The world’s forests absorb an estimated 16 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide annually, or about double the 8.1 billion metric tons of CO2 that forests emit each year, according to research published earlier this year by Nature Climate Change.
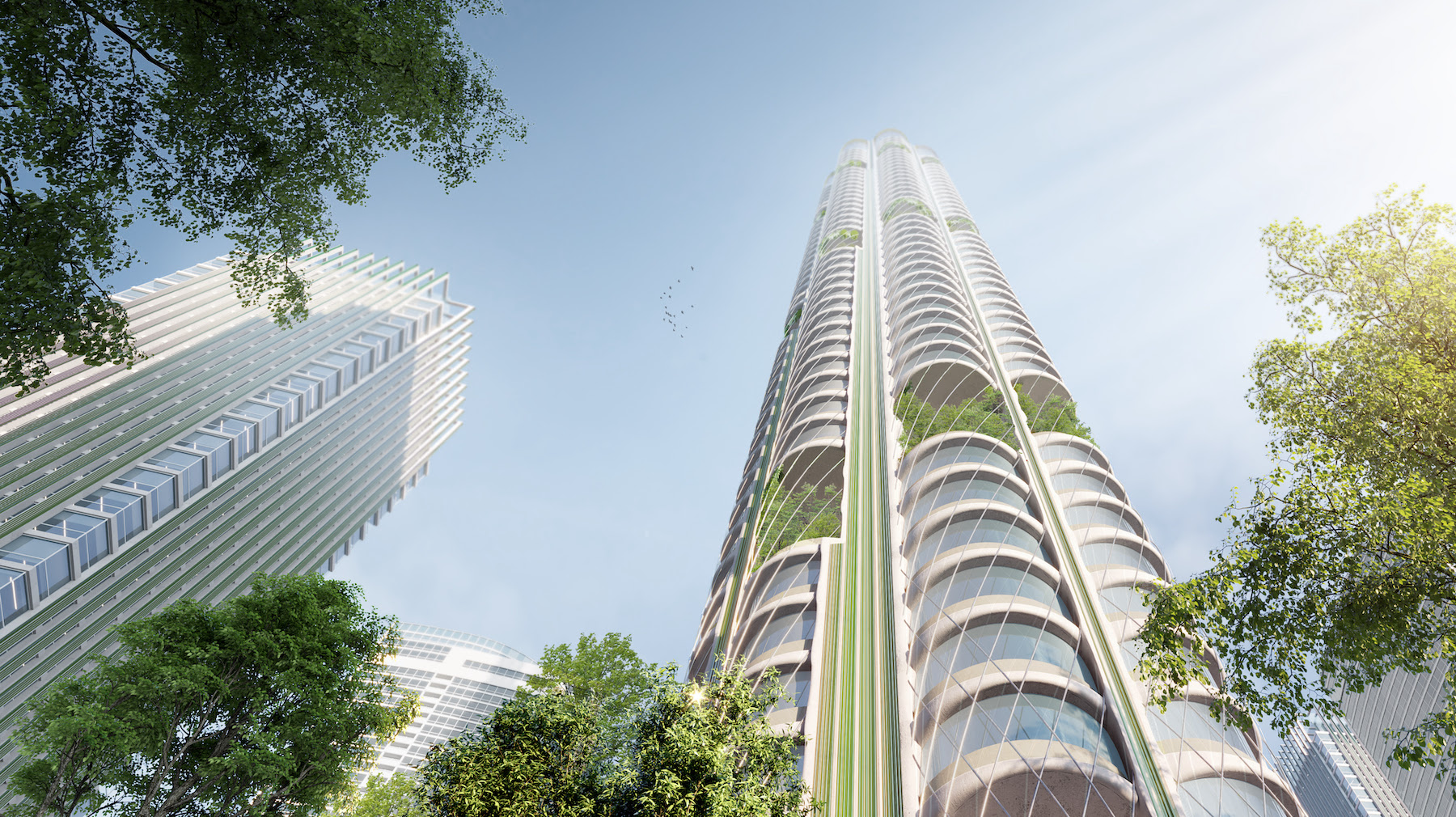
Could buildings—which generate, directly or indirectly, nearly two-fifths of CO2 emissions—act like trees to capture and absorb carbon and keep the air pure? The architecture, engineering, and urban planning firm Skidmore, Owings & Merrill envisions that provocative suggestion in a concept it calls Urban Sequoia, which SOM presented during COP26, the 2021 UNN Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, Scotland.
