The world’s forests absorb an estimated 16 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide annually, or about double the 8.1 billion metric tons of CO2 that forests emit each year, according to research published earlier this year by Nature Climate Change.
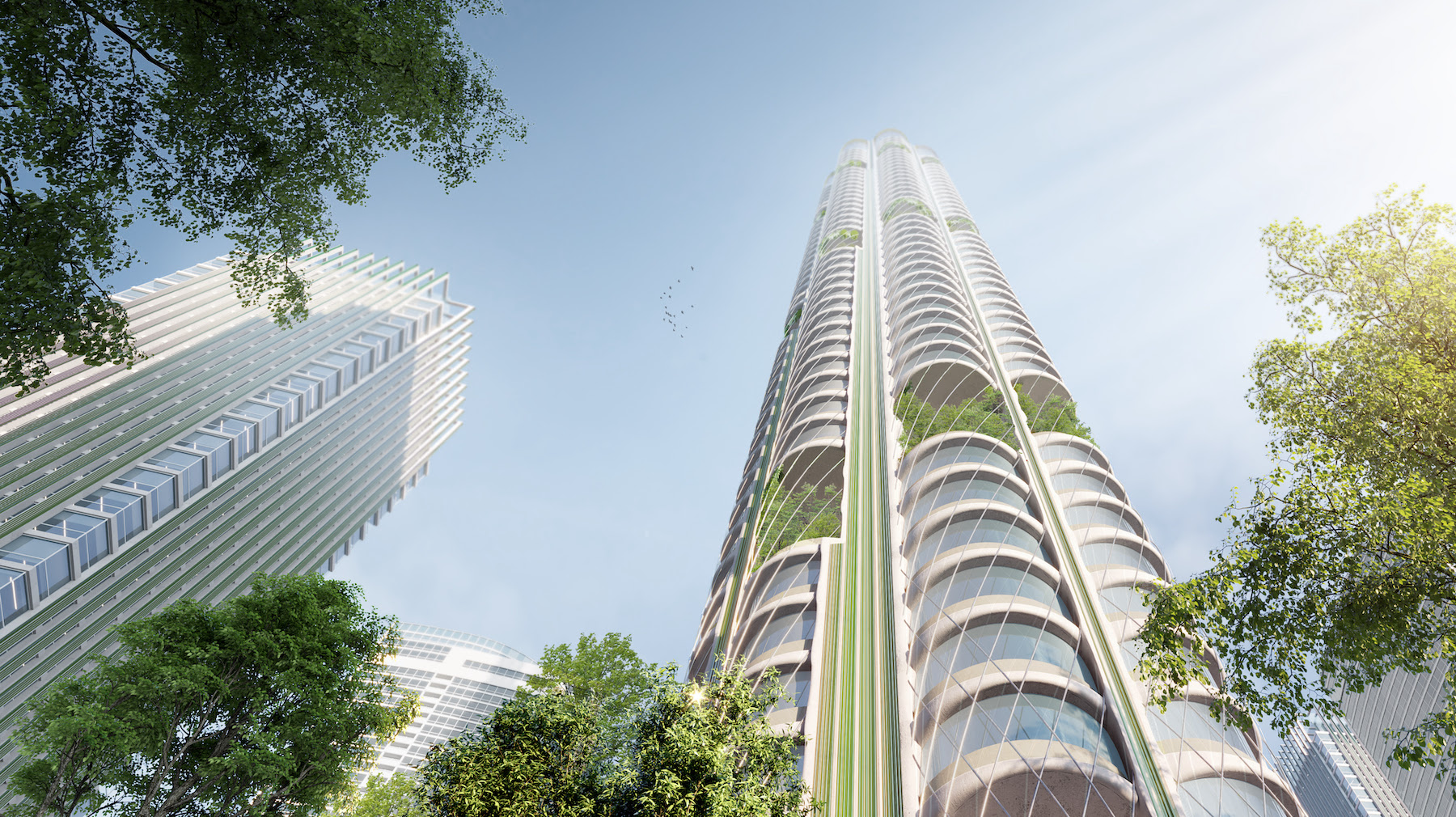
Could buildings—which generate, directly or indirectly, nearly two-fifths of CO2 emissions—act like trees to capture and absorb carbon and keep the air pure? The architecture, engineering, and urban planning firm Skidmore, Owings & Merrill envisions that provocative suggestion in a concept it calls Urban Sequoia, which SOM presented during COP26, the 2021 UNN Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, Scotland.
