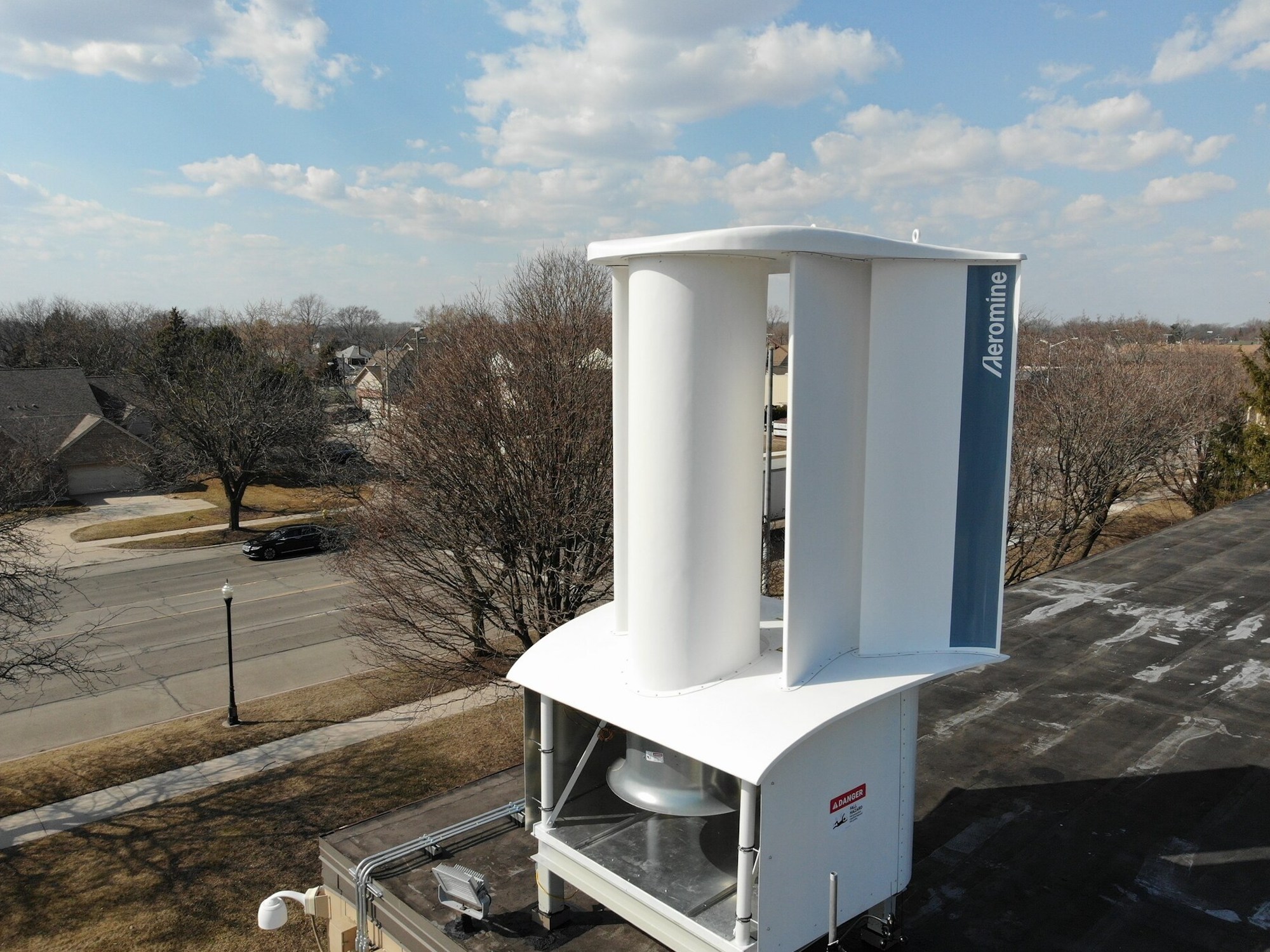
Typically, “wind energy” conjures up images of massive turbines in large fields or out at sea. Aeromine Technologies has created a bladeless wind energy system that sits on the rooftops of commercial properties and provides onsite renewable energy. The motionless system integrates with a building’s existing electrical and rooftop solar systems.