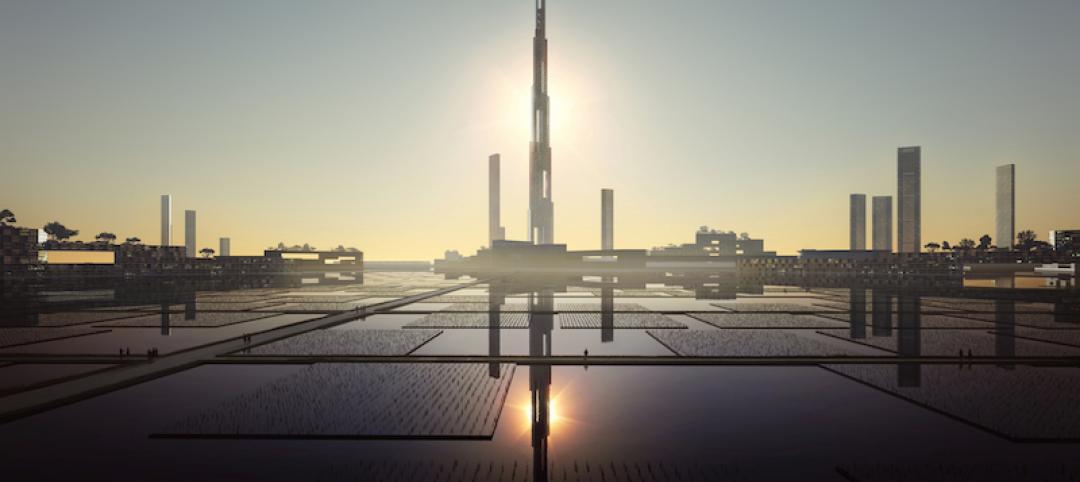
SOM pitched its concept at a time when urban population growth rates are dictating the need for an estimated additional 2.48 trillion sf of new buildings by 2060.
How would buildings absorb more carbon than they leak out? By designing and building them specifically to sequester emissions, says Chris Cooper, an SOM Partner. Kent Jackson, another SOM Partner who presented Urban Sequoia at COP26, adds that this concept could be applied