SOM pitched its concept at a time when urban population growth rates are dictating the need for an estimated additional 2.48 trillion sf of new buildings by 2060.
How would buildings absorb more carbon than they leak out? By designing and building them specifically to sequester emissions, says Chris Cooper, an SOM Partner. Kent Jackson, another SOM Partner who presented Urban Sequoia at COP26, adds that this concept could be applied and adapted for any metro area in the world, and to all sizes and types of buildings.
IT’S ALL ABOUT THE MATERIALS
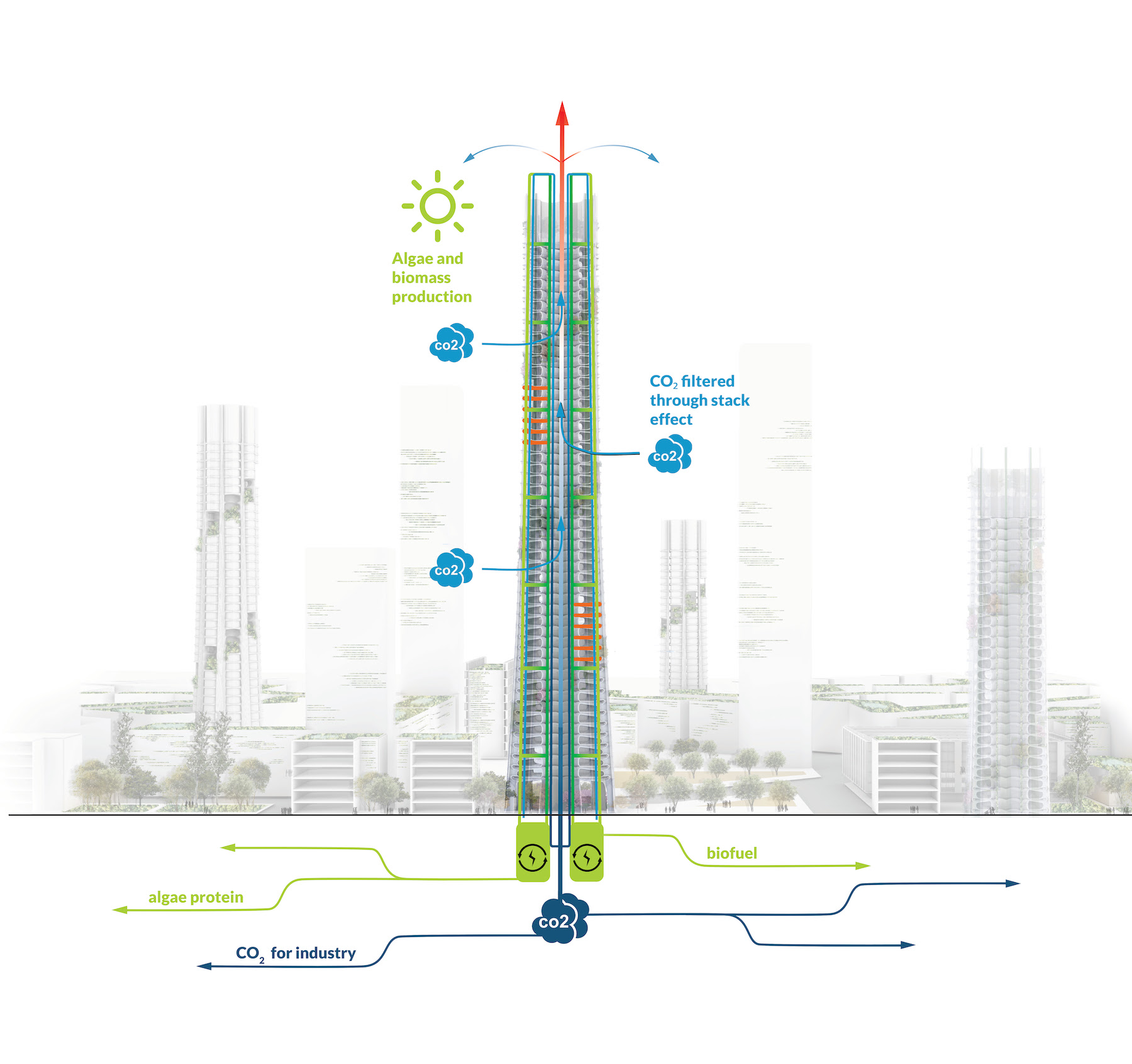
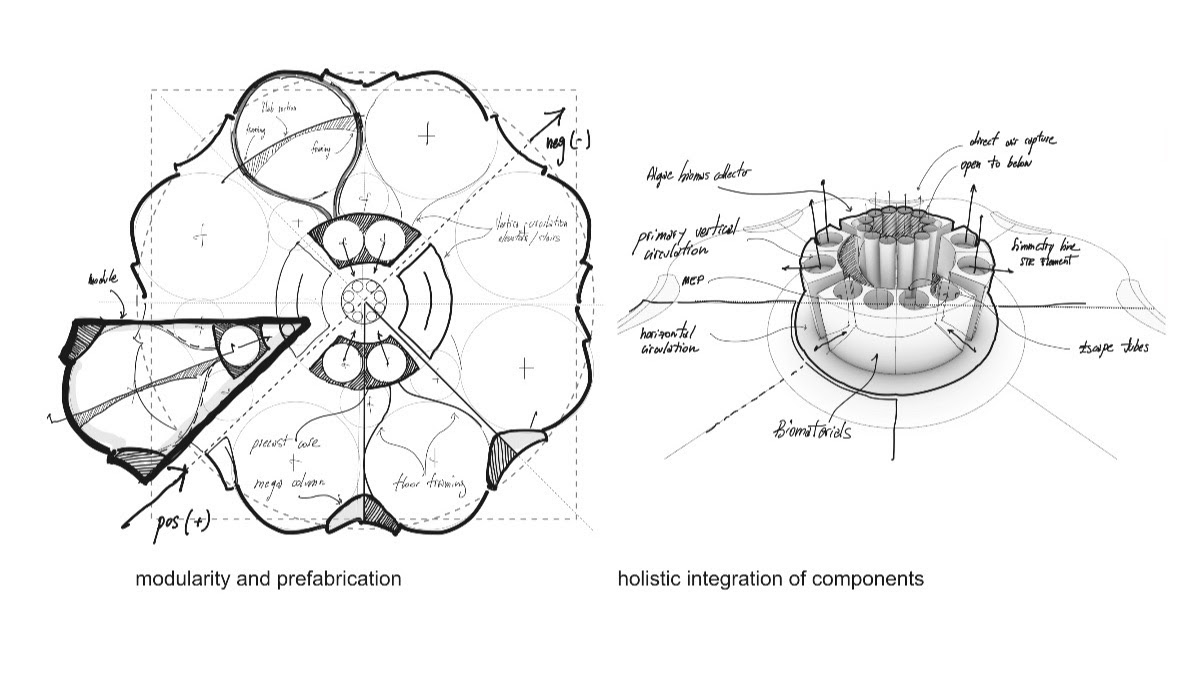
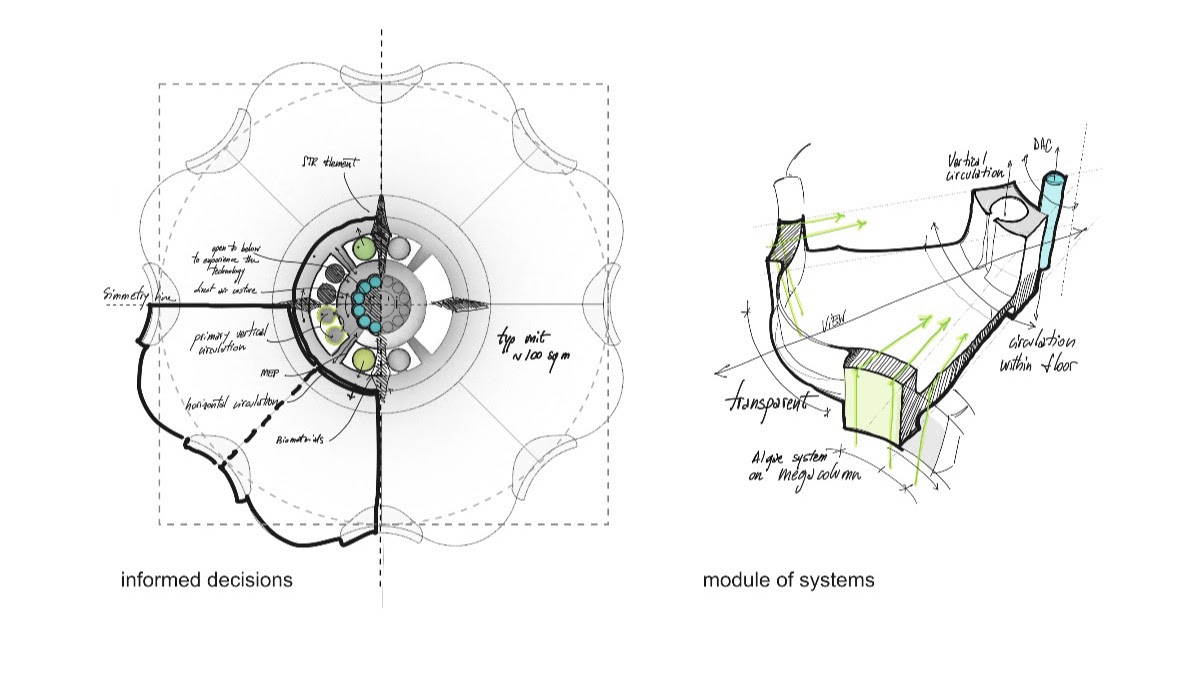
Urban Sequoia is an amalgam of the latest thinking about sustainable design coupled with emerging technologies. Carbon reductions can be achieved, SOM