In January, AEC Angels, an investment platform focused on emerging technologies in the architecture, engineering, and construction sectors, announced that it has endorsed Aeromine and that AEC Angels member Thornton Tomasetti has invested in the Houston-based company. AEC Angels is an alliance of industry veterans that evaluate and invest in early-stage companies with promising technological advances. Its members also include STO Building Group, Syska Hennessy, and SHoP Architects.
“Aeromine’s proprietary and innovative technology makes the promise of bringing the performance of wind energy to the built environment a reality that can increase on site generation 100-200% for any given project when paired with solar and battery storage,” Grant McCullagh, director at Thornton Tomasetti and AEC Angels’ managing director, said in a statement.
Building-integrated wind turbine with zero external moving parts
Aeromine has no external moving parts and no vibration. Like airfoils on a race car, the technology captures and amplifies a building’s airflow. Needing 10% of the roof space used by solar panels, the stationary and silent Aeromine unit can generate energy at any time and in any weather. Aeromine systems typically comprise 20-40 units on a building’s edge, facing the predominant wind direction.
Aeromine Technologies says its system is up to 50% more productive than other renewable energy alternatives. Combining Aeromine with rooftop solar can generate up to 100% of a building’s onsite energy needs, while reducing the need for energy storage.
Companies piloting Aeromine’s technology include BASF Corporation, which is testing the wind energy system at its manufacturing plant in Wyandotte, Mich.
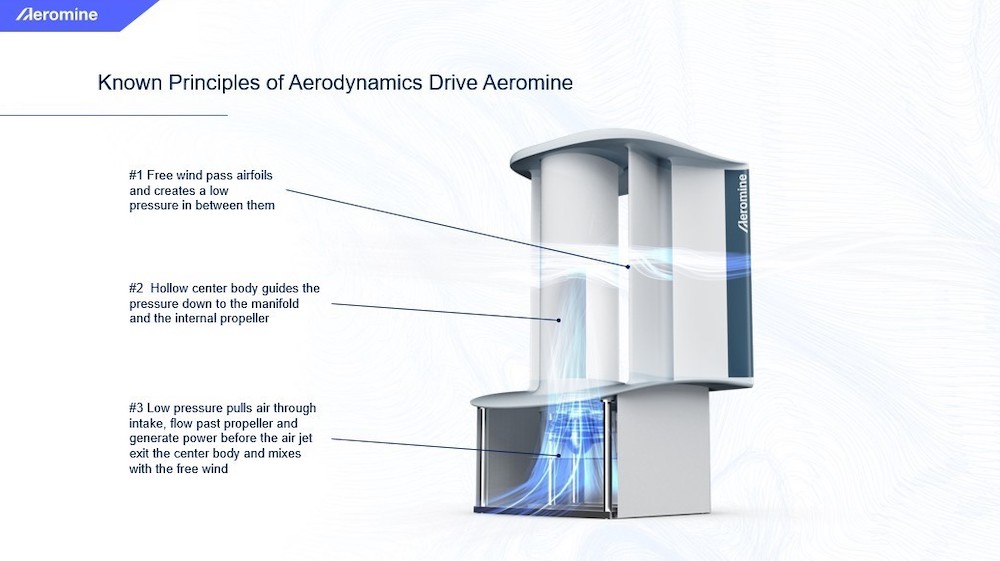
Here is how the bladeless wind energy system works:
Related Stories
Sustainability | Apr 4, 2017
Six connected CLT towers create an urban forest in India
The mixed-use towers would each rise 36 stories into the sky and connect via rooftop skybridges.
Urban Planning | Apr 3, 2017
Capturing the waterfront draw
People seem to experience a gravitation toward the water’s edge acutely and we traverse concrete and asphalt just to gaze out over an open expanse or to dip our toes in the blue stuff.
Mixed-Use | Mar 27, 2017
The Plant brings terrace-to-table living to Toronto
Curated Properties and Windmill Developments have teamed up to create a mixed-use building with food as the crux of the project.
Sustainability | Feb 28, 2017
Workplace wellbeing
Organizations are starting to realize that there are benefits to addressing employee wellbeing.
Sustainability | Feb 20, 2017
‘Forest cities’ could help solve China’s air pollution problem
The architect behind China’s first vertical forest skyscraper has bigger plans for entire cities filled with vertical forests.
Green | Feb 6, 2017
A to Z: Seoul’s elevated park features 24,000 alphabetized plants
The plants will represent 250 species found in South Korea.
Green | Feb 3, 2017
Nanjing Green Towers will be Asia’s first vertical forest
The project will be covered in 1,100 trees and 2,500 cascading plants and shrubs.
