Investors in healthcare buildings view multi-tenant medical offices as their best bets for returns on investments whose financing, to an increasing degree, leans toward cash rather than debt.
Those are some of the findings in a 15-page report that CBRE’s U.S. Healthcare Capital Markets Group has released, based on responses from 80 healthcare real estate investors answering 26 questions. The largest group of respondents (32%) was healthcare real estate developers, followed by healthcare REITs and private capital healthcare investors (27% each).
Nearly one-third (32%) of all respondents say they target transactions that fall between $20 million and $50 million. Another 31% say that their preferred transaction range is $10 million to $20 million. Nearly all of the respondents—96%—are most interested in medical office buildings as the type of building that meets their acquisition criteria. The next preferred building type is ambulatory surgery centers (63%), wellness centers (41%), and assisted living facilities (39%).
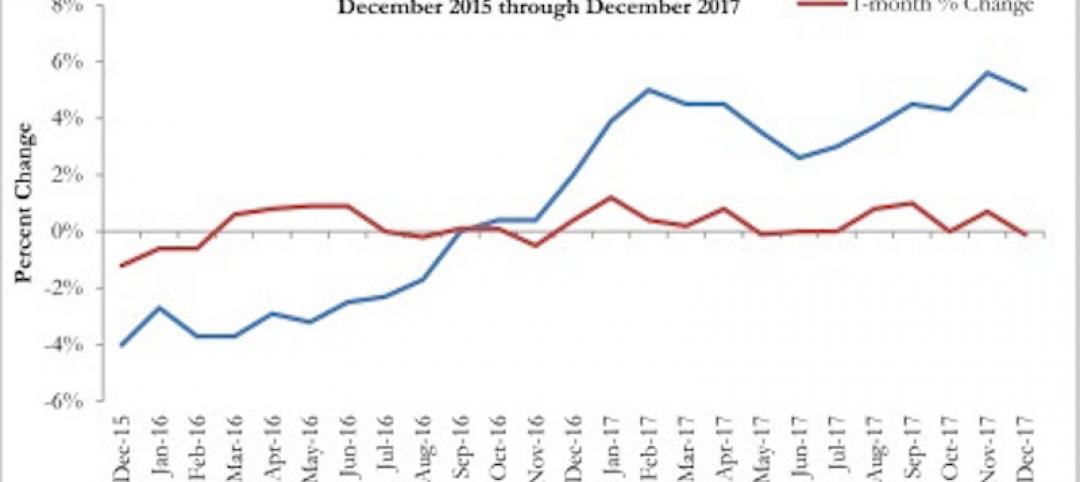
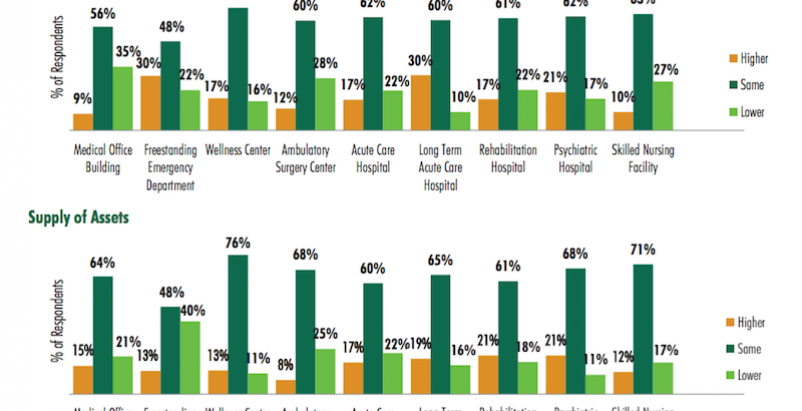 With some notable exceptions, supply (lower row) and demand (upper row) of acqusition properties in the healthcare building sector is expected to be about this same this year as it was in 2015, according to a survey of 80 healthcare real estate investors. Image: CBRE
With some notable exceptions, supply (lower row) and demand (upper row) of acqusition properties in the healthcare building sector is expected to be about this same this year as it was in 2015, according to a survey of 80 healthcare real estate investors. Image: CBRE
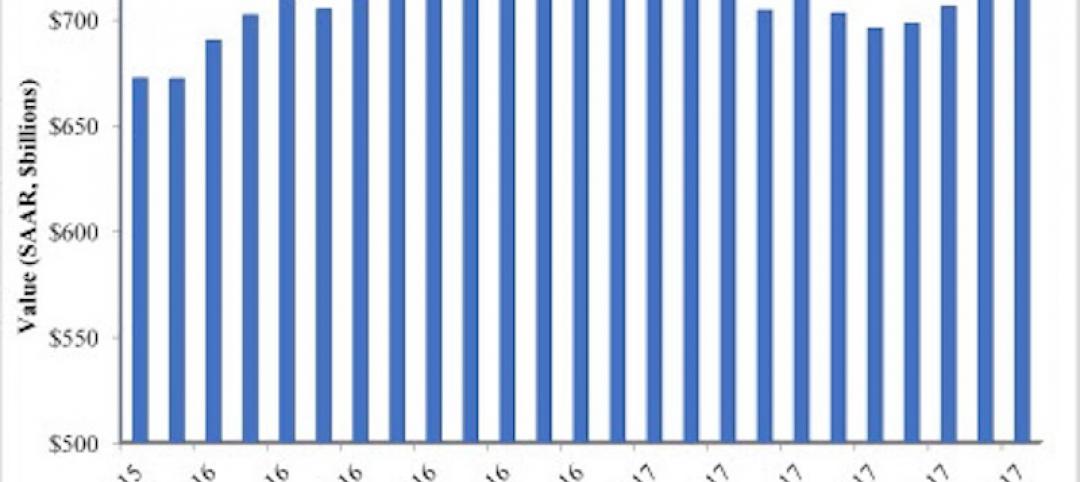