posits, by “holistically” optimizing building design, minimizing materials, and integrating biomaterials and advanced biomass.
To illustrate its concept, SOM’s prototype design is a high-rise building that, theoretically, could sequester up to 1,000 tons of carbon annually, or the absorption equivalent of 48,500 trees. The right combination of nature-based or environmentally friendlier materials—that might include hempcrete, bio-brick, timber, and so forth—could reduce the carbon impact of construction by anywhere from 50 to 95 percent compared to buildings made primarily with steel and concrete.
Over a 60-year lifespan, this prototype building would absorb up to 400 percent more CO2 than it would have emitted during construction, states SOM (which is a little vague about what “industrial applications” the captured carbon would be used for). And the use of bio-materials could turn the building into a biofuel source that would bring the building’s operations beyond net zero.
 The goal, in essence, is to turn cities into carbon sinks. SOM contends that if every city around the world built Urban Sequoias, the built environment could remove up to 1.6 billion tons of carbon from the air every year. Such a strategy might also include converting urban hardscapes into gardens, designing intense carbon-absorbing landscapes, and retrofitting streets with additional carbon-capturing technology, former grey infrastructure can sequester up to 120 tons of carbon per square kilometer (0.38 miles). When replicating these strategies in parks and other greenspaces, up to 300 tons per square kilometer of carbon could be saved annually.