Sustainability | Jan 27, 2017
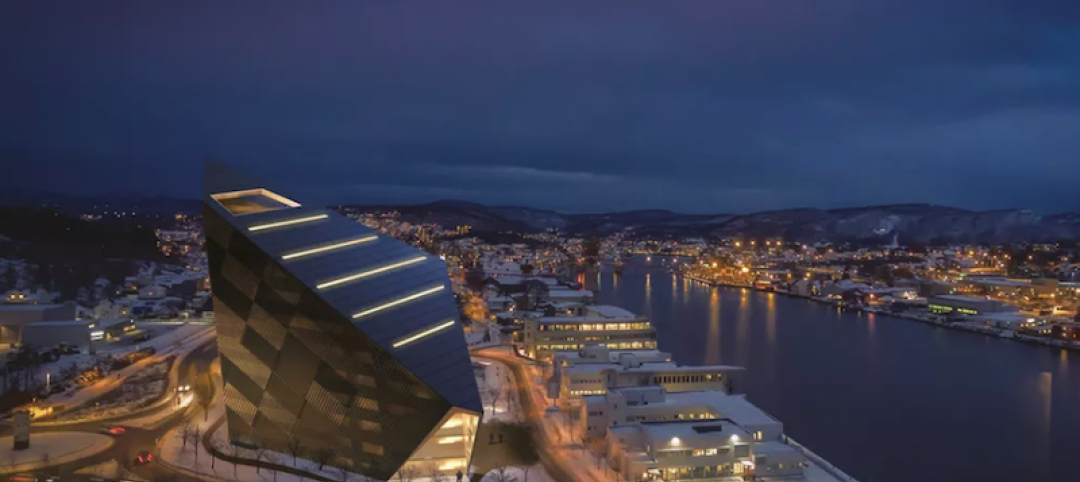
An office building proposed for Norway would generate more power than it uses
Over it’s 60-year lifespan, the power generated form the project would cover the energy cost of construction, production, and material transportation.
Sustainability | Jan 24, 2017
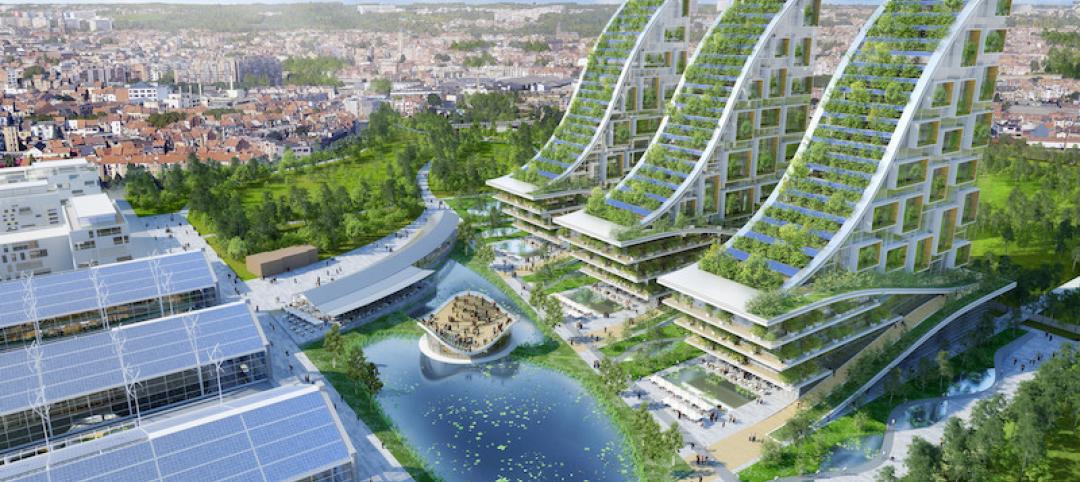
From an industrial park to an eco-neighborhood in Brussels, Belgium
At the heart of Vincent Callebaut Architectures’ eco-neighborhood will be three 100-meter-tall Vertical Forests.
Sustainability | Jan 19, 2017
How NYC is slashing 80% of greenhouse gas emissions by 2050
To help one of the most complex cities in the world develop an actionable strategy to meet visionary GHG reduction goals, we focused on strategies for deep carbon reductions for the city’s entire building stock, which constitutes 73% of citywide emissions, writes HDR's Jennifer Bienemann.

















