 2014
Williams Scotsman plugs into the jobsite
Many of our customers conduct important business from their temporary modular jobsite office and most require access to technology to get their job done effectively and efficiently. SPONSORED CONTENT
| Nov 5, 2014
AEC firms leverage custom scripts to bridge the ‘BIM language gap'
Without a common language linking BIM/VDC software platforms, firms seek out interoperability solutions to assist with the data transfer between design tools.
| Nov 3, 2014
How facility owners can make the most of BIM
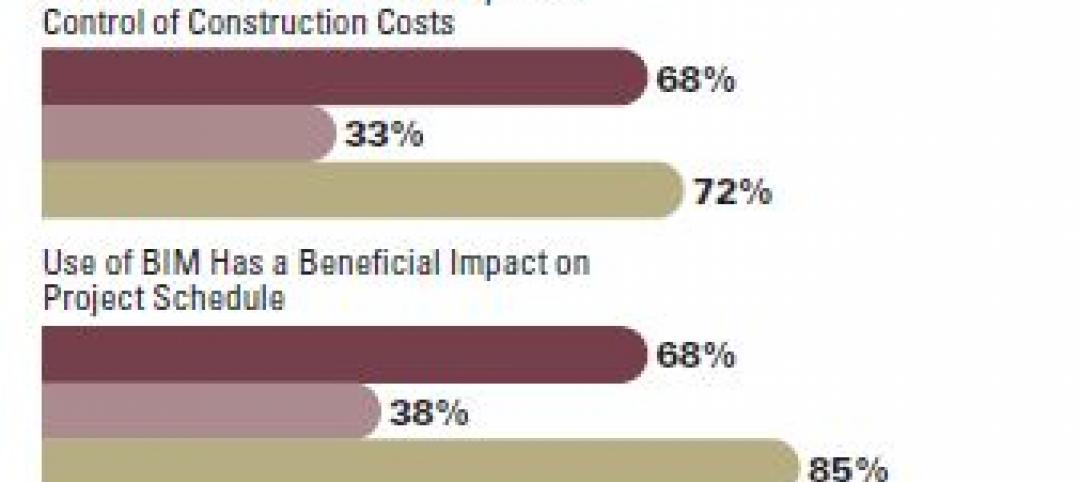
More and more facility owners are seeing the benefits that building information modeling can bring to their projects, according to a new McGraw Hill Construction SmartMarket Report, “The Business Value of BIM for Owners.”
| Oct 15, 2014
Drones may soon assist code inspectors for construction in the UAE
The United Arab Emirates’ Ministry of Labour announced that they will start using drones to help inspectors record when construction sites are breaking laws.
| Oct 13, 2014
Debunking the 5 myths of health data and sustainable design
The path to more extensive use of health data in green building is blocked by certain myths that have to be debunked before such data can be successfully incorporated into the project delivery process.
Sponsored | | Oct 13, 2014
William Duff Architects successfully increases revenue while decreasing accounts receivable workload
William Duff Architects has seen immediate benefits to their business since the implementation of ArchiOffice. Within a couple of months, they increased billable staff utilization and reduced accounts receivable workload. SPONSORED CONTENT