The goal, in essence, is to turn cities into carbon sinks. SOM contends that if every city around the world built Urban Sequoias, the built environment could remove up to 1.6 billion tons of carbon from the air every year. Such a strategy might also include converting urban hardscapes into gardens, designing intense carbon-absorbing landscapes, and retrofitting streets with additional carbon-capturing technology, former grey infrastructure can sequester up to 120 tons of carbon per square kilometer (0.38 miles). When replicating these strategies in parks and other greenspaces, up to 300 tons per square kilometer of carbon could be saved annually.
Related Stories
Urban Planning | Oct 14, 2016
Architecture firm proposes a ‘Border City’ between the United States and Mexico
The city would be situated around New Mexico, Texas, and Chihuahua.
Urban Planning | Oct 3, 2016
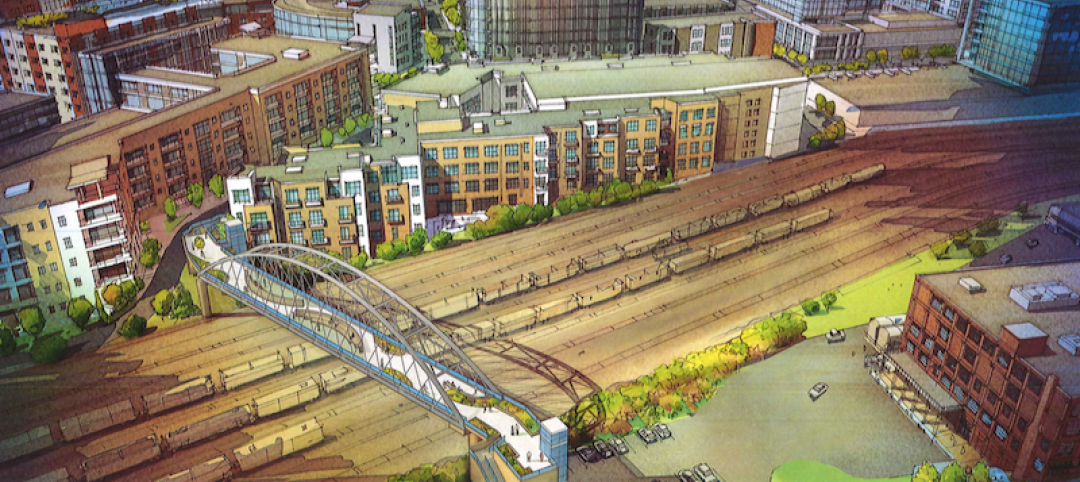
A pedestrian bridge linking two of Nashville’s highest-profile neighborhoods is making progress
The project has stalled since being proposed two years ago by former Mayor Karl Dean.
Urban Planning | Sep 20, 2016
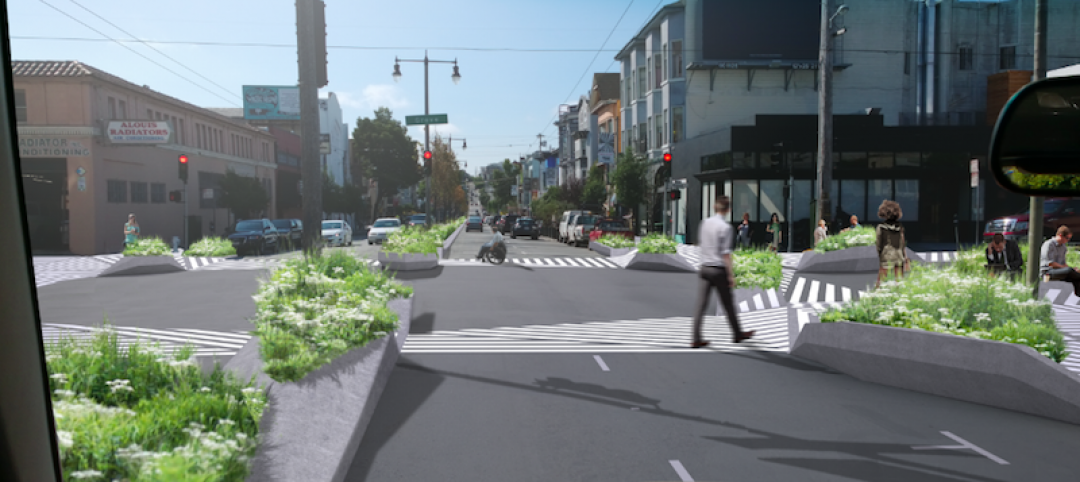
Can redesigning crosswalks make cities safer?