and adapted for any metro area in the world, and to all sizes and types of buildings.
IT’S ALL ABOUT THE MATERIALS
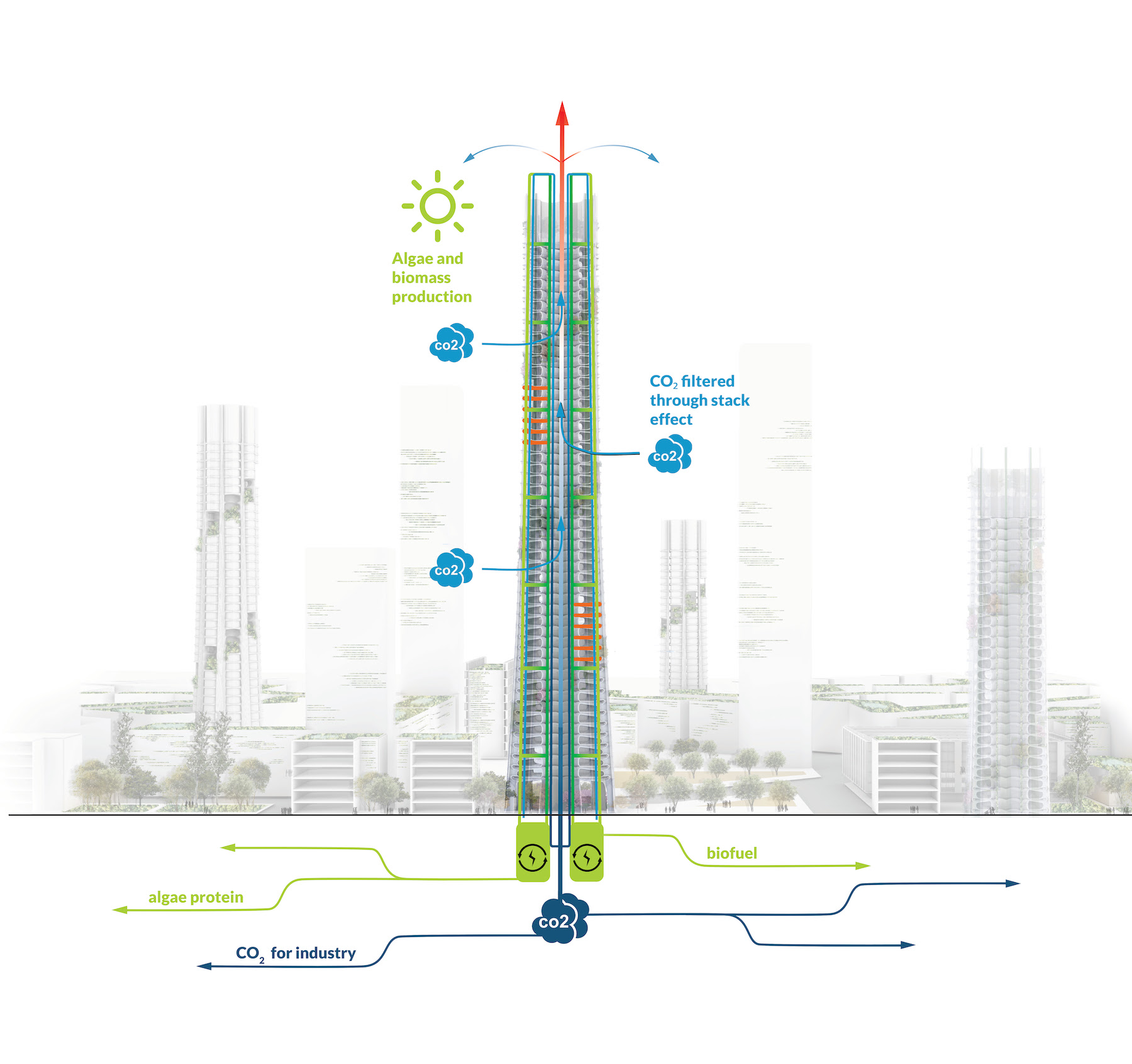
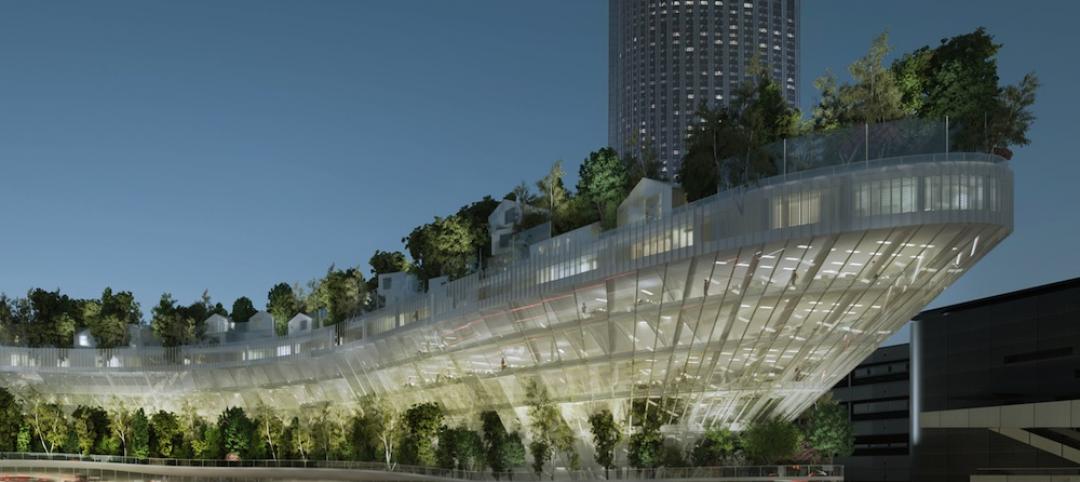
Urban Sequoia is an amalgam of the latest thinking about sustainable design coupled with emerging technologies. Carbon reductions can be achieved, SOM posits, by “holistically” optimizing building design, minimizing materials, and integrating biomaterials and advanced biomass.