The total amount of equity that firms allocated for healthcare real estate investment this year, nearly $14.5 billion, was about 7% less than the $15.5 billion estimate from the 2015 survey. But the 2016 number is still considerably higher than estimates in the years 2011 through 2014, and is actually 132% of the total market transaction volume that traded in the healthcare sector in 2015.
The greatest portion of respondents (29%) says leveraged internal rate of return (IRR) is the investment return measurement they rely on most. However, that’s down from 33% in the 2015 survey. On the other hand, all-cash IRR saw a big jump—to 22% from 12% in 2015—as a relied-upon investment metric.
Interestingly, all-cash financing finished second, behind bank debt, as the type of financing the respondents used. Nearly nine of 10 REITs surveyed say they would use all-cash financing, whereas more than three-quarters of the developers would use bank debt to pay for their investments.
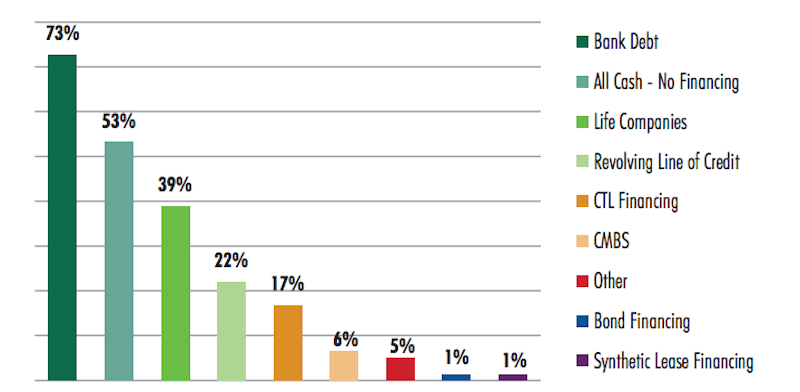
Healthcare REITs says they are more disposed to pay cash for acquisitions of medical office buildings, versus developers that lean more thoward bank financing of their deals. Image: CBRE
There’s wide variation in how long respondents hold onto healthcare investments. The greatest number—31%—say 10 years or more. But another 23% say they will hold only an investment for between five and seven years, and the same percentage are holding onto properties for only two and four year.
Class A on-campus medical office buildings are the healthcare product type that continues to price most aggressively, vis-à-vis Class A off-campus medical offices, although the differences are narrowing, according to this year’s survey. About 49% of respondents indicate that a market cap rate for Class A on-campus medical offices would be below 6%, compared to 53% who say the cap rate for Class A off-campus product would be below 6.5%.