A proposal from Ogrydziak Prillinger Architects redesigns San Francisco’s crosswalks to make them more park-like, changing the way cars and pedestrians interact.
Steel Buildings | Sep 15, 2016
New York’s Hudson Yards to feature 16-story staircase sculpture
The installation is designed by British architect Thomas Heatherwick and will be the centerpiece of the $200 million plaza project
Urban Planning | Sep 12, 2016
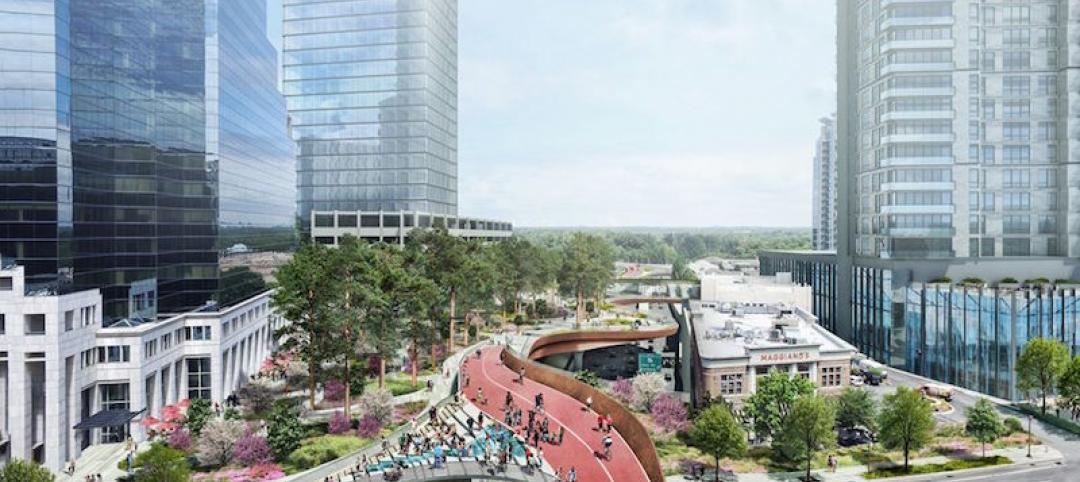
An Atlanta business group proposes a ‘floating’ park over a busy highway
The half-mile thoroughfare would connect to surrounding streets and companies.
Sustainability | Sep 7, 2016
New plans call for hundreds of thousands of British homes to be heated by factory machines
An expansion of ‘heat networks’ is viewed as a possible means for Britain to accomplish its goal of slashing carbon emissions by 2050.
High-rise Construction | Sep 7, 2016
Shenzhen Kingkey Group submits re-planning package for what could become China’s tallest tower
The high-rise, H700 Shenzhen Tower, is one of a group of towers being built in Shenzhen’s Caiwuwei financial and commercial area.
Building Team | Sep 6, 2016
Letting your resource take center stage: A guide to thoughtful site selection for interpretive centers
Thoughtful site selection is never about one factor, but rather a confluence of several components that ultimately present trade-offs for the owner.
Urban Planning | Jul 19, 2016
New game challenges players to create a utopian city block
By treating the neighborhood as a living entity, players of Block’hood take part in the creation, death, and rebirth of their own city blocks
Augmented Reality | Jul 15, 2016
Pokémon Go is helping people discover their cities
While catching them all may be the main goal, the wildly popular mobile game is also leading people to trek to unexplored corners of their cities

