To illustrate its concept, SOM’s prototype design is a high-rise building that, theoretically, could sequester up to 1,000 tons of carbon annually, or the absorption equivalent of 48,500 trees. The right combination of nature-based or environmentally friendlier materials—that might include hempcrete, bio-brick, timber, and so forth—could reduce the carbon impact of construction by anywhere from 50 to 95 percent compared to buildings made primarily with steel and concrete.
Over a 60-year lifespan, this prototype building would absorb up to 400 percent more CO2 than it would have emitted during construction, states SOM (which is a little vague about what “industrial applications” the captured carbon would be used for). And the use of bio-materials could turn the building into a biofuel source that would bring the building’s operations beyond net zero.
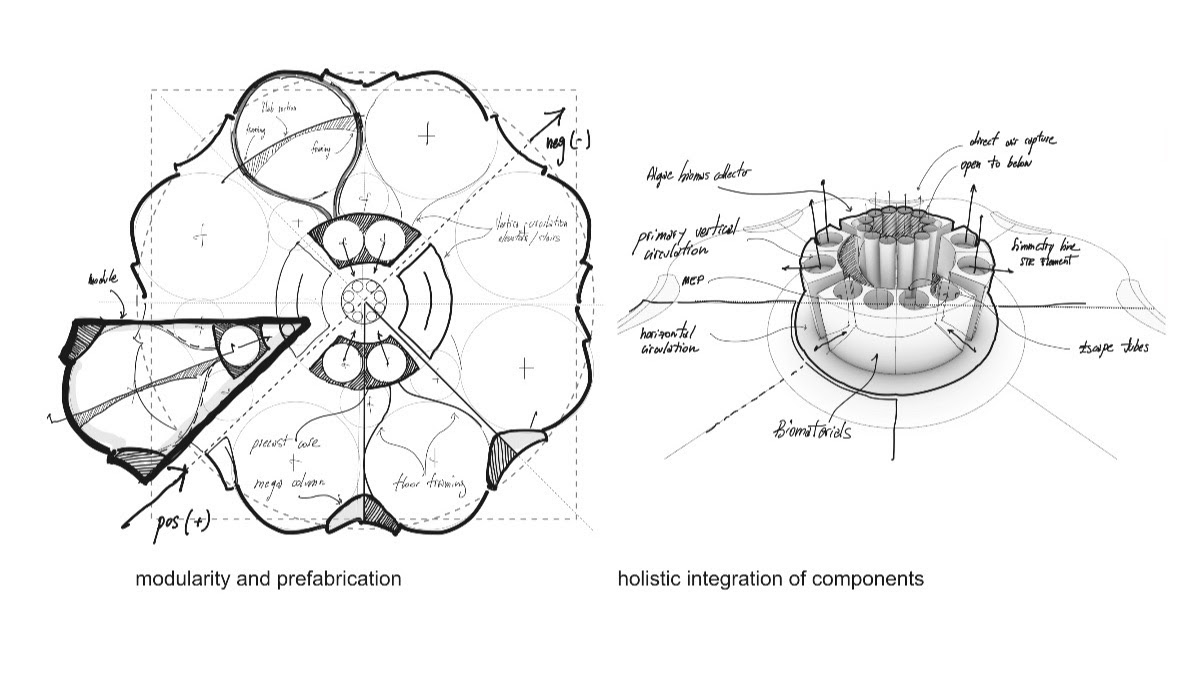
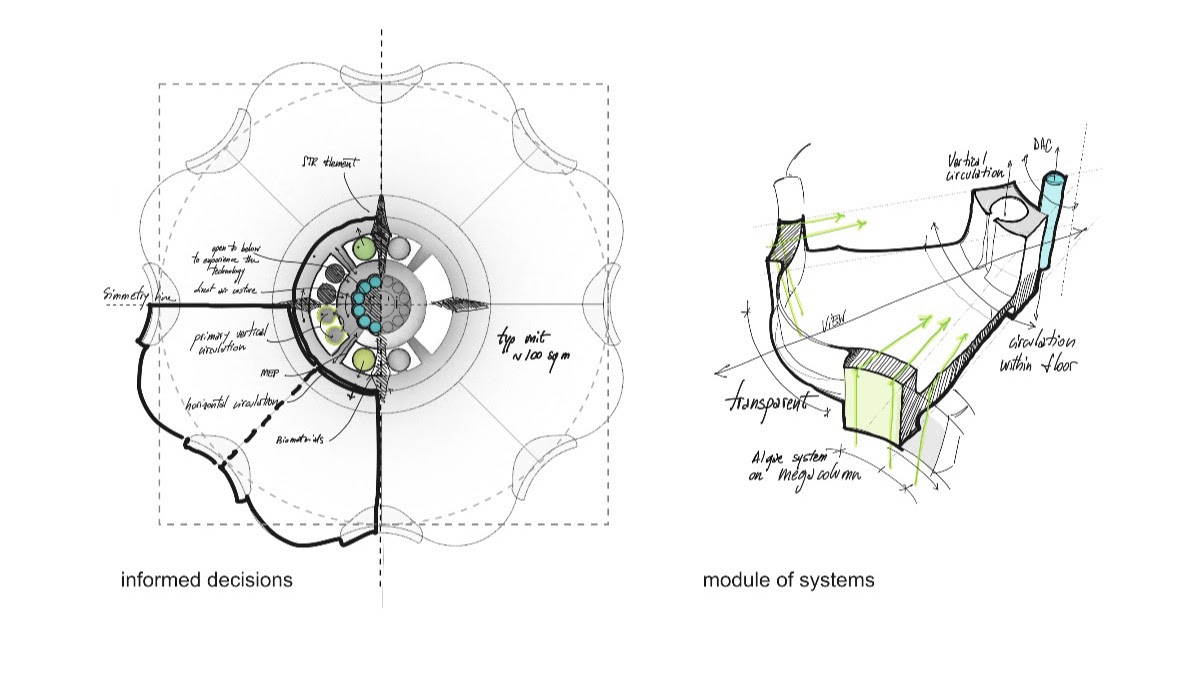 The goal, in essence, is to turn cities into carbon sinks. SOM contends that if every city around the world built Urban Sequoias, the built environment could remove up to 1.6 billion tons of carbon from the air every year. Such a strategy might also include converting urban hardscapes into gardens, designing intense carbon-absorbing landscapes, and retrofitting streets with additional carbon-capturing technology, former grey infrastructure can sequester up to 120 tons of carbon per square kilometer (0.38 miles). When replicating these strategies in parks and other greenspaces, up to 300 tons per square kilometer of carbon could be saved annually.
The goal, in essence, is to turn cities into carbon sinks. SOM contends that if every city around the world built Urban Sequoias, the built environment could remove up to 1.6 billion tons of carbon from the air every year. Such a strategy might also include converting urban hardscapes into gardens, designing intense carbon-absorbing landscapes, and retrofitting streets with additional carbon-capturing technology, former grey infrastructure can sequester up to 120 tons of carbon per square kilometer (0.38 miles). When replicating these strategies in parks and other greenspaces, up to 300 tons per square kilometer of carbon could be saved annually.