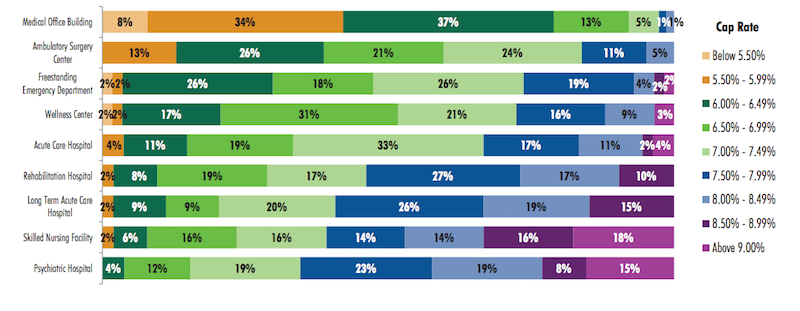
CBRE's survey finds that the market cap rate that investors target varies considerably by product type in the healthcare sector. Image: CBRE
When discussing their target 10-year IRR for all-cash investments in multi-tenant medical office buildings, 42% of respondents say it falls between 7% and 9.49%. Another 31% say their IRR target for this product type would be between 9.5% and 11.99%. “Respondents indicated a lack of desire for the most aggressively priced product, with only 4% indicating a target all-cash IRR below 7%, compared to 17% in 2015,” CBRE reports.
Single-tenant medical office buildings are pricing the most aggressively, with the largest group of respondents (37%) indicating a cap rate range of 6% to 6.49%, and another 42% indicating a cap rate lower than 5.99% In contrast, more than one quarter of respondents indicates a cap rate of 6% to 6.49% for ambulatory surgery centers, while 31% indicate a cap rate range of 6.5% to 6.99% for wellness centers, and 33% a 7% to 7.49% range for acute care hospitals.
The product types with the least-aggressive pricing, according to the survey’s respondents, are long-term acute care hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, and psychiatric hospitals.
The vast majority of respondents—82%—say their medical office investments this year would make them "net buyers."
Majorities of respondents expect supply of and demand for healthcare sector buildings in general to remain pretty much the same this year as in 2015, with some intriguing collisions: for example 30% of respondents think demand for freestanding emergency departments would be higher even as 40% expect supply of that product type would be lower.
Rents for medical office buildings were up between 2% and 3% for the respondents’ portfolios, and none is predicting much growth beyond that in the next 12 months, which is curious given that 59% of those surveyed say their portfolio’s occupancy rates were higher than the year before.
CBRE’s report touches on a host of other investment topics, including operating expenses, credit ratings, acceptable terms for sale-leasebacks (10 to 14 years appears to be the preferred threshold), and issues revolving around ground lease price floors and structuring.
And when the questions home in on developers specifically, nearly half (48%) of developers who responded predict that development request for proposal (RFP) activity would be similar to last year. The biggest number of developers—36%—says that a lease constant of below 7% was the minimum they would consider for a healthcare development opportunity that met their highest standards of investment. (Nearly half says they’d consider a lease constant below 8% for a new development.)
Most developers (44% of those who responded) prefer at least 50% to 60% of a project to be preleased, and a large majority (82%) of developer-respondents require that 50% to 80% of a project to be preleased before they’d invest.
Related Stories
Market Data | Jan 25, 2018
Renters are the majority in 42 U.S. cities
Over the past 10 years, the number of renters has increased by 23 million.
Market Data | Jan 12, 2018
Construction input prices inch down in December, Up YOY despite low inflation
Energy prices have been more volatile lately.
Market Data | Jan 4, 2018
Nonresidential construction spending ticks higher in November, down year-over-year
Despite the month-over-month expansion, nonresidential spending fell 1.3 percent from November 2016.
Market Data | Dec 14, 2017
ABC chief economist predicts stable 2018 construction economy
There are risks to the 2018 outlook as a number of potential cost increases could come into play.
Market Data | Dec 11, 2017
Global hotel construction pipeline is growing
The Total Pipeline stands at 12,427 Projects/2,084,940 Rooms.
Market Data | Dec 11, 2017
Construction backlog surges, sets record in third quarter
CBI is a leading economic indicator that reflects the amount of construction work under contract, but not yet completed.
Market Data | Dec 7, 2017
Buoyed by healthy economy, ABC Index finds contractors upbeat
Despite rising construction labor and materials costs, 55% of contractors expect their profit margins to expand in the first half of 2018.
Industry Research | Nov 28, 2017
2018 outlook: Economists point to slowdown, AEC professionals say ‘no way’
Multifamily housing and senior living developments head the list of the hottest sectors heading into 2018, according a survey of 356 AEC professionals.
Architects | Nov 28, 2017
Adding value through integrated technology requires a human touch
To help strike that delicate balance between the human and the high-tech, we must first have an in-depth understanding of our client’s needs as well as a manufacturer’s capabilities.
Market Data | Nov 27, 2017
Construction's contribution to U.S. economy highest in seven years
Thirty-seven states benefited from the rise in construction activity in their state, while 13 states experienced a reduction in activity.