Related Stories
Urban Planning | May 4, 2016
Brookings report details how different industries innovate
In the new report, “How Firms Learn: Industry Specific Strategies for Urban Economies,” Brookings' Scott Andes examines how manufacturing and software services firms develop new products, processes, and ideas.
Urban Planning | Apr 19, 2016
MVRDV wants to turn a former US Army barracks in Germany into a model for the future of suburban living
Blending traditional families with young couples and the newly retired, MVRDV hopes to transform traditional suburbs into diverse communities of shared experiences
High-rise Construction | Mar 10, 2016
Bigger, taller, wider: London’s skyline is about to have a major growth spurt
More than 100 tall buildings have been added to the plans for the capital city since this time last year, and the overall number of tall buildings planned for London is now over 400.
High-rise Construction | Feb 25, 2016
Kohn Pedersen Fox wants to build a mile-high tower in Tokyo
The tower would be the centerpiece of Next Tokyo, a mini city in Tokyo Bay adapted to climate change and rising tides.
Mixed-Use | Feb 18, 2016
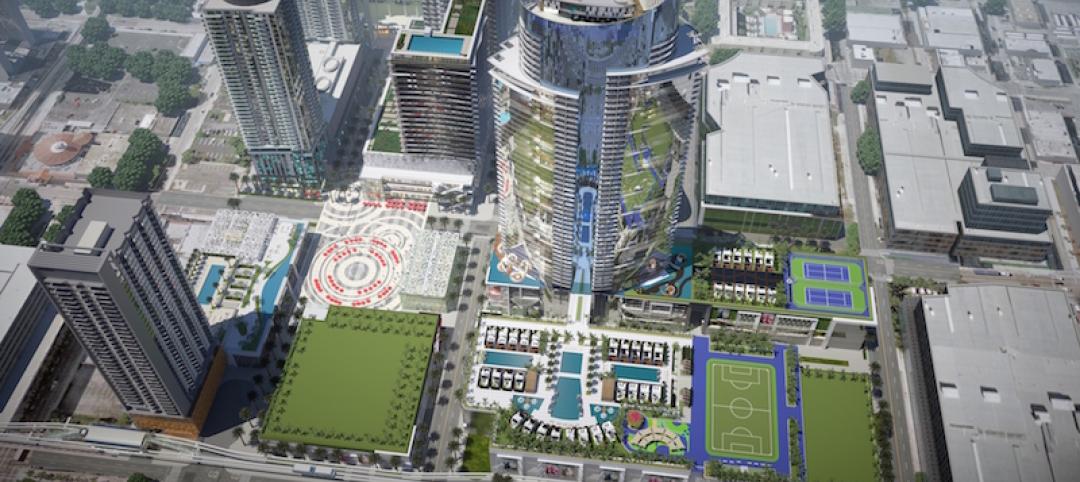
New renderings unveiled for Miami Worldcenter master plan
The ‘High Street’ retail promenade and plaza is one of the largest private master-planned projects in the U.S. and is set to break ground in early March.
Green | Feb 18, 2016
Best laid plans: Masdar City’s dreams of being the first net-zero city may have disappeared
The $22 billion experiment, to this point, has produced less than stellar results.
Urban Planning | Feb 9, 2016
Winners named in 'reinventing Paris' competition
Architects submitted projects that redeveloped key parts of the city and incorporated green space features.
Urban Planning | Feb 2, 2016
Report identifies 600 cities that will drive economic growth through 2025
Of them, 440 are in emerging economies in China, South Asia, and Southeast Asia.
Urban Planning | Jan 21, 2016
Anders Berensson Architects re-imagines Stockholm as a city of skywalks
The Swedish firm’s "Klarastaden" plan connects the city via clear skyways that weave in and around the city’s buildings.
Urban Planning | Jan 19, 2016
Cities are booming, but do they have what it takes to sustain growth?
While cities are creating new jobs and attracting new residents, there are warning signs that suggest this current urban boom lacks the necessary sustainability that comes with focusing on the macro issues of community, affordibility, and displacement, writes Gensler’s Peter Weingarten.
















